Dado un árbol que consta de N Nodes que tienen valores en el rango [0, N – 1] y (N – 1) bordes, y dos Nodes X e Y , la tarea es encontrar el número de caminos posibles en el árbol tal que el el Node X no aparece antes que el Node Y en la ruta.
Ejemplos:
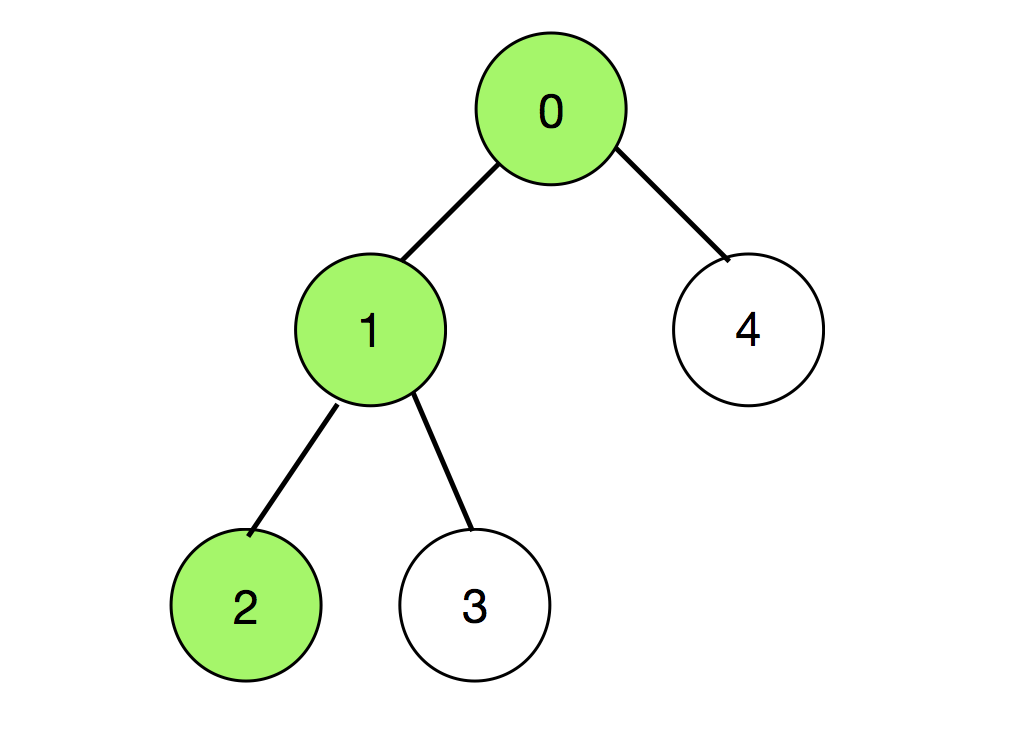
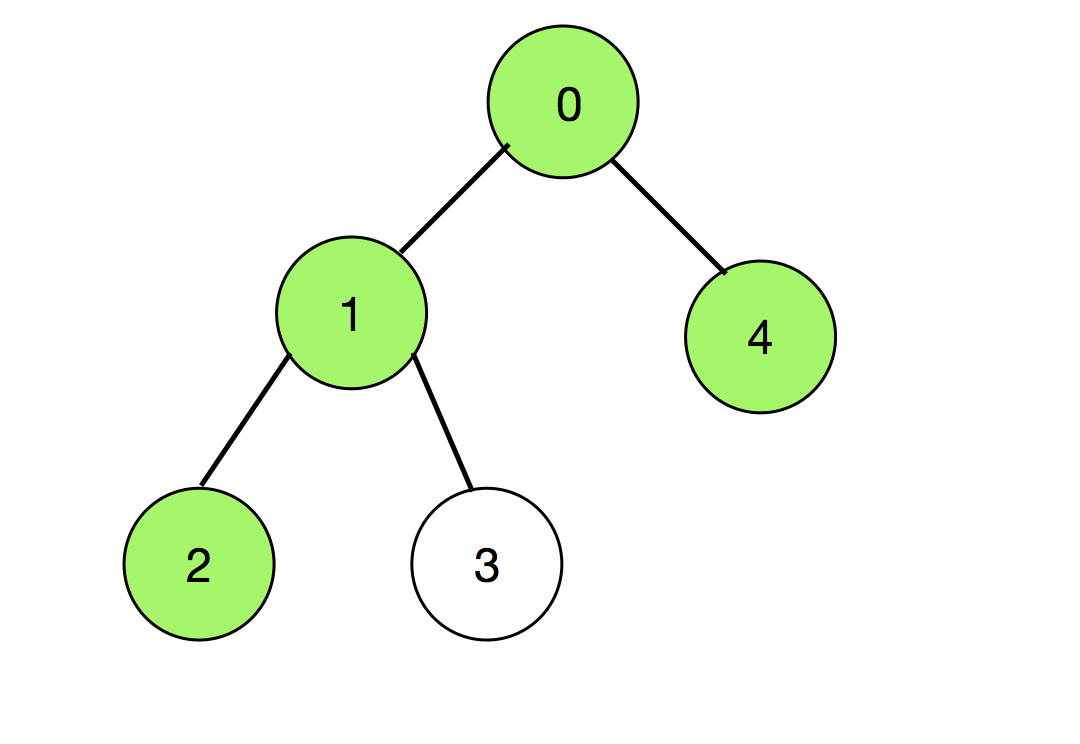
Entrada: N = 5, A = 2, B = 0, Edges[][] = { {0, 1}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {0, 4} }
Salida: 18
Explicación:
Dado que (X, Y) y (Y, X) se consideran diferentes, el recuento de todos los caminos posibles que conectan dos pares de vértices = 2 * 5 C 2 = 20.
De estos 20 pares, esos caminos no se pueden elegir , que consta de los Nodes 2 y 0, así como del Node 2 que aparece antes del Node 0.
Hay dos rutas de este tipo (de color verde) que se muestran a continuación:Así que hay un total de 20 – 2 = 18 de esos caminos.
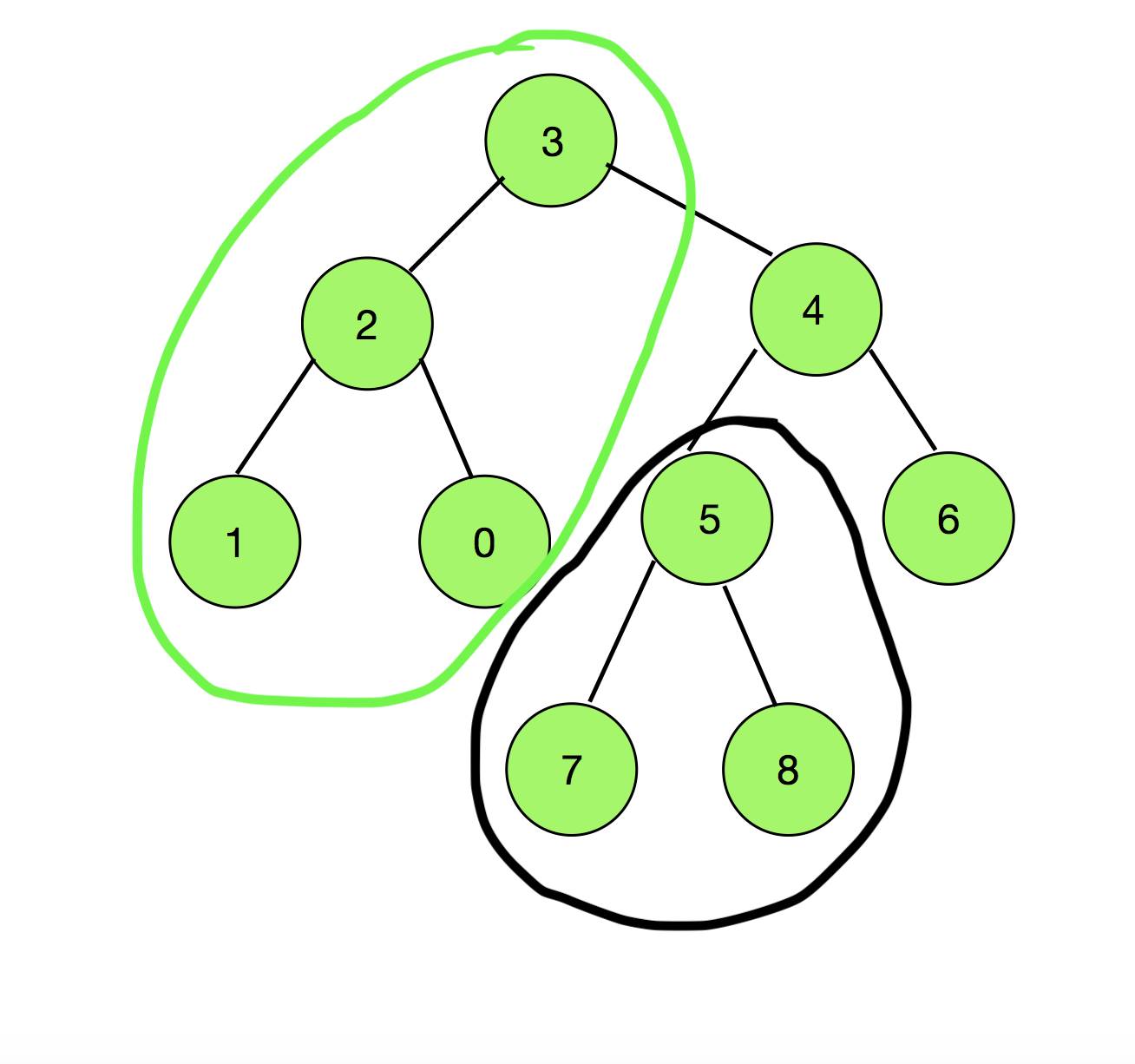
Entrada: N = 9, X = 5, Y = 3, Bordes[][] = { {0, 2}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 6} , {4, 5}, {5, 7}, {5, 8} }
Salida: 60
Explicación:
Dado que (X, Y) y (Y, X) se consideran diferentes, el recuento de todas las rutas posibles que conectan dos pares de vértices = N * (N – 1) = 9 * 8 = 72.
Al observar el siguiente diagrama, cualquier camino que parte de un Node en el subárbol del Node 5, denotado en negro, se conecta a los vértices que pasan por el Node 3, indicado en verde, siempre tendrá 5 antes de 3 en la ruta.Por lo tanto, número total de caminos posibles = (Nodes totales agrupados en negro) * (Nodes totales agrupados en verde) = 3 * 4 = 12.
Por lo tanto, la respuesta final = 72 – 12 = 60
Enfoque:
La idea es encontrar la combinación de pares de Nodes que siempre tendrán el Node X apareciendo antes que el Node Y en la ruta que los conecta. Luego, reste el recuento de dichos pares del número total de pares de Nodes posibles = N C 2 . Considere el Node Y como el Node raíz. Ahora, cualquier ruta que primero encuentre X y luego Y, comienza desde el Node en el subárbol del Node X y termina en un Node en el subárbol del Node Y pero no en el subárbol del Node W , donde W es un hijo inmediato de Node Y y se encuentra entre X e Yen estos caminos.
Por lo tanto, la respuesta final puede ser calculada por:
Recuento = N * (N – 1) – tamaño_del_subárbol(X) * (tamaño_del_subárbol(Y) – tamaño_del_subárbol(W))
Si se toma Y como la raíz del árbol. Entonces, size_of_subtree(Y) = N .
Recuento = N * (N – 1) – tamaño_del_subárbol(X) * (N- tamaño_del_subárbol(W))
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice las arrays subtree_size [] , visited [] y check_subtree [] cada una de tamaño N + 1 . Inicializar elementos de visitado [] como 0 .
- Realice el DFS Traversal con Y como Node raíz para completar check_subtree[] y subtree_size [] para cada Node. El check_subtree[] comprueba si el subárbol del Node actual contiene el Node X o no.
- Encuentre el hijo (digamos Node v) de Y que está en el camino de X a Y. Inicializa una variable entera, por ejemplo, difference .
- Asigne ( número total de Nodes – subtree_size[v] ) a difference .
- Devuelve (N * (N – 1) ) – (subtree_size[A] * (diferencia)) como respuesta.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to implement
// the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long int
using namespace std;
// Maximum number of nodes
const int NN = 3e5;
// Vector to store the tree
vector<int> G[NN + 1];
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
int dfs(int node, int A, int* subtree_size,
int* visited, int* check_subtree)
{
// Mark the node as visited
visited[node] = true;
// Initialize the subtree size
// of each node as 1
subtree_size[node] = 1;
// If the node is same as A
if (node == A) {
// Mark check_subtree[node] as true
check_subtree[node] = true;
}
// Otherwise
else
check_subtree[node] = false;
// Iterate over the adjacent nodes
for (int v : G[node]) {
// If the adjacent node
// is not visited
if (!visited[v]) {
// Update the size of the
// subtree of current node
subtree_size[node]
+= dfs(v, A, subtree_size,
visited, check_subtree);
// Check if the subtree of
// current node contains node A
check_subtree[node] = check_subtree[node]
| check_subtree[v];
}
}
// Return size of subtree of node
return subtree_size[node];
}
// Function to add edges to the tree
void addedge(int node1, int node2)
{
G[node1].push_back(node2);
G[node2].push_back(node1);
}
// Function to calculate the number of
// possible paths
int numberOfPairs(int N, int B, int A)
{
// Stores the size of subtree
// of each node
int subtree_size[N + 1];
// Stores which nodes are
// visited
int visited[N + 1];
// Initialize all nodes as unvisited
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
// Stores if the subtree of
// a node contains node A
int check_subtree[N + 1];
// DFS Call
dfs(B, A, subtree_size,
visited, check_subtree);
// Stores the difference between
// total number of nodes and
// subtree size of an immediate
// child of Y lies between the
// path from A to B
int difference;
// Iterate over the adjacent nodes B
for (int v : G[B]) {
// If the node is in the path
// from A to B
if (check_subtree[v]) {
// Calculate the difference
difference = N - subtree_size[v];
break;
}
}
// Return the final answer
return (N * (N - 1))
- difference * (subtree_size[A]);
}
// Driver Code
int32_t main()
{
int N = 9;
int X = 5, Y = 3;
// Insert Edges
addedge(0, 2);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(2, 3);
addedge(3, 4);
addedge(4, 6);
addedge(4, 5);
addedge(5, 7);
addedge(5, 8);
cout << numberOfPairs(N, Y, X);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Maximum number of nodes
static int NN = (int) 3e5;
// Vector to store the tree
static Vector<Integer> []G = new Vector[NN + 1];
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
static int dfs(int node, int A, int[] subtree_size,
int[] visited, int[] check_subtree)
{
// Mark the node as visited
visited[node] = 1;
// Initialize the subtree size
// of each node as 1
subtree_size[node] = 1;
// If the node is same as A
if (node == A)
{
// Mark check_subtree[node] as true
check_subtree[node] = 1;
}
// Otherwise
else
check_subtree[node] = 0;
// Iterate over the adjacent nodes
for (int v : G[node])
{
// If the adjacent node
// is not visited
if (visited[v] == 0)
{
// Update the size of the
// subtree of current node
subtree_size[node] += dfs(v, A, subtree_size,
visited, check_subtree);
// Check if the subtree of
// current node contains node A
check_subtree[node] = check_subtree[node] |
check_subtree[v];
}
}
// Return size of subtree of node
return subtree_size[node];
}
// Function to add edges to the tree
static void addedge(int node1, int node2)
{
G[node1].add(node2);
G[node2].add(node1);
}
// Function to calculate the number of
// possible paths
static int numberOfPairs(int N, int B, int A)
{
// Stores the size of subtree
// of each node
int []subtree_size = new int[N + 1];
// Stores which nodes are
// visited
int []visited = new int[N + 1];
// Stores if the subtree of
// a node contains node A
int []check_subtree = new int[N + 1];
// DFS Call
dfs(B, A, subtree_size,
visited, check_subtree);
// Stores the difference between
// total number of nodes and
// subtree size of an immediate
// child of Y lies between the
// path from A to B
int difference = 0;
// Iterate over the adjacent nodes B
for (int v : G[B])
{
// If the node is in the path
// from A to B
if (check_subtree[v] > 0)
{
// Calculate the difference
difference = N - subtree_size[v];
break;
}
}
// Return the final answer
return (N * (N - 1)) -
difference * (subtree_size[A]);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 9;
int X = 5, Y = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < G.length; i++)
G[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
// Insert Edges
addedge(0, 2);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(2, 3);
addedge(3, 4);
addedge(4, 6);
addedge(4, 5);
addedge(5, 7);
addedge(5, 8);
System.out.print(numberOfPairs(N, Y, X));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Python3
# Python3 program to implement # the above approach # Maximum number of nodes NN = int(3e5) # Vector to store the tree G = [] for i in range(NN + 1): G.append([]) # Function to perform DFS Traversal def dfs(node, A, subtree_size, visited, check_subtree): # Mark the node as visited visited[node] = True # Initialize the subtree size # of each node as 1 subtree_size[node] = 1 # If the node is same as A if (node == A): # Mark check_subtree[node] as true check_subtree[node] = True # Otherwise else: check_subtree[node] = False # Iterate over the adjacent nodes for v in G[node]: # If the adjacent node # is not visited if (not visited[v]): # Update the size of the # subtree of current node subtree_size[node] += dfs(v, A, subtree_size, visited, check_subtree) # Check if the subtree of # current node contains node A check_subtree[node] = (check_subtree[node] | check_subtree[v]) # Return size of subtree of node return subtree_size[node] # Function to add edges to the tree def addedge(node1, node2): G[node1] += [node2] G[node2] += [node1] # Function to calculate the number of # possible paths def numberOfPairs(N, B, A): # Stores the size of subtree # of each node subtree_size = [0] * (N + 1) # Stores which nodes are # visited visited = [0] * (N + 1) # Stores if the subtree of # a node contains node A check_subtree = [0] * (N + 1) # DFS Call dfs(B, A, subtree_size, visited, check_subtree) # Stores the difference between # total number of nodes and # subtree size of an immediate # child of Y lies between the # path from A to B difference = 0 # Iterate over the adjacent nodes B for v in G[B]: # If the node is in the path # from A to B if (check_subtree[v]): # Calculate the difference difference = N - subtree_size[v] break # Return the final answer return ((N * (N - 1)) - difference * (subtree_size[A])) # Driver Code N = 9 X = 5 Y = 3 # Insert Edges addedge(0, 2) addedge(1, 2) addedge(2, 3) addedge(3, 4) addedge(4, 6) addedge(4, 5) addedge(5, 7) addedge(5, 8) # Function call print(numberOfPairs(N, Y, X)) # This code is contributed by Shivam Singh
C#
// C# Program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Maximum number of nodes
static int NN = (int) 3e5;
// List to store the tree
static List<int> []G = new List<int>[NN + 1];
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
static int dfs(int node, int A, int[] subtree_size,
int[] visited, int[] check_subtree)
{
// Mark the node as visited
visited[node] = 1;
// Initialize the subtree size
// of each node as 1
subtree_size[node] = 1;
// If the node is same as A
if (node == A)
{
// Mark check_subtree[node] as true
check_subtree[node] = 1;
}
// Otherwise
else
check_subtree[node] = 0;
// Iterate over the adjacent nodes
foreach (int v in G[node])
{
// If the adjacent node
// is not visited
if (visited[v] == 0)
{
// Update the size of the
// subtree of current node
subtree_size[node] += dfs(v, A, subtree_size,
visited, check_subtree);
// Check if the subtree of
// current node contains node A
check_subtree[node] = check_subtree[node] |
check_subtree[v];
}
}
// Return size of subtree of node
return subtree_size[node];
}
// Function to add edges to the tree
static void addedge(int node1, int node2)
{
G[node1].Add(node2);
G[node2].Add(node1);
}
// Function to calculate the number of
// possible paths
static int numberOfPairs(int N, int B, int A)
{
// Stores the size of subtree
// of each node
int []subtree_size = new int[N + 1];
// Stores which nodes are
// visited
int []visited = new int[N + 1];
// Stores if the subtree of
// a node contains node A
int []check_subtree = new int[N + 1];
// DFS Call
dfs(B, A, subtree_size,
visited, check_subtree);
// Stores the difference between
// total number of nodes and
// subtree size of an immediate
// child of Y lies between the
// path from A to B
int difference = 0;
// Iterate over the adjacent nodes B
foreach (int v in G[B])
{
// If the node is in the path
// from A to B
if (check_subtree[v] > 0)
{
// Calculate the difference
difference = N - subtree_size[v];
break;
}
}
// Return the readonly answer
return (N * (N - 1)) -
difference * (subtree_size[A]);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 9;
int X = 5, Y = 3;
for (int i = 0; i < G.Length; i++)
G[i] = new List<int>();
// Insert Edges
addedge(0, 2);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(2, 3);
addedge(3, 4);
addedge(4, 6);
addedge(4, 5);
addedge(5, 7);
addedge(5, 8);
Console.Write(numberOfPairs(N, Y, X));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript Program to implement the above approach
// Maximum number of nodes
let NN = 3e5;
// Vector to store the tree
let G = new Array(NN + 1);
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
function dfs(node, A, subtree_size, visited, check_subtree)
{
// Mark the node as visited
visited[node] = 1;
// Initialize the subtree size
// of each node as 1
subtree_size[node] = 1;
// If the node is same as A
if (node == A)
{
// Mark check_subtree[node] as true
check_subtree[node] = 1;
}
// Otherwise
else
check_subtree[node] = 0;
// Iterate over the adjacent nodes
for (let v = 0; v < G[node].length; v++)
{
// If the adjacent node
// is not visited
if (visited[G[node][v]] == 0)
{
// Update the size of the
// subtree of current node
subtree_size[node] += dfs(G[node][v], A, subtree_size,
visited, check_subtree);
// Check if the subtree of
// current node contains node A
check_subtree[node] = check_subtree[node] |
check_subtree[G[node][v]];
}
}
// Return size of subtree of node
return subtree_size[node];
}
// Function to add edges to the tree
function addedge(node1, node2)
{
G[node1].push(node2);
G[node2].push(node1);
}
// Function to calculate the number of
// possible paths
function numberOfPairs(N, B, A)
{
// Stores the size of subtree
// of each node
let subtree_size = new Array(N + 1);
subtree_size.fill(0);
// Stores which nodes are
// visited
let visited = new Array(N + 1);
visited.fill(0);
// Stores if the subtree of
// a node contains node A
let check_subtree = new Array(N + 1);
check_subtree.fill(0);
// DFS Call
dfs(B, A, subtree_size, visited, check_subtree);
// Stores the difference between
// total number of nodes and
// subtree size of an immediate
// child of Y lies between the
// path from A to B
let difference = 0;
// Iterate over the adjacent nodes B
for (let v = 0; v < G[B].length; v++)
{
// If the node is in the path
// from A to B
if (check_subtree[G[B][v]] > 0)
{
// Calculate the difference
difference = N - subtree_size[G[B][v]];
break;
}
}
// Return the final answer
return (N * (N - 1)) -
difference * (subtree_size[A]);
}
let N = 9;
let X = 5, Y = 3;
for (let i = 0; i < G.length; i++)
G[i] = [];
// Insert Edges
addedge(0, 2);
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(2, 3);
addedge(3, 4);
addedge(4, 6);
addedge(4, 5);
addedge(5, 7);
addedge(5, 8);
document.write(numberOfPairs(N, Y, X));
</script>
60
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por mohitkumarbt2k18 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA