El teorema de paréntesis se usa en DFS de gráfico . Establece que los descendientes en un árbol de búsqueda primero en profundidad tienen una propiedad interesante. Si v es un descendiente de u , entonces el tiempo de descubrimiento de v es posterior al tiempo de descubrimiento de u .
En cualquier recorrido DFS de un gráfico g = (V, E), para dos vértices cualesquiera u y v se cumple exactamente uno de los siguientes:
- Los intervalos [d[u], f[u]] y [d[v], f[v]] son completamente disjuntos y ni u ni v son descendientes del otro en el bosque de profundidad primero.
- El intervalo [d[u], f[u]] está contenido dentro del intervalo [d[v], f[v]] , y u es un descendiente de v en un árbol de profundidad.
- El intervalo [d[v], f[v]] está contenido completamente dentro del intervalo [d[u], f[u]] , y v es un descendiente de u en un árbol de profundidad.
Clasificación de bordes: el
recorrido DFS se puede utilizar para clasificar los bordes del gráfico de entrada G = (V, E). Se pueden definir cuatro tipos de bordes en términos de un bosque primero en profundidad:
- Tree Edge: Es un borde que está presente en el árbol obtenido después de aplicar DFS en el gráfico.
- Borde delantero: es un borde (u, v) tal que v es descendiente pero no forma parte del árbol DFS.
- Borde posterior: es un borde (u, v) tal que v es el ancestro del borde u pero no forma parte del árbol DFS. La presencia del borde posterior indica un ciclo en un gráfico dirigido.
- Cross Edge: Es un borde que conecta dos Nodes de tal manera que no tienen ningún antepasado y una relación descendiente entre ellos.
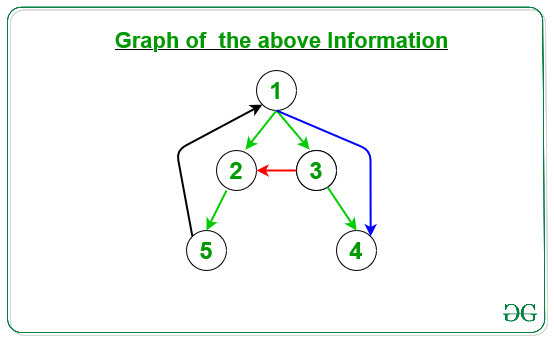
Dado un gráfico de N vértices y M aristas, la tarea es clasificar las aristas M en aristas de árbol, aristas delanteras, aristas traseras y aristas cruzadas .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 5, M = 7, arr[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 3, 4 }, { 1, 4 }, { 2, 5 }, { 5, 1 }, { 3, 2 } } }
Salida:
{1, 2} -> Borde del árbol
{1, 3} -> Borde del árbol
{3, 4} -> Borde del árbol
{1, 4} -> Borde anterior
{2 , 5} -> Borde del árbol
{5, 1} -> Borde posterior
{3, 2} -> Borde cruzado
Explicación:
1. Bordes verdes: Borde del árbol
2. Bordes azules: Borde delantero
3. Bordes negros: Borde trasero
4. Bordes rojos: borde cruzado
A continuación se muestra el gráfico dado para la información anterior:
Entrada: N = 5, M = 4, arr[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 3, 4 }, { 1, 4 } }
Salida:
{1, 2} -> Borde del árbol
{1, 3} -> Borde del árbol
{3, 4} -> Borde del árbol
{1, 4} -> Borde delantero
Explicación:
1. Bordes verdes: Borde del árbol
2. Bordes azules: Borde delantero
3. Bordes negros: Borde posterior
4. Bordes rojos: borde cruzado
A continuación se muestra el gráfico para la información anterior:
Acercarse:
- Use DFS Traversal en el gráfico dado para encontrar el tiempo de descubrimiento y el tiempo de finalización y el padre de cada Node.
- Usando el teorema de paréntesis, clasifique los bordes dados en las siguientes condiciones:
- Borde del árbol: para cualquier borde (U, V) , si el Node U es el padre del Node V, entonces (U, V) es el borde del árbol del gráfico dado.
- Borde delantero: para cualquier borde (U, V) , si el tiempo de descubrimiento y el tiempo de finalización del Node V se superponen completamente con el tiempo de descubrimiento y el tiempo de finalización del Node U , entonces (U, V) es el borde delantero del gráfico dado.
- Borde hacia atrás: para cualquier borde (U, V) , si el tiempo de descubrimiento y el tiempo de finalización del Node U se superponen completamente con el tiempo de descubrimiento y el tiempo de finalización del Node V , entonces (U, V) es el borde hacia atrás del gráfico dado.
- Borde cruzado: para cualquier borde (U, V) , si el tiempo de descubrimiento y el tiempo de finalización del Node U no se superponen con el tiempo de descubrimiento y el tiempo de finalización del Node V , entonces (U, V) es el borde cruzado del gráfico dado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// For recording time
int tim = 0;
// For creating Graph
vector<list<int> > G;
// For calculating Discovery time
// and finishing time of nodes
vector<int> disc, fin;
// For finding Parent of node
vector<int> Par;
// For storing color of node
vector<char> Color;
// Recursive function for DFS
// to update the
void DFS_Visit(int v)
{
// Make the current nodes as visited
Color[v] = 'G';
// Increment the time
tim = tim + 1;
// Assign the Discovery node of
// node v
disc[v] = tim;
// Traverse the adjacency list of
// vertex v
for (auto& it : G[v]) {
// If the nodes is not visited,
// then mark the parent of the
// current node and call DFS_Visit
// for the current node
if (Color[it] == 'W') {
Par[it] = v;
DFS_Visit(it);
}
}
Color[v] = 'B';
tim = tim + 1;
fin[v] = tim;
}
void DFS(vector<list<int> >& G)
{
// Initialise Par, disc, fin and
// Color vector to size of graph
Par.resize(G.size());
disc.resize(G.size());
fin.resize(G.size());
Color.resize(G.size());
// Initialise the Par[], Color[],
// disc[], fin[]
for (int i = 1; i < G.size(); i++) {
Color[i] = 'W';
Par[i] = 0;
disc[i] = 0;
fin[i] = 0;
}
// For every vertex if nodes is
// not visited then call DFS_Visit
// to update the discovery and
// finishing time of the node
for (int i = 1; i < G.size(); i++) {
// If color is 'W', then
// node is not visited
if (Color[i] == 'W') {
DFS_Visit(i);
}
}
}
// Function to check whether
// time intervals of x and y overlaps
// or not
bool checkOverlap(int x, int y)
{
// Find the time intervals
int x1 = disc[x], y1 = fin[x];
int x2 = disc[y], y2 = fin[y];
// Complete overlaps
if (x2 > x1 && y1 > y2) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
// Function to check which Edges
// (x, y) belongs
string checkEdge(int x, int y)
{
// For Tree Edge
// If x is parent of y, then it
// is Tree Edge
if (Par[y] == x) {
return "Tree Edge";
}
// For Forward Edge
else if (checkOverlap(x, y)) {
return "Forward Edge";
}
// For Backward Edge
else if (checkOverlap(y, x)) {
return "Backward Edge";
}
else {
return "Cross Edge";
}
}
// Function call to find the Tree Edge,
// Back Edge, Forward Edge, and Cross Edge
void solve(int arr[][2], int N, int M)
{
// Create graph of N size
G.resize(N + 1);
// Traverse each edges
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int x = arr[i][0];
int y = arr[i][1];
// Make Directed graph
G[x].push_back(y);
}
// DFS call to calculate discovery
// and finishing time for each node
DFS(G);
// Condition for Tree Edge, Forward
// Edges, Backward Edge and Cross Edge
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int x = arr[i][0];
int y = arr[i][1];
// Function call to check Edges
cout << "{" << x << ", " << y
<< "} -> " << checkEdge(x, y)
<< endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Number of Nodes
int N = 5;
// Number of Edges
int M = 7;
// Edges for the graph
int arr[M][2]
= { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 },
{ 3, 4 }, { 1, 4 },
{ 2, 5 }, { 5, 1 },
{ 3, 1 } };
// Function Call
solve(arr, N, M);
return 0;
}
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# For recording time
tim = 0
# For creating Graph
G=[]
# For calculating Discovery time
# and finishing time of nodes
disc, fin=[],[]
# For finding Parent of node
Par=[]
# For storing color of node
Color=[]
# Recursive function for DFS
# to update the
def DFS_Visit(v):
global tim
# Make the current nodes as visited
Color[v] = 'G'
# Increment the time
tim += 1
# Assign the Discovery node of
# node v
disc[v] = tim
# Traverse the adjacency list of
# vertex v
for it in G[v]:
# If the nodes is not visited,
# then mark the parent of the
# current node and call DFS_Visit
# for the current node
if (Color[it] == 'W') :
Par[it] = v
DFS_Visit(it)
Color[v] = 'B'
tim = tim + 1
fin[v] = tim
def DFS(G):
global Par,disc,fin,Color
# Initialise Par, disc, fin and
# Color vector to size of graph
Par=[-1]*len(G)
disc=[-1]*len(G)
fin=[-1]*len(G)
Color=['']*len(G)
# Initialise the Par[], Color[],
# disc[], fin[]
for i in range(1,len(G)):
Color[i] = 'W'
Par[i] = 0
disc[i] = 0
fin[i] = 0
# For every vertex if nodes is
# not visited then call DFS_Visit
# to update the discovery and
# finishing time of the node
for i in range(1,len(G)):
# If color is 'W', then
# node is not visited
if (Color[i] == 'W') :
DFS_Visit(i)
# Function to check whether
# time intervals of x and y overlaps
# or not
def checkOverlap(x, y):
# Find the time intervals
x1 = disc[x]; y1 = fin[x]
x2 = disc[y]; y2 = fin[y]
# Complete overlaps
if (x2 > x1 and y1 > y2) :
return True
else :
return False
# Function to check which Edges
# (x, y) belongs
def checkEdge(x, y):
# For Tree Edge
# If x is parent of y, then it
# is Tree Edge
if (Par[y] == x) :
return "Tree Edge"
# For Forward Edge
elif (checkOverlap(x, y)) :
return "Forward Edge"
# For Backward Edge
elif (checkOverlap(y, x)) :
return "Backward Edge"
else :
return "Cross Edge"
# Function call to find the Tree Edge,
# Back Edge, Forward Edge, and Cross Edge
def solve(arr, N, M):
global G
# Create graph of N size
G=[[] for _ in range(N + 1)]
# Traverse each edges
for i in range(M):
x = arr[i][0]
y = arr[i][1]
# Make Directed graph
G[x].append(y)
# DFS call to calculate discovery
# and finishing time for each node
DFS(G)
# Condition for Tree Edge, Forward
# Edges, Backward Edge and Cross Edge
for i in range(M):
x = arr[i][0]
y = arr[i][1]
# Function call to check Edges
print("({0},{1})->".format(x,y),checkEdge(x, y))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Number of Nodes
N = 5
# Number of Edges
M = 7
# Edges for the graph
arr= [[1, 2] , [1, 3 ],
[3, 4] , [1, 4 ],
[2, 5] , [5, 1 ],
[3, 1]]
# Function Call
solve(arr, N, M)
{1, 2} -> Tree Edge
{1, 3} -> Tree Edge
{3, 4} -> Tree Edge
{1, 4} -> Forward Edge
{2, 5} -> Tree Edge
{5, 1} -> Backward Edge
{3, 1} -> Backward Edge
Complejidad temporal: O(N), donde N es el número total de Nodes en el gráfico.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por _mridul_bhardwaj_ y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA