Dado un entero K y una array arr[] , la tarea es encontrar el número de subsecuencias de la array dada de modo que cada subsecuencia consista exactamente en K números primos.
Ejemplo:
Entrada: K = 2, arr = [2, 3, 4, 6]
Salida: 4
Explicación:
Hay 4 subsecuencias que consisten exactamente en 2 números primos {2, 3} {2, 3, 4} {2, 3, 6 } {2, 3, 4, 6}
Entrada: K = 3, arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Salida: 32
Explicación:
Hay 32 subsecuencias que consisten exactamente en 3 números primos.
Enfoque: para resolver el problema mencionado anteriormente, tenemos que encontrar la cantidad de números primos en la array dada .
- Deje que la cuenta de números primos es m .
- Podemos elegir cualquier K entero entre m números primos.
- Entonces, la posible combinación de elegir números primos en la subsecuencia es
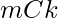 y en la subsecuencia podemos agregar cualquier número de números no primos porque no hay restricción en los números no primos donde el conteo de números no primos será (N – m).
y en la subsecuencia podemos agregar cualquier número de números no primos porque no hay restricción en los números no primos donde el conteo de números no primos será (N – m). - Podemos elegir cualquier subconjunto de (N – m) para números no primos en nuestra subsecuencia.
- La posibilidad de elegir todo el subconjunto de tamaño (N – m) es pow(2, (m – N)) .
- Para generar subsecuencias, multiplicaremos la posibilidad de números primos con la posibilidad de números no primos.
Recuento de subsecuencias = (Recuento de números primos) C (K) * pow(2, recuento de números no primos)
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to find
// the count of subsequences
// which consist exactly K primes
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Returns factorial of n
int fact(int n)
{
int res = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
res = res * i;
return res;
}
// Function to return total
// number of combinations
int nCr(int n, int r)
{
return fact(n)
/ (fact(r)
* fact(n - r));
}
// Function check whether a number
// is prime or not
bool isPrime(int n)
{
// Corner case
if (n <= 1)
return false;
// Check from 2 to n-1
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++)
if (n % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// Function for finding number of subsequences
// which consists exactly K primes
int countSubsequences(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
int countPrime = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (isPrime(arr[i]))
countPrime++;
}
// if number of primes are less thn k
if (countPrime < k)
return 0;
return nCr(countPrime, k)
* pow(2, (n - countPrime));
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int K = 3;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << countSubsequences(arr, n, K);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to find the
// count of subsequences which
// consist exactly K primes
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Returns factorial of n
static int fact(int n)
{
int res = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
res = res * i;
return res;
}
// Function to return total
// number of combinations
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
return fact(n) / (fact(r) *
fact(n - r));
}
// Function check whether a number
// is prime or not
static boolean isPrime(int n)
{
// Corner case
if (n <= 1)
return false;
// Check from 2 to n-1
for(int i = 2; i < n; i++)
if (n % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// Function for finding number of subsequences
// which consists exactly K primes
static int countSubsequences(int arr[],
int n, int k)
{
int countPrime = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (isPrime(arr[i]))
countPrime++;
}
// If number of primes are less thn k
if (countPrime < k)
return 0;
return nCr(countPrime, k) *
(int)Math.pow(2, (n - countPrime));
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int K = 3;
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(countSubsequences(arr, n, K));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ANKITKUMAR34
Python3
# Python3 implementation to find the # count of subsequences which consist # exactly K primes # Returns factorial of n def fact(n): res = 1; for i in range(2, n + 1): res = res * i return res # Function to return total # number of combinations def nCr(n, r): return (fact(n) // (fact(r) * fact(n - r))) # Function check whether a number # is prime or not def isPrime(n): # Corner case if (n <= 1): return False; # Check from 2 to n-1 for i in range(2, n): if (n % i == 0): return False return True # Function for finding number of subsequences # which consists exactly K primes def countSubsequences(arr, n, k): countPrime = 0 for i in range(n): if (isPrime(arr[i])): countPrime += 1 # If number of primes are less than k if (countPrime < k): return 0 return (nCr(countPrime, k) * pow(2, (n - countPrime))) # Driver code arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ] K = 3 n = len(arr) print(countSubsequences(arr, n, K)) # This code is contributed by ANKITKUMAR34
C#
// C# implementation to find the
// count of subsequences which
// consist exactly K primes
using System;
class GFG{
// Returns factorial of n
static int fact(int n)
{
int res = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
res = res * i;
return res;
}
// Function to return total
// number of combinations
static int nCr(int n, int r)
{
return fact(n) / (fact(r) *
fact(n - r));
}
// Function check whether a number
// is prime or not
static bool isPrime(int n)
{
// Corner case
if (n <= 1)
return false;
// Check from 2 to n-1
for(int i = 2; i < n; i++)
if (n % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// Function for finding number of subsequences
// which consists exactly K primes
static int countSubsequences(int []arr,
int n, int k)
{
int countPrime = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (isPrime(arr[i]))
countPrime++;
}
// If number of primes are less than k
if (countPrime < k)
return 0;
return nCr(countPrime, k) *
(int)Math.Pow(2, (n - countPrime));
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int K = 3;
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(countSubsequences(arr, n, K));
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to find
// the count of subsequences
// which consist exactly K primes
// Returns factorial of n
function fact(n)
{
var res = 1;
for (var i = 2; i <= n; i++)
res = res * i;
return res;
}
// Function to return total
// number of combinations
function nCr(n, r)
{
return fact(n)
/ (fact(r)
* fact(n - r));
}
// Function check whether a number
// is prime or not
function isPrime(n)
{
// Corner case
if (n <= 1)
return false;
// Check from 2 to n-1
for (var i = 2; i < n; i++)
if (n % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
// Function for finding number of subsequences
// which consists exactly K primes
function countSubsequences(arr, n, k)
{
var countPrime = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (isPrime(arr[i]))
countPrime++;
}
// if number of primes are less thn k
if (countPrime < k)
return 0;
return nCr(countPrime, k)
* Math.pow(2, (n - countPrime));
}
// Driver code
var arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ];
var K = 3;
var n = arr.length;
document.write( countSubsequences(arr, n, K));
</script>
32
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N^2) .
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1) .