Dado un arreglo 2D, encuentre el subarreglo de suma máxima en él. Por ejemplo, en la siguiente array 2D, el subarreglo de suma máxima se resalta con un rectángulo azul y la suma de este subarreglo es 29.
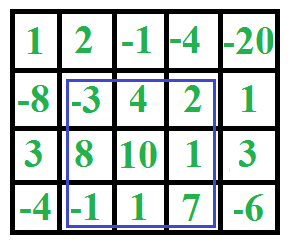
Este problema es principalmente una extensión del subarreglo contiguo de suma más grande para un arreglo 1D .
La solución ingenua para este problema es verificar todos los rectángulos posibles en la array 2D dada. Esta solución requiere 6 bucles anidados:
- 4 para la coordenada inicial y final de los 2 ejes O(n 4 )
- y 2 para la sumatoria de la subarray O(n 2 ).
La complejidad temporal total de esta solución sería O(n 6 ).
Enfoque eficiente –
El algoritmo de Kadane para array 1D se puede usar para reducir la complejidad del tiempo a O (n ^ 3). La idea es arreglar las columnas izquierda y derecha una por una y encontrar la suma máxima de filas contiguas para cada par de columnas izquierda y derecha. Básicamente, encontramos números de fila superior e inferior (que tienen una suma máxima) para cada par de columnas fijas izquierda y derecha. Para encontrar los números de las filas superior e inferior, calcule la suma de los elementos en cada fila de izquierda a derecha y almacene estas sumas en una array, digamos temp[]. Entonces temp[i] indica la suma de los elementos de izquierda a derecha en la fila i. Si aplicamos el algoritmo 1D de Kadane en temp[] y obtenemos el subarreglo de suma máxima de temp, esta suma máxima sería la suma máxima posible con izquierda y derecha como columnas límite. Para obtener la suma máxima general, comparamos esta suma con la suma máxima hasta el momento.
Implementación:
C++
// Program to find maximum sum subarray
// in a given 2D array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ROW 4
#define COL 5
// Implementation of Kadane's algorithm for
// 1D array. The function returns the maximum
// sum and stores starting and ending indexes
// of the maximum sum subarray at addresses
// pointed by start and finish pointers
// respectively.
int kadane(int* arr, int* start, int* finish, int n)
{
// initialize sum, maxSum and
int sum = 0, maxSum = INT_MIN, i;
// Just some initial value to check
// for all negative values case
*finish = -1;
// local variable
int local_start = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
sum += arr[i];
if (sum < 0)
{
sum = 0;
local_start = i + 1;
}
else if (sum > maxSum)
{
maxSum = sum;
*start = local_start;
*finish = i;
}
}
// There is at-least one
// non-negative number
if (*finish != -1)
return maxSum;
// Special Case: When all numbers
// in arr[] are negative
maxSum = arr[0];
*start = *finish = 0;
// Find the maximum element in array
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] > maxSum)
{
maxSum = arr[i];
*start = *finish = i;
}
}
return maxSum;
}
// The main function that finds
// maximum sum rectangle in M[][]
void findMaxSum(int M[][COL])
{
// Variables to store the final output
int maxSum = INT_MIN,
finalLeft,
finalRight,
finalTop,
finalBottom;
int left, right, i;
int temp[ROW], sum, start, finish;
// Set the left column
for (left = 0; left < COL; ++left) {
// Initialize all elements of temp as 0
memset(temp, 0, sizeof(temp));
// Set the right column for the left
// column set by outer loop
for (right = left; right < COL; ++right) {
// Calculate sum between current left
// and right for every row 'i'
for (i = 0; i < ROW; ++i)
temp[i] += M[i][right];
// Find the maximum sum subarray in temp[].
// The kadane() function also sets values
// of start and finish. So 'sum' is sum of
// rectangle between (start, left) and
// (finish, right) which is the maximum sum
// with boundary columns strictly as left
// and right.
sum = kadane(temp, &start, &finish, ROW);
// Compare sum with maximum sum so far.
// If sum is more, then update maxSum and
// other output values
if (sum > maxSum) {
maxSum = sum;
finalLeft = left;
finalRight = right;
finalTop = start;
finalBottom = finish;
}
}
}
// Print final values
cout << "(Top, Left) ("
<< finalTop << ", "
<< finalLeft
<< ")" << endl;
cout << "(Bottom, Right) ("
<< finalBottom << ", "
<< finalRight << ")" << endl;
cout << "Max sum is: " << maxSum << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int M[ROW][COL] = { { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 },
{ -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 },
{ 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 },
{ -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } };
// Function call
findMaxSum(M);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by
// rathbhupendra
C
// Program to find maximum sum subarray
// in a given 2D array
#include <limits.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define ROW 4
#define COL 5
// Implementation of Kadane's algorithm
// for 1D array. The function returns the
// maximum sum and stores starting and
// ending indexes of the maximum sum subarray
// at addresses pointed by start and finish
// pointers respectively.
int kadane(int* arr, int* start,
int* finish, int n)
{
// initialize sum, maxSum and
int sum = 0, maxSum = INT_MIN, i;
// Just some initial value to check for all negative
// values case
*finish = -1;
// local variable
int local_start = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
sum += arr[i];
if (sum < 0) {
sum = 0;
local_start = i + 1;
}
else if (sum > maxSum)
{
maxSum = sum;
*start = local_start;
*finish = i;
}
}
// There is at-least one non-negative number
if (*finish != -1)
return maxSum;
// Special Case: When all numbers in arr[]
// are negative
maxSum = arr[0];
*start = *finish = 0;
// Find the maximum element in array
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] > maxSum)
{
maxSum = arr[i];
*start = *finish = i;
}
}
return maxSum;
}
// The main function that finds maximum
// sum rectangle in
// M[][]
void findMaxSum(int M[][COL])
{
// Variables to store the final output
int maxSum = INT_MIN,
finalLeft,
finalRight,
finalTop,
finalBottom;
int left, right, i;
int temp[ROW], sum, start, finish;
// Set the left column
for (left = 0; left < COL; ++left)
{
// Initialize all elements of temp as 0
memset(temp, 0, sizeof(temp));
// Set the right column for the left column set by
// outer loop
for (right = left; right < COL; ++right) {
// Calculate sum between current left and right
// for every row 'i'
for (i = 0; i < ROW; ++i)
temp[i] += M[i][right];
// Find the maximum sum subarray in temp[].
// The kadane() function also sets values of
// start and finish. So 'sum' is sum of
// rectangle between (start, left) and (finish,
// right) which is the maximum sum with boundary
// columns strictly as left and right.
sum = kadane(temp, &start, &finish, ROW);
// Compare sum with maximum sum so far. If sum
// is more, then update maxSum and other output
// values
if (sum > maxSum)
{
maxSum = sum;
finalLeft = left;
finalRight = right;
finalTop = start;
finalBottom = finish;
}
}
}
// Print final values
printf("(Top, Left) (%d, %d)\n", finalTop, finalLeft);
printf("(Bottom, Right) (%d, %d)\n", finalBottom,
finalRight);
printf("Max sum is: %d\n", maxSum);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int M[ROW][COL] = { { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 },
{ -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 },
{ 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 },
{ -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } };
// Function call
findMaxSum(M);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to find max sum rectangular submatrix
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class MaximumSumRectangle
{
// Function to find maximum sum rectangular
// submatrix
private static int maxSumRectangle(int[][] mat)
{
int m = mat.length;
int n = mat[0].length;
int preSum[][] = new int[m + 1][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
preSum[i + 1][j] =
preSum[i][j] + mat[i][j];
}
}
int maxSum = -1;
int minSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int negRow = 0, negCol = 0;
int rStart = 0, rEnd = 0, cStart = 0, cEnd = 0;
for (int rowStart = 0;
rowStart < m;
rowStart++)
{
for (int row = rowStart; row < m; row++)
{
int sum = 0;
int curColStart = 0;
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
sum += preSum[row + 1][col]
- preSum[rowStart][col];
if (sum < 0) {
if (minSum < sum) {
minSum = sum;
negRow = row;
negCol = col;
}
sum = 0;
curColStart = col + 1;
}
else if (maxSum < sum)
{
maxSum = sum;
rStart = rowStart;
rEnd = row;
cStart = curColStart;
cEnd = col;
}
}
}
}
// Printing final values
if (maxSum == -1) {
System.out.println("from row - " + negRow
+ " to row - " + negRow);
System.out.println("from col - " + negCol
+ " to col - " + negCol);
}
else {
System.out.println("from row - " + rStart
+ " to row - " + rEnd);
System.out.println("from col - " + cStart
+ " to col - " + cEnd);
}
return maxSum == -1 ? minSum : maxSum;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[][] = new int[][] { { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 },
{ -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 },
{ 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 },
{ -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } };
// Function call
System.out.println(maxSumRectangle(arr));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Nayanava De
Python3
# Python3 program to find maximum sum
# subarray in a given 2D array
# Implementation of Kadane's algorithm
# for 1D array. The function returns the
# maximum sum and stores starting and
# ending indexes of the maximum sum subarray
# at addresses pointed by start and finish
# pointers respectively.
def kadane(arr, start, finish, n):
# initialize sum, maxSum and
Sum = 0
maxSum = -999999999999
i = None
# Just some initial value to check
# for all negative values case
finish[0] = -1
# local variable
local_start = 0
for i in range(n):
Sum += arr[i]
if Sum < 0:
Sum = 0
local_start = i + 1
elif Sum > maxSum:
maxSum = Sum
start[0] = local_start
finish[0] = i
# There is at-least one
# non-negative number
if finish[0] != -1:
return maxSum
# Special Case: When all numbers
# in arr[] are negative
maxSum = arr[0]
start[0] = finish[0] = 0
# Find the maximum element in array
for i in range(1, n):
if arr[i] > maxSum:
maxSum = arr[i]
start[0] = finish[0] = i
return maxSum
# The main function that finds maximum
# sum rectangle in M[][]
def findMaxSum(M):
global ROW, COL
# Variables to store the final output
maxSum, finalLeft = -999999999999, None
finalRight, finalTop, finalBottom = None, None, None
left, right, i = None, None, None
temp = [None] * ROW
Sum = 0
start = [0]
finish = [0]
# Set the left column
for left in range(COL):
# Initialize all elements of temp as 0
temp = [0] * ROW
# Set the right column for the left
# column set by outer loop
for right in range(left, COL):
# Calculate sum between current left
# and right for every row 'i'
for i in range(ROW):
temp[i] += M[i][right]
# Find the maximum sum subarray in
# temp[]. The kadane() function also
# sets values of start and finish.
# So 'sum' is sum of rectangle between
# (start, left) and (finish, right) which
# is the maximum sum with boundary columns
# strictly as left and right.
Sum = kadane(temp, start, finish, ROW)
# Compare sum with maximum sum so far.
# If sum is more, then update maxSum
# and other output values
if Sum > maxSum:
maxSum = Sum
finalLeft = left
finalRight = right
finalTop = start[0]
finalBottom = finish[0]
# Prfinal values
print("(Top, Left)", "(", finalTop,
finalLeft, ")")
print("(Bottom, Right)", "(", finalBottom,
finalRight, ")")
print("Max sum is:", maxSum)
# Driver Code
ROW = 4
COL = 5
M = [[1, 2, -1, -4, -20],
[-8, -3, 4, 2, 1],
[3, 8, 10, 1, 3],
[-4, -1, 1, 7, -6]]
# Function call
findMaxSum(M)
# This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# Given a 2D array, find the
// maximum sum subarray in it
using System;
class GFG {
/**
* To find maxSum in 1d array
*
* return {maxSum, left, right}
*/
public static int[] kadane(int[] a)
{
int[] result = new int[] { int.MinValue, 0, -1 };
int currentSum = 0;
int localStart = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
currentSum += a[i];
if (currentSum < 0)
{
currentSum = 0;
localStart = i + 1;
}
else if (currentSum > result[0])
{
result[0] = currentSum;
result[1] = localStart;
result[2] = i;
}
}
// all numbers in a are negative
if (result[2] == -1)
{
result[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
if (a[i] > result[0]) {
result[0] = a[i];
result[1] = i;
result[2] = i;
}
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* To find and print maxSum,
(left, top),(right, bottom)
*/
public static void findMaxSubMatrix(int[, ] a)
{
int cols = a.GetLength(1);
int rows = a.GetLength(0);
int[] currentResult;
int maxSum = int.MinValue;
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
int right = 0;
int bottom = 0;
for (int leftCol = 0; leftCol < cols; leftCol++)
{
int[] tmp = new int[rows];
for (int rightCol = leftCol; rightCol < cols;
rightCol++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
tmp[i] += a[i, rightCol];
}
currentResult = kadane(tmp);
if (currentResult[0] > maxSum)
{
maxSum = currentResult[0];
left = leftCol;
top = currentResult[1];
right = rightCol;
bottom = currentResult[2];
}
}
}
Console.Write("MaxSum: " + maxSum + ", range: [("
+ left + ", " + top + ")(" + right
+ ", " + bottom + ")]");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[, ] arr = { { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 },
{ -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 },
{ 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 },
{ -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } };
// Function call
findMaxSubMatrix(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by PrinciRaj1992
Javascript
<script>
// Program to find maximum sum subarray
// in a given 2D array
var ROW = 4
var COL = 5
var start = 0
var finish = 0
// Implementation of Kadane's algorithm for
// 1D array. The function returns the maximum
// sum and stores starting and ending indexes
// of the maximum sum subarray at addresses
// pointed by start and finish pointers
// respectively.
function kadane(arr, n)
{
// initialize sum, maxSum and
var sum = 0, maxSum = -1000000000, i;
// Just some initial value to check
// for all negative values case
finish = -1;
// local variable
var local_start = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
sum += arr[i];
if (sum < 0)
{
sum = 0;
local_start = i + 1;
}
else if (sum > maxSum)
{
maxSum = sum;
start = local_start;
finish = i;
}
}
// There is at-least one
// non-negative number
if (finish != -1)
return maxSum;
// Special Case: When all numbers
// in arr[] are negative
maxSum = arr[0];
start = finish = 0;
// Find the maximum element in array
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] > maxSum)
{
maxSum = arr[i];
start = finish = i;
}
}
return maxSum;
}
// The main function that finds
// maximum sum rectangle in M[][]
function findMaxSum(M)
{
// Variables to store the final output
var maxSum = -1000000000,
finalLeft=0,
finalRight=0,
finalTop=0,
finalBottom=0;
var left, right, i;
var temp = Array(ROW);
var sum;
// Set the left column
for (left = 0; left < COL; ++left) {
// Initialize all elements of temp as 0
temp = Array(ROW).fill(0);
// Set the right column for the left
// column set by outer loop
for (right = left; right < COL; ++right) {
// Calculate sum between current left
// and right for every row 'i'
for (i = 0; i < ROW; ++i)
temp[i] += M[i][right];
// Find the maximum sum subarray in temp[].
// The kadane() function also sets values
// of start and finish. So 'sum' is sum of
// rectangle between (start, left) and
// (finish, right) which is the maximum sum
// with boundary columns strictly as left
// and right.
sum = kadane(temp, ROW);
// Compare sum with maximum sum so far.
// If sum is more, then update maxSum and
// other output values
if (sum > maxSum) {
maxSum = sum;
finalLeft = left;
finalRight = right;
finalTop = start;
finalBottom = finish;
}
}
}
// Print final values
document.write("(Top, Left) ("
+ finalTop + ", "
+ finalLeft
+ ")" + "<br>");
document.write("(Bottom, Right) ("
+ finalBottom + ", "
+ finalRight + ")" + "<br>");
document.write("Max sum is: " + maxSum + "<br>");
}
// Driver Code
var M = [ [ 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 ],
[ -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 ],
[ 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 ],
[ -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 ] ];
// Function call
findMaxSum(M);
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56.
</script>
(Top, Left) (1, 1) (Bottom, Right) (3, 3) Max sum is: 29
Complejidad de tiempo: O(c*c*r), donde c representa el número de columnas y r representa el número de filas en la array dada.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(r), donde r representa el número de filas en la array dada.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA