Dadas dos strings binarias A y B de igual longitud N , la tarea es encontrar el número de XOR distintos posibles reordenando arbitrariamente las dos strings binarias. Dado que el número puede ser lo suficientemente grande, encuentra el número módulo 10 9 + 7
Ejemplos:
Entrada: A = “00”, B = “01”
Salida: 2
Explicación:
Hay dos posibles resultados reordenando los dígitos de la string B.
Son: “10” y “01”Entrada: A = “010”, B = “100”
Salida: 4
Explicación:
Hay cuatro resultados posibles al reorganizar los dígitos de ambas strings.
Ellos son: “000”, “110”, “011”, “101”
Acercarse:
- Ya que sabemos que
0 XOR 0 = 0 0 XOR 1 = 1 1 XOR 0 = 1 1 XOR 1 = 0
Por lo tanto, para obtener un valor XOR como ‘1’ en cualquier índice de la string de resultados, las strings de entrada deben tener un número impar de 1 en ese índice.
- Ahora, intentaremos reorganizar las strings binarias de manera que el número máximo de índices tenga un número impar de 1 en ellos. Esto se puede visualizar con el siguiente ejemplo:
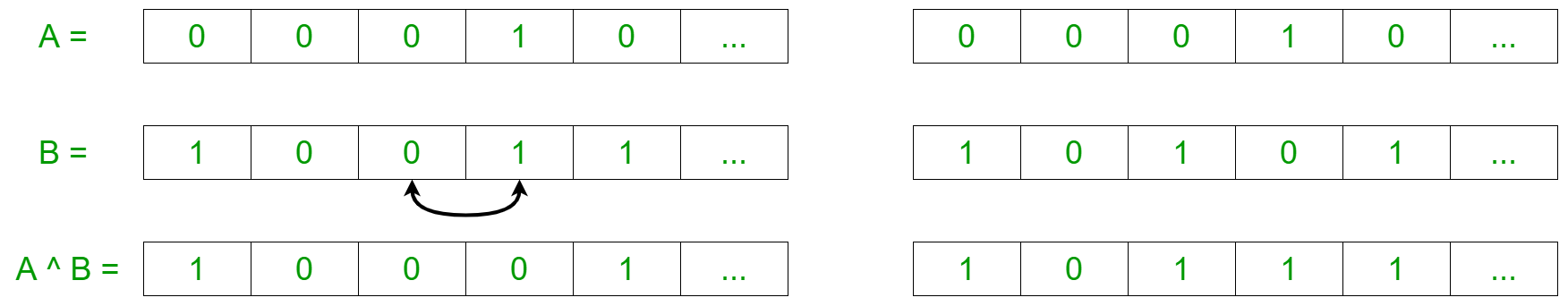
- Por lo tanto, a partir de la observación anterior, la idea es encontrar el número mínimo y máximo de 1 posibles reordenando las strings.
- Para encontrar el máximo de ‘1’: El máximo de ‘1’ en el resultado ocurrirá cuando se formen los pares máximos {0, 1} y {1, 0}. Por lo tanto,
Número máximo de {0, 1} pares = mínimo (recuento de ‘0’ en A, recuento de ‘1’ en B)
Número máximo de {1, 0} pares = mínimo (recuento de ‘1’ en A, recuento de ‘0’ en B)
Por lo tanto, Número máximo de ‘1’ en el XOR = Número máximo de {0, 1} pares + Número máximo de {1, 0} pares
- Para encontrar los ‘1’ mínimos: este caso puede verse como el inverso del número máximo de ‘0’ en el resultado. De manera similar, el máximo de ‘0’ en el resultado ocurriría cuando se formen los pares máximos {0, 0} y {1, 1}. Por lo tanto,
Número máximo de {0, 0} pares = mínimo (recuento de ‘0’ en A, recuento de ‘0’ en B)
Número máximo de {1, 1} pares = mínimo (recuento de ‘1’ en A, recuento de ‘1’ en B)
Número máximo de ‘0’ en el XOR = Número máximo de {0, 0} pares + Número máximo de {1, 1} pares
Por lo tanto, Número mínimo de ‘1’ en el XOR = N – Número máximo de ‘0’s en el XOR
- Todas las combinaciones de 1 se pueden formar entre estos dos números (mínimo y máximo) con la diferencia de 2.
- Finalmente, el número total de formas posibles de obtener el resultado se puede calcular mediante el número de combinaciones del número mínimo de 1 y el número máximo de 1 con un paso de 2.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++14
// C++ program to find the number of
// distinct XORs formed by rearranging
// two binary strings
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// function to compute modulo power
long long power(long long a, long long b, long long mod)
{
long long aa = 1;
while(b)
{
if(b&1)
{
aa = aa * a;
aa %= mod;
}
a = a * a;
a %= mod;
b /= 2;
}
return aa;
}
// Function to calculate nCr % p
// over a range
long long nCrRangeSum(long long n, long long r1,
long long r2, long long p)
{
// Initialize the numerator
// and denominator
long long num = 1, den = 1;
// Initialize the sum
long long sum = 0;
// nC0 is 1
if (r1 == 0)
sum += 1;
// Traversing till the range
for (int i = 0; i < r2; i++)
{
// Computing the numerator
num = (num * (n - i)) % p;
// Computing the denominator
den = (den * (i + 1)) % p;
// If 'i' lies between the given range
// and is at an even long long interval from
// the starting range because
// the combinations at a step of 2
// is required
if(i - r1 >= -1 and (i - r1 + 1) % 2 == 0)
{
// Computing nCr and adding the value
// sum
sum += (num * power(den, p - 2, p)) % p;
sum %= p;
}
}
return sum;
}
// Function to find the number of
// distinct XORs formed by
// rearranging two binary strings
int compute(string A, string B, int N)
{
// Initializing the count variable
// to 0
int c0A = 0, c1A = 0, c0B = 0, c1B = 0;
// Iterating through A
for (char c:A) {
// Increment the c1A variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1A += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0A += 1;
}
// Iterating through B
for (char c:B){
// Increment the c1B variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1B += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0B += 1;
}
// Finding the minimum number of '1's in the XOR
// and the maximum number of '1's in the XOR
int max1xor = min(c0A, c1B) + min(c1A, c0B);
int min1xor = N - min(c0B, c0A) - min(c1A, c1B);
// Compute the number of combinations between
// the minimum number of 1's and the maximum
// number of 1's and perform % with 10^9 + 7
int ans = nCrRangeSum(N, min1xor, max1xor, 1000000000 + 7);
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
long long N = 3;
string A = "010";
string B = "100";
cout << compute(A, B,N);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
Java
// JAVA program to find the number of
// distinct Bitwise XORs formed by rearranging
// two binary strings
class GFG
{
// function to compute modular exponentiation
// i.e. to find (a^b) % mod
static long mod_power(long a, long b,
long mod)
{
long result = 1l;
while(b > 0)
{
if((b&1) == 0) // b is even
{
result = a * a;
a %= mod;
b /= 2;
}
else // b is odd
{
result = result * a;
result %= mod;
}
}
return result;
}
// method to evaluate nCr modulo p
// over an interval
static long nCr_RangeSum(long n, long r1,
long r2, long p)
{
// initializing numerator
// and denominator
long num = 1, den = 1;
// initialize the sum
long sum = 0l;
// nC0 is 1
if(r1 == 0)
sum += 1l;
// Iterating through the range
for(int i = 0; i < r2; i++)
{
// computing the numerator
num = (num * (n - i)) % p;
// computing the denominator
den = (den * (i + 1)) % p;
// If 'i' lies between the given range
// and is at an even interval from
// the starting range because
// the combinations at a step of 2
// is required
if(i - r1 >= -1 && (i - r1 + 1) % 2 == 0)
{
// Computing nCr and adding the value
// to the sum
sum += (num * mod_power(den, p - 2, p)) % p;
sum %= p;
}
}
return sum;
}
// method to find the number of
// distinct XORs formed by
// rearrangement of two binary strings
static long compute(String A, String B, int N)
{
// Initializing the counter variables
// to 0
int c0A = 0, c1A = 0, c0B = 0, c1B = 0;
// Iterating through A's characters
for (char c : A.toCharArray())
{
// Increment the c1A variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1A += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0A += 1;
}
// Iterating through B's characters
for (char c : B.toCharArray())
{
// Increment the c1B variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1B += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0B += 1;
}
// Finding the minimum number of '1's in the XOR
// and the maximum number of '1's in the XOR
int max1xor = Math.min(c0A, c1B) + Math.min(c1A, c0B);
int min1xor = N - Math.min(c0B, c0A) - Math.min(c1A, c1B);
// Compute the number of combinations between
// the minimum number of 1's and the maximum
// number of 1's and perform modulo with 10^9 + 7
long ans = nCr_RangeSum(N, min1xor, max1xor, 1000000000 + 7);
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 3; // length of each string
String A = "010";
String B = "100";
System.out.print(compute(A, B, N));
}
}
// This Code is contributed by Soumitri Chattopadhyay.
Python3
# Python3 program to find the number of # distinct XORs formed by rearranging # two binary strings # Function to calculate nCr % p # over a range def nCrRangeSum(n, r1, r2, p): # Initialize the numerator # and denominator num = den = 1 # Initialize the sum sum = 0 # nC0 is 1 if r1 == 0: sum += 1 # Traversing till the range for i in range(r2): # Computing the numerator num = (num * (n - i)) % p # Computing the denominator den = (den * (i + 1)) % p # If 'i' lies between the given range # and is at an even interval from # the starting range because # the combinations at a step of 2 # is required if(i - r1 >= -1 and (i - r1 + 1) % 2 == 0): # Computing nCr and adding the value # sum sum += (num * pow(den, p - 2, p)) % p sum %= p return sum # Function to find the number of # distinct XORs formed by # rearranging two binary strings def compute(A, B): # Initializing the count variable # to 0 c0A = c1A = c0B = c1B = 0 # Iterating through A for c in A: # Increment the c1A variable # if the current element is 1 if c == '1': c1A += 1 # Increment the c0A variable # if the current element is 0 elif c == '0': c0A += 1 # Iterating through B for c in B: # Increment the c1B variable # if the current element is 1 if c == '1': c1B += 1 # Increment the c0A variable # if the current element is 0 elif c == '0': c0B += 1 # Finding the minimum number of '1's in the XOR # and the maximum number of '1's in the XOR max1xor = min(c0A, c1B) + min(c1A, c0B) min1xor = N - min(c0B, c0A) - min(c1A, c1B) # Compute the number of combinations between # the minimum number of 1's and the maximum # number of 1's and perform % with 10^9 + 7 ans = nCrRangeSum(N, min1xor, max1xor, 10**9 + 7) # Return the answer return ans # Driver code if __name__ == "__main__": N = 3 A = "010" B = "100" print(compute(A, B))
C#
// C# program to find the number of
// distinct Bitwise XORs formed by
// rearranging two binary strings
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to compute modular exponentiation
// i.e. to find (a^b) % mod
static long mod_power(long a, long b,
long mod)
{
long result = 1;
while (b > 0)
{
if ((b & 1) == 0) // b is even
{
result = a * a;
a %= mod;
b /= 2;
}
else // b is odd
{
result = result * a;
result %= mod;
}
}
return result;
}
// Function to evaluate nCr modulo p
// over an interval
static long nCr_RangeSum(long n, long r1,
long r2, long p)
{
// Initializing numerator
// and denominator
long num = 1, den = 1;
// Initialize the sum
long sum = 0;
// nC0 is 1
if (r1 == 0)
sum += 1;
// Iterating through the range
for(int i = 0; i < r2; i++)
{
// Computing the numerator
num = (num * (n - i)) % p;
// Computing the denominator
den = (den * (i + 1)) % p;
// If 'i' lies between the given range
// and is at an even interval from
// the starting range because
// the combinations at a step of 2
// is required
if (i - r1 >= -1 && (i - r1 + 1) % 2 == 0)
{
// Computing nCr and adding the value
// to the sum
sum += (num * mod_power(
den, p - 2, p)) % p;
sum %= p;
}
}
return sum;
}
// Function to find the number of distinct
// XORs formed by rearrangement of two
// binary strings
static long compute(string A, string B, int N)
{
// Initializing the counter variables
// to 0
int c0A = 0, c1A = 0, c0B = 0, c1B = 0;
// Iterating through A's characters
foreach(char c in A)
{
// Increment the c1A variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1A += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0A += 1;
}
// Iterating through B's characters
foreach(char c in B)
{
// Increment the c1B variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1B += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0B += 1;
}
// Finding the minimum number of
// '1's in the XOR and the maximum
// number of '1's in the XOR
int max1xor = Math.Min(c0A, c1B) +
Math.Min(c1A, c0B);
int min1xor = N - Math.Min(c0B, c0A) -
Math.Min(c1A, c1B);
// Compute the number of combinations
// between the minimum number of 1's
// and the maximum number of 1's and
// perform modulo with 10^9 + 7
long ans = nCr_RangeSum(N, min1xor,
max1xor, 1000000000 + 7);
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Driver code
static public void Main()
{
// Length of each string
int N = 3;
string A = "010";
string B = "100";
Console.WriteLine(compute(A, B, N));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat
Javascript
// JavaScript program to find the number of
// distinct XORs formed by rearranging
// two binary strings
// function to compute modulo power
function power(a, b, mod)
{
var aa = 1n;
while (b) {
if (BigInt(b) & 1n) {
aa = aa * a;
aa %= mod;
}
a = a * a;
a %= mod;
b = Math.floor(Number(BigInt(b) / 2n));
}
return aa;
}
// Function to calculate nCr % p
// over a range
function nCrRangeSum(n, r1, r2, p)
{
// Initialize the numerator
// and denominator
var num = 1n;
var den = 1n;
// Initialize the sum
var sum = 0n;
// nC0 is 1
if (r1 == 0)
sum += 1n;
// Traversing till the range
for (var i = 0; i < r2; i++) {
// Computing the numerator
num = (num * (BigInt(n) - BigInt(i))) % p;
// Computing the denominator
den = BigInt(den * (BigInt(i) + 1n)) % p;
// If 'i' lies between the given range
// and is at an even long long interval from
// the starting range because
// the combinations at a step of 2
// is required
if (i - r1 >= -1 && (i - r1 + 1) % 2 == 0) {
// Computing nCr and adding the value
// sum
sum += BigInt(num * power(den, p - 2n, p)) % p;
sum %= p;
}
}
return Number(sum);
}
// Function to find the number of
// distinct XORs formed by
// rearranging two binary strings
function compute(A, B, N)
{
// Initializing the count variable
// to 0
var c0A = 0;
var c1A = 0;
var c0B = 0;
var c1B = 0;
// Iterating through A
for (var c of A) {
// Increment the c1A variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1A += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0A += 1;
}
// Iterating through B
for (var c of B) {
// Increment the c1B variable
// if the current element is 1
if (c == '1')
c1B += 1;
// Increment the c0A variable
// if the current element is 0
else if (c == '0')
c0B += 1;
}
// Finding the minimum number of '1's in the XOR
// and the maximum number of '1's in the XOR
var max1xor = Math.min(c0A, c1B) + Math.min(c1A, c0B);
var min1xor
= N - Math.min(c0B, c0A) - Math.min(c1A, c1B);
// Compute the number of combinations between
// the minimum number of 1's and the maximum
// number of 1's and perform % with 10^9 + 7
var ans = nCrRangeSum(N, min1xor, max1xor,
BigInt(1000000000 + 7));
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Driver code
var N = 3;
var A = "010";
var B = "100";
// Function call
console.log(compute(A, B, N));
// This code is contributed by phasing17
4
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por koustavdhar3105 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA