La transformación de ventana a ventana gráfica es el proceso de transformar objetos de coordenadas mundiales 2D en coordenadas de dispositivo. Los objetos dentro del mundo o la ventana de recorte se asignan a la ventana gráfica, que es el área de la pantalla donde se asignan las coordenadas del mundo para que se muestren.

Términos generales :
- Coordenada mundial: es la coordenada cartesiana con la que definimos el diagrama, como X wmin , X wmax , Y wmin , Y wmax
- Coordenada del dispositivo: es la coordenada de la pantalla donde se mostrarán los objetos, como X vmin , X vmax , Y vmin , Y vmax
- Ventana: es el área en la coordenada mundial seleccionada para mostrar.
- ViewPort: es el área en la coordenada del dispositivo donde se mostrarán los gráficos.
Cálculo matemático de ventana a ventana gráfica:
es posible que el tamaño de la ventana gráfica sea mucho más pequeño o más grande que la ventana. En estos casos, tenemos que aumentar o disminuir el tamaño de la Ventana según el Viewport y para ello necesitamos algunos cálculos matemáticos.
(xw, yw): A point on Window (xv, yv): Corresponding point on Viewport
- tenemos que calcular el punto (x v , y v )

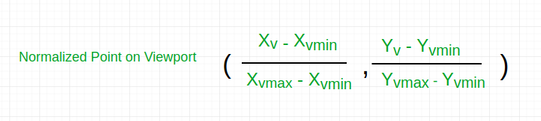
- Ahora la posición relativa del objeto en Window y Viewport es la misma.
For x coordinate,

For y coordinate,

- entonces, después de calcular las coordenadas x e y, obtenemos


- donde s x es el factor de escala de la coordenada x y s y es el factor de escala de la coordenada y


Ejemplo:
Supongamos,
- para ventana, X wmin = 20, X wmax = 80, Y wmin = 40, Y wmax = 80 .
- para ventana gráfica, X vmin = 30, X vmax = 60, Y vmin = 40, Y vmax = 60 .
- Ahora un punto ( X w , Y w ) sea ( 30, 80 ) en la ventana. Tenemos que calcular ese punto en la ventana gráfica ,
es decir (X v , Y v ) . - En primer lugar, calcule el factor de escala de la coordenada x S x y el factor de escala de la coordenada y S y usando la fórmula mencionada anteriormente.
Sx = ( 60 - 30 ) / ( 80 - 20 ) = 30 / 60 Sy = ( 60 - 40 ) / ( 80 - 40 ) = 20 / 40
- Entonces, ahora calcule el punto en la ventana gráfica ( X v , Y v ).
Xv = 30 + ( 30 - 20 ) * ( 30 / 60 ) = 35 Yv = 40 + ( 80 - 40 ) * ( 20 / 40 ) = 60
- Entonces, el punto en la ventana ( X w , Y w ) = ( 30, 80 ) será ( X v , Y v ) = ( 35, 60 ) en la ventana gráfica.
Aquí está la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to implement
// Window to ViewPort Transformation
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function for window to viewport transformation
void WindowtoViewport(int x_w, int y_w, int x_wmax,
int y_wmax, int x_wmin, int y_wmin,
int x_vmax, int y_vmax, int x_vmin,
int y_vmin)
{
// point on viewport
int x_v, y_v;
// scaling factors for x coordinate and y coordinate
float sx, sy;
// calculating Sx and Sy
sx = (float)(x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (float)(y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin);
// calculating the point on viewport
x_v = x_vmin + (float)((x_w - x_wmin) * sx);
y_v = y_vmin + (float)((y_w - y_wmin) * sy);
cout<< "The point on viewport: ("<<x_v <<","<< y_v<<")" ;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// boundary values for window
int x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80, x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
// boundary values for viewport
int x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60, x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
// point on window
int x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20, 40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
}
// This code is contributed by khusboogoyal499.
C
// C program to implement
// Window to ViewPort Transformation
#include <stdio.h>
// Function for window to viewport transformation
void WindowtoViewport(int x_w, int y_w, int x_wmax,
int y_wmax, int x_wmin, int y_wmin,
int x_vmax, int y_vmax, int x_vmin,
int y_vmin)
{
// point on viewport
int x_v, y_v;
// scaling factors for x coordinate and y coordinate
float sx, sy;
// calculating Sx and Sy
sx = (float)(x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (float)(y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin);
// calculating the point on viewport
x_v = x_vmin + (float)((x_w - x_wmin) * sx);
y_v = y_vmin + (float)((y_w - y_wmin) * sy);
printf("The point on viewport: (%d, %d )\n ", x_v, y_v);
}
// Driver Code
void main()
{
// boundary values for window
int x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80, x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
// boundary values for viewport
int x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60, x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
// point on window
int x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20, 40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
}
//this code is added by khushboogoyal499
Java
// Java program to implement
// Window to ViewPort Transformation
class GFG
{
// Function for window to viewport transformation
static void WindowtoViewport(int x_w, int y_w, int x_wmax,
int y_wmax, int x_wmin, int y_wmin,
int x_vmax, int y_vmax, int x_vmin,
int y_vmin)
{
// point on viewport
int x_v, y_v;
// scaling factors for x coordinate and y coordinate
float sx, sy;
// calculating Sx and Sy
sx = (float)(x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (float)(y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin);
// calculating the point on viewport
x_v = (int) (x_vmin + (float)((x_w - x_wmin) * sx));
y_v = (int) (y_vmin + (float)((y_w - y_wmin) * sy));
System.out.printf("The point on viewport: (%d, %d )\n ", x_v, y_v);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// boundary values for window
int x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80, x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
// boundary values for viewport
int x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60, x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
// point on window
int x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20, 40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 program to implement
# Window to ViewPort Transformation
# Function for window to viewport transformation
def WindowtoViewport(x_w, y_w, x_wmax, y_wmax,
x_wmin, y_wmin, x_vmax,
y_vmax, x_vmin, y_vmin):
# point on viewport
# calculating Sx and Sy
sx = (x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin)
sy = (y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin)
# calculating the point on viewport
x_v = x_vmin + ((x_w - x_wmin) * sx)
y_v = y_vmin + ((y_w - y_wmin) * sy)
print("The point on viewport:(", int(x_v),
",", int(y_v), ")")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# boundary values for window
x_wmax = 80
y_wmax = 80
x_wmin = 20
y_wmin = 40
# boundary values for viewport
x_vmax = 60
y_vmax = 60
x_vmin = 30
y_vmin = 40
# point on window
x_w = 30
y_w = 80
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20,
40, 60, 60, 30, 40)
# This code is contributed by Surendra_Gangwar
C#
// C# program to implement
// Window to ViewPort Transformation
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function for window to viewport transformation
static void WindowtoViewport(int x_w, int y_w,
int x_wmax, int y_wmax,
int x_wmin, int y_wmin,
int x_vmax, int y_vmax,
int x_vmin, int y_vmin)
{
// point on viewport
int x_v, y_v;
// scaling factors for x coordinate
// and y coordinate
float sx, sy;
// calculating Sx and Sy
sx = (float)(x_vmax - x_vmin) /
(x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (float)(y_vmax - y_vmin) /
(y_wmax - y_wmin);
// calculating the point on viewport
x_v = (int) (x_vmin +
(float)((x_w - x_wmin) * sx));
y_v = (int) (y_vmin +
(float)((y_w - y_wmin) * sy));
Console.Write("The point on viewport: " +
"({0}, {1} )\n ", x_v, y_v);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// boundary values for window
int x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80,
x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
// boundary values for viewport
int x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60,
x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
// point on window
int x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20,
40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to implement
// Window to ViewPort Transformation
// Function for window to viewport transformation
function WindowtoViewport(x_w, y_w, x_wmax,y_wmax, x_wmin,
y_wmin,x_vmax, y_vmax, x_vmin,y_vmin)
{
// point on viewport
let x_v, y_v;
// scaling factors for x coordinate and y coordinate
let sx, sy;
// calculating Sx and Sy
sx = (x_vmax - x_vmin) / (x_wmax - x_wmin);
sy = (y_vmax - y_vmin) / (y_wmax - y_wmin);
// calculating the point on viewport
x_v = x_vmin + ((x_w - x_wmin) * sx);
y_v = y_vmin + ((y_w - y_wmin) * sy);
document.write("The point on viewport: (" + x_v + ", "
+ y_v + " )<br>");
}
// Driver Code
// boundary values for window
let x_wmax = 80, y_wmax = 80, x_wmin = 20, y_wmin = 40;
// boundary values for viewport
let x_vmax = 60, y_vmax = 60, x_vmin = 30, y_vmin = 40;
// point on window
let x_w = 30, y_w = 80;
WindowtoViewport(30, 80, 80, 80, 20, 40, 60, 60, 30, 40);
</script>
Producción:
The point on viewport: (35, 60 )