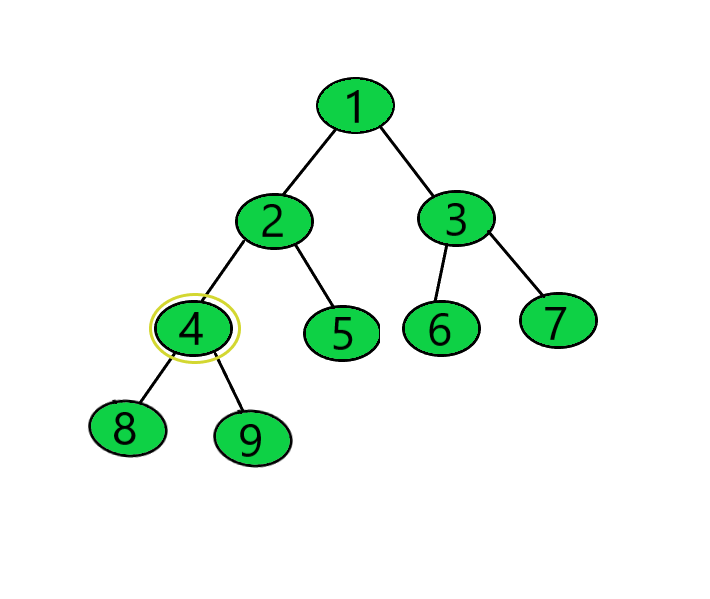
Dado un árbol binario y un objetivo entero , que denota el valor de un Node, la tarea es encontrar la suma de las distancias de todos los Nodes desde el Node dado.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: objetivo = 3
Salida: 19
Explicación:Distancia de los Nodes 1, 6, 7 al Node 3 = 1
Distancia del Node 2 al Node 3 = 2
Distancia de los Nodes 4, 5 al Node 3 = 3
Distancia de los Nodes 8, 9 al Node 3 = 4
Suma de las distancias = (1 + 1 + 1) + (2) + (3 + 3) + (4 + 4) = 19.Entrada: objetivo = 4
Salida: 18
Enfoque ingenuo: la idea más simple para resolver este problema es que, cada vez que se atraviesa un Node a la izquierda o a la derecha de un Node, las distancias de los Nodes a sus subárboles se reducen en 1, y la distancia del resto de los Nodes desde ese Node aumenta en 1.
Por lo tanto, la siguiente relación da la suma de las distancias de todos los Nodes desde un Node, digamos u :
sumDists(u)= sumDists(parent(u)) – (Nodes en el subárbol izquierdo y derecho de u) + (N – Nodes en el subárbol izquierdo y derecho de u)
donde,
sumDists(u): Suma de las distancias de todos los Nodes desde el Node u
sumDists(parent(u)): Suma de las distancias de todos los Nodes desde el Node padre de u
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Cree una función para encontrar la cantidad de Nodes en el subárbol izquierdo y derecho del Node dado (incluido el Node dado).
- Cree una función para encontrar la suma de las profundidades del Node y la variable suma denota la suma de la distancia de todos los Nodes desde el objetivo.
- Atraviese el árbol usando DFS (búsqueda primero en profundidad) y para cada Node realice lo siguiente:
- Si el objetivo coincide con el Node actual, actualice la suma como distancia .
- Más:
- Si root->left no es nulo , encuentre el número de Nodes en el subárbol izquierdo y pase la suma de la distancia de todos los Nodes desde el Node root->left como tempSum .
- Si root->right no es nulo , busque el número de Nodes en el subárbol derecho y pase la suma de la distancia de todos los Nodes desde root->rightnode como tempSum .
- Al llegar al Node de destino, imprima la suma de la distancia de los Nodes desde el Node de destino.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of a
// Binary Tree Node
class TreeNode {
public:
int data;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to its
// left and right pointers
TreeNode* newNode(int data)
{
// Allocate the node
TreeNode* Node = new TreeNode();
// Allocate Memory
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return (Node);
}
// Function which calculates sum
// of depths of all nodes
int sumofdepth(TreeNode* root, int l)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Return recursively
return l + sumofdepth(root->left,
l + 1)
+ sumofdepth(root->right,
l + 1);
}
// Function to count of nodes
// in the left and right subtree
int Noofnodes(TreeNode* root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Return recursively
return Noofnodes(root->left)
+ Noofnodes(root->right)
+ 1;
}
// Stores the sum of distances
// of all nodes from given node
int sum = 0;
// Function to find sum of distances
// of all nodes from a given node
void distance(TreeNode* root,
int target,
int distancesum,
int n)
{
// If target node matches
// with the current node
if (root->data == target) {
sum = distancesum;
return;
}
// If left of current node exists
if (root->left) {
// Count number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(
root->left);
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- nodes
+ (n - nodes);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root->left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If right is not null
if (root->right) {
// Find number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(
root->right);
// Applying the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- nodes + (n - nodes);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root->right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input tree
TreeNode* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->left->left->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left->right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
// Sum of depth of all
// nodes from root node
int distanceroot
= sumofdepth(root, 0);
// Number of nodes in the
// left and right subtree
int totalnodes = Noofnodes(root);
distance(root, target, distanceroot,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
cout << sum;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Structure of a
// Binary Tree Node
static class TreeNode
{
int data;
TreeNode left, right;
}
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to its
// left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = Node.right = null;
return (Node);
}
// Function which calculates sum
// of depths of all nodes
static int sumofdepth(TreeNode root, int l)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recursively
return l + sumofdepth(root.left, l + 1) +
sumofdepth(root.right, l + 1);
}
// Function to count of nodes
// in the left and right subtree
static int Noofnodes(TreeNode root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recursively
return Noofnodes(root.left) +
Noofnodes(root.right) + 1;
}
// Stores the sum of distances
// of all nodes from given node
public static int sum = 0;
// Function to find sum of distances
// of all nodes from a given node
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches
// with the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
return;
}
// If left of current node exists
if (root.left != null)
{
// Count number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(root.left);
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum - nodes +
(n - nodes);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n);
}
// If right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Find number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(root.right);
// Applying the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum - nodes +
(n - nodes);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
// Sum of depth of all
// nodes from root node
int distanceroot = sumofdepth(root, 0);
// Number of nodes in the
// left and right subtree
int totalnodes = Noofnodes(root);
distance(root, target, distanceroot,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Dharanendra L V
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Structure of a # Binary Tree Node class TreeNode: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Function which calculates sum # of depths of all nodes def sumofdepth(root, l): # Base Case if (root == None): return 0 # Return recursively return l + sumofdepth(root.left, l + 1)+ sumofdepth(root.right, l + 1) # Function to count of nodes # in the left and right subtree def Noofnodes(root): # Base Case if (root == None): return 0 # Return recursively return Noofnodes(root.left) + Noofnodes(root.right) + 1 # Stores the sum of distances # of all nodes from given node sum = 0 # Function to find sum of distances # of all nodes from a given node def distance(root, target, distancesum, n): global sum # If target node matches # with the current node if (root.data == target): sum = distancesum return # If left of current node exists if (root.left): # Count number of nodes # in the left subtree nodes = Noofnodes(root.left) # Update sum tempsum = distancesum - nodes + (n - nodes) # Recur for the left subtree distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n) # If right is not null if (root.right): # Find number of nodes # in the left subtree nodes = Noofnodes(root.right) # Applying the formula given # in the approach tempsum = distancesum - nodes + (n - nodes) # Recur for the right subtree distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Input tree root = TreeNode(1) root.left = TreeNode(2) root.right = TreeNode(3) root.left.left = TreeNode(4) root.left.right = TreeNode(5) root.right.left = TreeNode(6) root.right.right = TreeNode(7) root.left.left.left = TreeNode(8) root.left.left.right = TreeNode(9) target = 3 # Sum of depth of all # nodes from root node distanceroot = sumofdepth(root, 0) # Number of nodes in the # left and right subtree totalnodes = Noofnodes(root) distance(root, target, distanceroot, totalnodes) # Print the sum of distances print (sum) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG{
// Structure of a
// Binary Tree Node
class TreeNode
{
public int data;
public TreeNode left, right;
}
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to its
// left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = Node.right = null;
return (Node);
}
// Function which calculates sum
// of depths of all nodes
static int sumofdepth(TreeNode root, int l)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recursively
return l + sumofdepth(root.left, l + 1) +
sumofdepth(root.right, l + 1);
}
// Function to count of nodes
// in the left and right subtree
static int Noofnodes(TreeNode root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recursively
return Noofnodes(root.left) +
Noofnodes(root.right) + 1;
}
// Stores the sum of distances
// of all nodes from given node
public static int sum = 0;
// Function to find sum of distances
// of all nodes from a given node
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches
// with the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
return;
}
// If left of current node exists
if (root.left != null)
{
// Count number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(root.left);
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum - nodes +
(n - nodes);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n);
}
// If right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Find number of nodes
// in the left subtree
int nodes = Noofnodes(root.right);
// Applying the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum - nodes +
(n - nodes);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
// Sum of depth of all
// nodes from root node
int distanceroot = sumofdepth(root, 0);
// Number of nodes in the
// left and right subtree
int totalnodes = Noofnodes(root);
distance(root, target, distanceroot,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
Console.WriteLine(sum);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Structure of a
// Binary Tree Node
class TreeNode
{
constructor(data) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = data;
}
}
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to its
// left and right pointers
function newNode(data)
{
let Node = new TreeNode(data);
return (Node);
}
// Function which calculates sum
// of depths of all nodes
function sumofdepth(root, l)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recursively
return l + sumofdepth(root.left, l + 1) +
sumofdepth(root.right, l + 1);
}
// Function to count of nodes
// in the left and right subtree
function Noofnodes(root)
{
// Base Case
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Return recursively
return Noofnodes(root.left) +
Noofnodes(root.right) + 1;
}
// Stores the sum of distances
// of all nodes from given node
let sum = 0;
// Function to find sum of distances
// of all nodes from a given node
function distance(root, target, distancesum, n)
{
// If target node matches
// with the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
return;
}
// If left of current node exists
if (root.left != null)
{
// Count number of nodes
// in the left subtree
let nodes = Noofnodes(root.left);
// Update sum
let tempsum = distancesum - nodes + (n - nodes);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n);
}
// If right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Find number of nodes
// in the left subtree
let nodes = Noofnodes(root.right);
// Applying the formula given
// in the approach
let tempsum = distancesum - nodes + (n - nodes);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n);
}
}
// Input tree
let root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
let target = 3;
// Sum of depth of all
// nodes from root node
let distanceroot = sumofdepth(root, 0);
// Number of nodes in the
// left and right subtree
let totalnodes = Noofnodes(root);
distance(root, target, distanceroot,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
document.write(sum);
// This code is contributed by suresh07.
</script>
19
Complejidad de Tiempo: O(N 2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Enfoque eficiente: el enfoque anterior se puede optimizar agregando una variable adicional, digamos tamaño , para indicar el recuento de Nodes en sus subárboles izquierdo y derecho, en la estructura de un Node. Esto reduce la tarea de calcular el tamaño de los subárboles a un tiempo computacional constante.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
class TreeNode {
public:
int data, size;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and NULL to
// its left and right pointers
TreeNode* newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode* Node = new TreeNode();
Node->data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
// Return newly created node
return (Node);
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
pair<int, int> sumofsubtree(TreeNode* root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
pair<int, int> p = make_pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root->left) {
pair<int, int> ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root->left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root->right) {
pair<int, int> ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root->right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root->size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
int sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
void distance(TreeNode* root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root->data == target) {
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root->left is not null
if (root->left) {
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- root->left->size
+ (n - root->left->size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root->left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root->right is not null
if (root->right) {
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- root->right->size
+ (n - root->right->size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root->right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Input tree
TreeNode* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->left->left->left = newNode(8);
root->left->left->right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
pair<int, int> p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
int totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
static class TreeNode
{
int data, size;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and null to
// its left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = null;
Node.right = null;
// Return newly created node
return (Node);
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
static pair sumofsubtree(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
pair p = new pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root.left != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root.right != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root.size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
static int sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root.left is not null
if (root.left != null)
{
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.left.size
+ (n - root.left.size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root.right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.right.size
+ (n - root.right.size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
pair p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
int totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
System.out.print(sum +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Stores the sum of distances of all
# nodes from the given node
sum = 0
# Structure of a
# binary tree node
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.size = 0
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to count the number of
# nodes in the left and right subtrees
def sumofsubtree(root):
# Initialize a pair that stores
# the pair {number of nodes, depth}
p = [1, 0]
# Finding the number of nodes
# in the left subtree
if (root.left):
ptemp = sumofsubtree(root.left)
p[1] += ptemp[0] + ptemp[1]
p[0] += ptemp[0]
# Find the number of nodes
# in the right subtree
if (root.right):
ptemp = sumofsubtree(root.right)
p[1] += ptemp[0] + ptemp[1]
p[0] += ptemp[0]
# Filling up size field
root.size = p[0]
return p
# Function to find the total distance
def distance(root, target, distancesum, n):
global sum
# If target node matches with
# the current node
if (root.data == target):
sum = distancesum
# If root.left is not null
if (root.left):
# Update sum
tempsum = (distancesum - root.left.size +
(n - root.left.size))
# Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target, tempsum, n)
# If root.right is not null
if (root.right):
# Apply the formula given
# in the approach
tempsum = (distancesum - root.right.size +
(n - root.right.size))
# Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target, tempsum, n)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Input tree
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
root.left.right = TreeNode(5)
root.right.left = TreeNode(6)
root.right.right = TreeNode(7)
root.left.left.left = TreeNode(8)
root.left.left.right = TreeNode(9)
target = 3
p = sumofsubtree(root)
# Total number of nodes
totalnodes = p[0]
distance(root, target, p[1], totalnodes)
# Print the sum of distances
print(sum)
# This code is contributed by ipg2016107
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
public class GFG
{
class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
class TreeNode
{
public int data, size;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
};
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and null to
// its left and right pointers
static TreeNode newNode(int data)
{
TreeNode Node = new TreeNode();
Node.data = data;
Node.left = null;
Node.right = null;
// Return newly created node
return (Node);
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
static pair sumofsubtree(TreeNode root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
pair p = new pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root.left != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root.right != null)
{
pair ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root.size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
static int sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
static void distance(TreeNode root, int target,
int distancesum, int n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root.left is not null
if (root.left != null)
{
// Update sum
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.left.size
+ (n - root.left.size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root.right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
int tempsum = distancesum
- root.right.size
+ (n - root.right.size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Input tree
TreeNode root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.right.left = newNode(6);
root.right.right = newNode(7);
root.left.left.left = newNode(8);
root.left.left.right = newNode(9);
int target = 3;
pair p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
int totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
Console.Write(sum +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
class pair
{
constructor(first,second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Structure of a
// binary tree node
class Node
{
// Function that allocates a new node
// with the given data and null to
// its left and right pointers
constructor(data)
{
this.data=data;
this.size=0;
this.left=this.right=null;
}
}
// Function to count the number of
// nodes in the left and right subtrees
function sumofsubtree(root)
{
// Initialize a pair that stores
// the pair {number of nodes, depth}
let p = new pair(1, 0);
// Finding the number of nodes
// in the left subtree
if (root.left != null)
{
let ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.left);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Find the number of nodes
// in the right subtree
if (root.right != null)
{
let ptemp
= sumofsubtree(root.right);
p.second += ptemp.first
+ ptemp.second;
p.first += ptemp.first;
}
// Filling up size field
root.size = p.first;
return p;
}
// Stores the sum of distances of all
// nodes from the given node
let sum = 0;
// Function to find the total distance
function distance(root,target,distancesum,n)
{
// If target node matches with
// the current node
if (root.data == target)
{
sum = distancesum;
}
// If root.left is not null
if (root.left != null)
{
// Update sum
let tempsum = distancesum
- root.left.size
+ (n - root.left.size);
// Recur for the left subtree
distance(root.left, target,
tempsum, n);
}
// If root.right is not null
if (root.right != null)
{
// Apply the formula given
// in the approach
let tempsum = distancesum
- root.right.size
+ (n - root.right.size);
// Recur for the right subtree
distance(root.right, target,
tempsum, n);
}
}
// Driver Code
// Input tree
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.left.left.left = new Node(8);
root.left.left.right = new Node(9);
let target = 3;
let p = sumofsubtree(root);
// Total number of nodes
let totalnodes = p.first;
distance(root, target, p.second,
totalnodes);
// Print the sum of distances
document.write(sum +"<br>");
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
19
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por nishkarshmaitry0864 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA