Tenemos que rotar un objeto en un ángulo dado sobre un punto de pivote dado e imprimir las nuevas coordenadas.
Ejemplos:
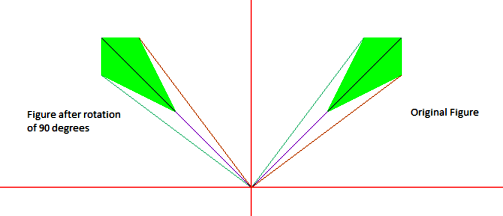
Input : {(100, 100), (150, 200), (200, 200),
(200, 150)} is to be rotated about
(0, 0) by 90 degrees
Output : (-100, 100), (-200, 150), (-200, 200), (-150, 200)
C
// C program to rotate an object by
// a given angle about a given point
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// Using macros to convert degree to radian
// and call sin() and cos() as these functions
// take input in radians
#define SIN(x) sin(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
#define COS(x) cos(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
// To rotate an object
void rotate(float a[][2], int n, int x_pivot, int y_pivot,
int angle)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
// Shifting the pivot point to the origin
// and the given points accordingly
int x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot;
int y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot;
// Calculating the rotated point co-ordinates
// and shifting it back
a[i][0] = x_pivot
+ (x_shifted * COS(angle)
- y_shifted * SIN(angle));
a[i][1] = y_pivot
+ (x_shifted * SIN(angle)
+ y_shifted * COS(angle));
printf("(%f, %f) ", a[i][0], a[i][1]);
i++;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// 1st Example
// The following figure is to be
// rotated about (0, 0) by 90 degrees
int size1 = 4; // No. of vertices
// Vertex co-ordinates must be in order
float points_list1[][2] = { { 100, 100 },
{ 150, 200 },
{ 200, 200 },
{ 200, 150 } };
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90);
// 2nd Example
// The following figure is to be
// rotated about (50, -50) by -45 degrees
/*int size2 = 3;//No. of vertices
float points_list2[][2] = {{100, 100}, {100, 200},
{200, 200}};
rotate(points_list2, size2, 50, -50, -45);*/
return 0;
}
CPP
// C++ program to rotate an object by
// a given angle about a given point
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
// Using macros to convert degree to radian
// and call sin() and cos() as these functions
// take input in radians
#define SIN(x) sin(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
#define COS(x) cos(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
// To rotate an object given as order set of points in a[]
// (x_pivot, y_pivot)
void rotate(float a[][2], int n, int x_pivot, int y_pivot,
int angle)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
// Shifting the pivot point to the origin
// and the given points accordingly
int x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot;
int y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot;
// Calculating the rotated point co-ordinates
// and shifting it back
a[i][0] = x_pivot
+ (x_shifted * COS(angle)
- y_shifted * SIN(angle));
a[i][1] = y_pivot
+ (x_shifted * SIN(angle)
+ y_shifted * COS(angle));
cout << "(" << a[i][0] << ", " << a[i][1] << ") ";
i++;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// 1st Example
// The following figure is to be
// rotated about (0, 0) by 90 degrees
int size1 = 4; // No. of vertices
// Vertex co-ordinates must be in order
float points_list1[][2] = { { 100, 100 },
{ 150, 200 },
{ 200, 200 },
{ 200, 150 } };
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90);
// 2nd Example
// The following figure is to be
// rotated about (50, -50) by -45 degrees
/*int size2 = 3;//No. of vertices
float points_list2[][2] = {{100, 100}, {100, 200},
{200, 200}};
rotate(points_list2, size2, 50, -50, -45);*/
return 0;
}
Python3
# Python3 program to rotate an object by
# a given angle about a given point
import math
SIN=lambda x: int(math.sin(x * 3.141592653589 / 180))
COS=lambda x: int(math.cos(x * 3.141592653589 / 180))
# To rotate an object
def rotate(a, n, x_pivot, y_pivot, angle):
i = 0
while (i < n) :
# Shifting the pivot point to the origin
# and the given points accordingly
x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot
y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot
# Calculating the rotated point co-ordinates
# and shifting it back
a[i][0] = x_pivot + (x_shifted * COS(angle) - y_shifted * SIN(angle))
a[i][1] = y_pivot + (x_shifted * SIN(angle) + y_shifted * COS(angle))
print("({}, {}) ".format(a[i][0], a[i][1]),end=" ")
i+=1
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
# 1st Example
# The following figure is to be
# rotated about (0, 0) by 90 degrees
size1 = 4 # No. of vertices
# Vertex co-ordinates must be in order
points_list1 = [[ 100, 100],
[ 150, 200],
[ 200, 200],
[ 200, 150],]
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90)
# 2nd Example
# The following figure is to be
# rotated about (50, -50) by -45 degrees
# size2 = 3#No. of vertices
# points_list2 = [[100, 100],
# [100, 200],
# [200, 200]]
# rotate(points_list2, size2, 50, -50, -45)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA