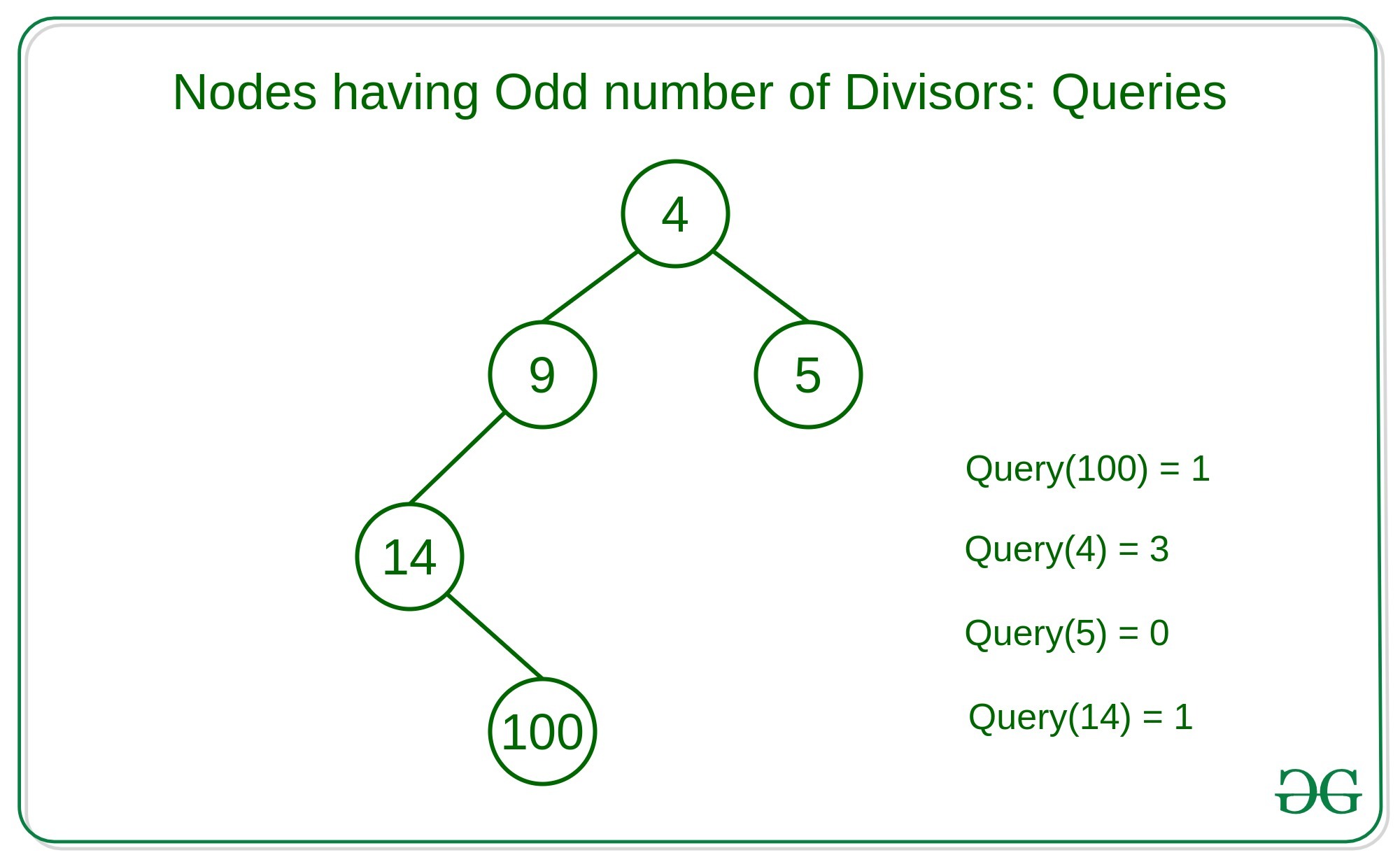
Dado un árbol N-ario y consultas Q donde cada consulta contiene un Node del árbol N-ario, la tarea es contar el número de Nodes que tienen un número impar de divisores en el subárbol para consultas Q.
Ejemplos:
Aporte:
Salida: 1 3 0 1
Explicación:
Consulta 1: En el subárbol con raíz en el Node 100, solo hay un Node que es 100 que tiene 9 divisores {1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50, 100}. Por lo tanto, solo hay un Node que tiene el número impar de divisores.
Consulta 2: en el subárbol con raíz en el Node 4, hay 5 Nodes de los cuales 3 Nodes tienen un número impar de divisores. Eso es {4, 9, 100}
Consulta 3: En el subárbol con raíz en el Node 5, solo hay un Node que es 5 que tiene dos divisores. Por lo tanto, hay cero Nodes que tienen un número impar de divisores.
Enfoque ingenuo: una solución simple es recorrer el subárbol para cada consulta y encontrar el recuento de Nodes que tienen un número impar de divisores.
Enfoque eficiente: la idea es calcular previamente el recuento de un número impar de divisores para cada subárbol y almacenar el recuento en hash-map . Para precalcular el conteo de Nodes que tienen un número impar de divisores, podemos usar el recorrido de búsqueda primero en profundidad . Finalmente, para verificar si el Node actual tiene un número impar de divisores o no, podemos usar el hecho de que todo número cuadrado perfecto tiene un número impar de divisores.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to count the
// number of nodes having odd
// number of divisors for each query
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 100001
// Adjacency list
// for tree.
vector<int> adj[N];
// Array for values and
// answer at ith node.
int a[N], ans[N];
// Function to check whether N
// has odd divisors or not
bool hasOddNumberOfDivisors(int n)
{
if ((double)sqrt(n) == (int)sqrt(n))
return true;
return false;
}
// DFS function to pre-compute
// the answers
int dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// Initialize the count
int count = 0;
for (auto i = adj[node].begin(); i != adj[node].end();
++i) {
if (*i != parent) {
// Repeat for every child
count += dfs(*i, node);
}
}
// Increase the count if current node
// has odd number of divisors
if (hasOddNumberOfDivisors(a[node]))
++count;
ans[node] = count;
return count;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 5, i;
vector<int> q = { 4, 1, 5, 3 };
// Adjacency List
adj[1].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(1);
adj[2].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(2);
adj[3].push_back(4);
adj[4].push_back(3);
adj[1].push_back(5);
adj[5].push_back(1);
a[1] = 4;
a[2] = 9;
a[3] = 14;
a[4] = 100;
a[5] = 5;
// Function call
dfs(1, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < q.size(); i++) {
cout << ans[q[i]] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to
// count the number of nodes
// having odd number of
// divisors for each query
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static final int N = 100001;
// Adjacency list
// for tree.
static Vector<Integer> []adj =
new Vector[N];
// Array for values and
// answer at ith node.
static int []a = new int[N];
static int []ans = new int[N];
// Function to check whether N
// has odd divisors or not
static boolean hasOddNumberOfDivisors(int n)
{
if ((double)Math.sqrt(n) ==
(int)Math.sqrt(n))
return true;
return false;
}
// DFS function to
// pre-compute the answers
static int dfs(int node,
int parent)
{
// Initialize the count
int count = 0;
for (int i : adj[node])
{
if (i != parent)
{
// Repeat for every child
count += dfs(i, node);
}
}
// Increase the count if
// current node has odd
// number of divisors
if (hasOddNumberOfDivisors(a[node]))
++count;
ans[node] = count;
return count;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int[] q = {4, 1, 5, 3};
for (int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
// Adjacency List
adj[1].add(2);
adj[2].add(1);
adj[2].add(3);
adj[3].add(2);
adj[3].add(4);
adj[4].add(3);
adj[1].add(5);
adj[5].add(1);
a[1] = 4;
a[2] = 9;
a[3] = 14;
a[4] = 100;
a[5] = 5;
// Function call
dfs(1, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < q.length; i++)
{
System.out.print(ans[q[i]] + " ");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 implementation to count the # number of nodes having odd # number of divisors for each query import math N = 100001 # Adjacency list # for tree. adj = [[] for i in range(N)] # Array for values and # answer at ith node. a = [0 for i in range(N)] ans = [0 for i in range(N)] # Function to check whether N # has odd divisors or not def hasOddNumberOfDivisors(n): if (math.sqrt(n) == int(math.sqrt(n))): return True return False # DFS function to pre-compute # the answers def dfs(node, parent): # Initialize the count count = 0 for i in adj[node]: if (i != parent): # Repeat for every child count += dfs(i, node) # Increase the count if current node # has odd number of divisors if (hasOddNumberOfDivisors(a[node])): count += 1 ans[node] = count return count # Driver Code if __name__=="__main__": n = 5 i = 0 q = [ 4, 1, 5, 3 ] # Adjacency List adj[1].append(2) adj[2].append(1) adj[2].append(3) adj[3].append(2) adj[3].append(4) adj[4].append(3) adj[1].append(5) adj[5].append(1) a[1] = 4 a[2] = 9 a[3] = 14 a[4] = 100 a[5] = 5 # Function call dfs(1, -1) for i in range(len(q)): print(ans[q[i]], end = ' ') # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# implementation to
// count the number of nodes
// having odd number of
// divisors for each query
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static readonly int N = 100001;
// Adjacency list
// for tree.
static List<int> []adj =
new List<int>[N];
// Array for values and
// answer at ith node.
static int []a = new int[N];
static int []ans = new int[N];
// Function to check whether N
// has odd divisors or not
static bool hasOddNumberOfDivisors(int n)
{
if ((double)Math.Sqrt(n) ==
(int)Math.Sqrt(n))
return true;
return false;
}
// DFS function to
// pre-compute the answers
static int dfs(int node,
int parent)
{
// Initialize the count
int count = 0;
foreach (int i in adj[node])
{
if (i != parent)
{
// Repeat for every child
count += dfs(i, node);
}
}
// Increase the count if
// current node has odd
// number of divisors
if (hasOddNumberOfDivisors(a[node]))
++count;
ans[node] = count;
return count;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int[] q = {4, 1, 5, 3};
for (int i = 0;
i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List<int>();
// Adjacency List
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(2);
adj[3].Add(4);
adj[4].Add(3);
adj[1].Add(5);
adj[5].Add(1);
a[1] = 4;
a[2] = 9;
a[3] = 14;
a[4] = 100;
a[5] = 5;
// Function call
dfs(1, -1);
for (int i = 0;
i < q.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(ans[q[i]] + " ");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to
// count the number of nodes
// having odd number of
// divisors for each query
let N = 100001;
// Adjacency list
// for tree.
let adj = new Array(N);
// Array for values and
// answer at ith node.
let a = new Array(N);
let ans = new Array(N);
// Function to check whether N
// has odd divisors or not
function hasOddNumberOfDivisors(n)
{
if (Math.sqrt(n) == parseInt(Math.sqrt(n), 10))
return true;
return false;
}
// DFS function to
// pre-compute the answers
function dfs(node, parent)
{
// Initialize the count
let count = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < adj[node].length; i++)
{
if (adj[node][i] != parent)
{
// Repeat for every child
count += dfs(adj[node][i], node);
}
}
// Increase the count if
// current node has odd
// number of divisors
if (hasOddNumberOfDivisors(a[node]))
++count;
ans[node] = count;
return count;
}
let n = 5;
let q = [4, 1, 5, 3];
for (let i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = [];
// Adjacency List
adj[1].push(2);
adj[2].push(1);
adj[2].push(3);
adj[3].push(2);
adj[3].push(4);
adj[4].push(3);
adj[1].push(5);
adj[5].push(1);
a[1] = 4;
a[2] = 9;
a[3] = 14;
a[4] = 100;
a[5] = 5;
// Function call
dfs(1, -1);
for (let i = 0; i < q.length; i++)
{
document.write(ans[q[i]] + " ");
}
// This code is contributed by decode2207.
</script>
1 3 0 1
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por mukulbindal170299 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA