Dado un entero positivo N , la tarea es encontrar el promedio de los cubos de los primeros N números naturales.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 2
Salida: 4.5
Explicación:
Para el número entero N = 2,
tenemos ( 1 3 + 2 3 ) = 1 + 8 = 9
promedio = 9 / 2 que es 4.5
Entrada: N = 3
Salida: 12
Explicación:
Para N = 3,
Tenemos ( 1 3 + 2 3 + 2 3 + 2 3 + 3 3 + 2 3 ) = 27 + 8 + 1 = 36
promedio = 36 / 3 que es 12
Enfoque ingenuo: El enfoque ingenuo es encontrar la suma de los cubos de los primeros N números naturales y dividirla por N.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C
// C program for the above approach
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to find average of cubes
double findAverageOfCube(int n)
{
// Store sum of cubes of
// numbers in the sum
double sum = 0;
// Calculate sum of cubes
int i;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += i * i * i;
}
// Return average
return sum / n;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given number
int n = 3;
// Function Call
printf("%lf", findAverageOfCube(n));
return 0;
}
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find average of cubes
double findAverageOfCube(int n)
{
// Storing sum of cubes
// of numbers in sum
double sum = 0;
// Calculate sum of cubes
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += i * i * i;
}
// Return average
return sum / n;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Number
int n = 3;
// Function Call
cout << findAverageOfCube(n);
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find average of cubes
static double findAverageOfCube(int n)
{
// Storing sum of cubes
// of numbers in sum
double sum = 0;
// Calculate sum of cubes
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
sum += i * i * i;
}
// Return average
return sum / n;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given Number
int n = 3;
// Function Call
System.out.print(findAverageOfCube(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function to find average of cubes def findAverageOfCube(n): # Storing sum of cubes # of numbers in sum sum = 0 # Calculate sum of cubes for i in range(1, n + 1): sum += i * i * i # Return average return round(sum / n, 6) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Given Number n = 3 # Function Call print(findAverageOfCube(n)) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find average of cubes
static double findAverageOfCube(int n)
{
// Storing sum of cubes
// of numbers in sum
double sum = 0;
// Calculate sum of cubes
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
sum += i * i * i;
}
// Return average
return sum / n;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given Number
int n = 3;
// Function Call
Console.Write(findAverageOfCube(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Nidhi_biet
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program for the above approach
// Function to find average of cubes
function findAverageOfCube( n)
{
// Store sum of cubes of
// numbers in the sum
let sum = 0;
// Calculate sum of cubes
let i;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += i * i * i;
}
// Return average
return sum / n;
}
// Driver Code
// Given number
let n = 3;
// Function Call
document.write(findAverageOfCube(n).toFixed(6));
// This code is contributed by todaysgaurav
</script>
12.000000
Complejidad del tiempo: O(N)
Complejidad del espacio : O(1)
Enfoque eficiente:
Sabemos que,
Suma de cubos de primeros N Números Naturales =
El promedio viene dado por:
=>
=>
=>
=>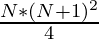
Por lo tanto, el promedio de la suma cúbica de los primeros N números naturales viene dado por ![]()
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C
// C program for the above approach
#include <stdio.h>
// function to find an average of cubes
double findAverageofCube(double n)
{
// Apply the formula n(n+1)^2/4
int ans = (n * (n + 1) * (n + 1)) / 4;
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Number
int n = 3;
// Function Call
printf("%f",findAverageofCube(n));
return 0;
}
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to find an average of cubes
double findAverageofCube(double n)
{
// Apply the formula n(n+1)^2/4
int ans = (n * (n + 1) * (n + 1)) / 4;
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Number
int n = 3;
// Function Call
cout << findAverageofCube(n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
class GFG{
// function to find an average of cubes
static double findAverageofCube(double n)
{
// Apply the formula n(n+1)^2/4
int ans = (int)((n * (n + 1) * (n + 1)) / 4);
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given Number
int n = 3;
// Function Call
System.out.print(findAverageofCube(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function to find average of cubes def findAverageOfCube (n): # Apply the formula n*(n+1)^2/4 ans = (n * (n + 1) * (n + 1)) / 4 return ans # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': # Given number n = 3 # Function call print(findAverageOfCube(n)) # This code is contributed by himanshu77
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// function to find an average of cubes
static double findAverageofCube(double n)
{
// Apply the formula n(n+1)^2/4
int ans = (int)((n * (n + 1) * (n + 1)) / 4);
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given Number
int n = 3;
// Function Call
Console.Write(findAverageofCube(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Code_Mech
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program for the above approach
// function to find an average of cubes
function findAverageofCube(n)
{
// Apply the formula n(n+1)^2/4
var ans = parseInt(((n * (n + 1) * (n + 1)) / 4));
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
// Given Number
var n = 3;
// Function Call
document.write(findAverageofCube(n));
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
</script>
12.000000
Complejidad de tiempo: O(1)
Complejidad del espacio: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por coder_nero y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA