Dados dos números X y N , la tarea es encontrar el último dígito de X elevado al último dígito de N factorial , es decir ![]() .
.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: X = 5, N = 2
Salida: 5
Explicación:
Dado que, 2! mod 10 = 2
por lo tanto 5 2 = 25 y el último dígito de 25 es 5.
Entrada: X = 10, N = 4
Salida: 0
Explicación:
Ya que, 4! mod 10 = 24 mod 10 = 4
por lo tanto 10 4 = 10000 y el último dígito de 10000 es 0.
Enfoque: ¡ La forma más eficiente de resolver este problema es encontrar cualquier patrón en el último dígito requerido, con la ayuda del último dígito de N! y el último dígito de X elevado a Y
A continuación se muestran varias observaciones de la ecuación anterior:
- Si N = 0 o N = 1 , entonces el último dígito es 1 o
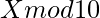 respectivamente.
respectivamente. - Desde las 5! es 120 , por lo que para N ≥ 5 el valor de (N! mod 10) será cero.
- Ahora nos queda el dígito 2, 3, 4. Para esto tenemos:
para N = 2,
N! módulo 10 = 2! módulo 10 = 2
para N = 3,
N! módulo 10 = 3! módulo 10 = 6
para N = 4,
N! módulo 10 = 4! mod 10 = 24 mod 10 = 4
Ahora, para X 2 , X 4 y X 6
comprobaremos que después de qué n- ésima potencia de X n se repite el valor del último dígito,
es decir, después de qué n- ésima potencia del último dígito de X n el valor de las repeticiones del último dígito.
- A continuación se muestra la tabla para qué potencia del último dígito del 0 al 9 en cualquier número se repite:
| Número | Ciclicidad |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 |
| 7 | 4 |
| 8 | 4 |
| 9 | 2 |
A continuación se muestran los pasos basados en las observaciones anteriores:
- Si X no es un múltiplo de 10 , divida el valor evaluado de
 por la ciclicidad del último dígito de X. Si el resto (digamos r ) es 0, haga lo siguiente:
por la ciclicidad del último dígito de X. Si el resto (digamos r ) es 0, haga lo siguiente:
- Si el último dígito de X es 2, 4, 6 u 8 , la respuesta será 6 .
- Si el último dígito de X es 1, 3, 7 o 9 , la respuesta será 1 .
- Si el último dígito de X es 5 , la respuesta será 5 .
- De lo contrario, si el resto (digamos r ) no es cero, la respuesta es
 , donde ‘l’ es el último dígito de X.
, donde ‘l’ es el último dígito de X. - De lo contrario, si X es un múltiplo de 10 , la respuesta siempre será 0 .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find a^b using
// binary exponentiation
long power(long a, long b, long c)
{
// Initialise result
long result = 1;
while (b > 0)
{
// If b is odd then,
// multiply result by a
if ((b & 1) == 1)
{
result = (result * a) % c;
}
// b must be even now
// Change b to b/2
b /= 2;
// Change a = a^2
a = (a * a) % c;
}
return result;
}
// Function to find the last digit
// of the given equation
long calculate(long X, long N)
{
int a[10];
// To store cyclicity
int cyclicity[11];
// Store cyclicity from 1 - 10
cyclicity[1] = 1;
cyclicity[2] = 4;
cyclicity[3] = 4;
cyclicity[4] = 2;
cyclicity[5] = 1;
cyclicity[6] = 1;
cyclicity[7] = 4;
cyclicity[8] = 4;
cyclicity[9] = 2;
cyclicity[10] = 1;
// Observation 1
if (N == 0 || N == 1)
{
return (X % 10);
}
// Observation 3
else if (N == 2 || N == 3 || N == 4)
{
long temp = (long)1e18;
// To store the last digits
// of factorial 2, 3, and 4
a[2] = 2;
a[3] = 6;
a[4] = 4;
// Find the last digit of X
long v = X % 10;
// Step 1
if (v != 0)
{
int u = cyclicity[(int)v];
// Divide a[N] by cyclicity
// of v
int r = a[(int)N] % u;
// If remainder is 0
if (r == 0)
{
// Step 1.1
if (v == 2 || v == 4 ||
v == 6 || v == 8)
{
return 6;
}
// Step 1.2
else if (v == 5)
{
return 5;
}
// Step 1.3
else if (v == 1 || v == 3 ||
v == 7 || v == 9)
{
return 1;
}
}
// If r is non-zero,
// then return (l^r) % 10
else
{
return (power(v, r, temp) % 10);
}
}
// Else return 0
else
{
return 0;
}
}
// Else return 1
return 1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Numbers
int X = 18;
int N = 4;
// Function Call
long result = calculate(X, N);
// Print the result
cout << result;
}
// This code is contributed by spp____
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class TestClass {
// Function to find a^b using
// binary exponentiation
public static long power(long a,
long b,
long c)
{
// Initialise result
long result = 1;
while (b > 0) {
// If b is odd then,
// multiply result by a
if ((b & 1) = = 1) {
result = (result * a) % c;
}
// b must be even now
// Change b to b/2
b / = 2;
// Change a = a^2
a = (a * a) % c;
}
return result;
}
// Function to find the last digit
// of the given equation
public static long calculate(long X,
long N)
{
int a[] = new int[10];
// To store cyclicity
int cyclicity[] = new int[11];
// Store cyclicity from 1 - 10
cyclicity[1] = 1;
cyclicity[2] = 4;
cyclicity[3] = 4;
cyclicity[4] = 2;
cyclicity[5] = 1;
cyclicity[6] = 1;
cyclicity[7] = 4;
cyclicity[8] = 4;
cyclicity[9] = 2;
cyclicity[10] = 1;
// Observation 1
if (N = = 0 || N = = 1) {
return (X % 10);
}
// Observation 3
else if (N = = 2
|| N
= = 3
|| N
= = 4) {
long temp = (long)1e18;
// To store the last digits
// of factorial 2, 3, and 4
a[2] = 2;
a[3] = 6;
a[4] = 4;
// Find the last digit of X
long v = X % 10;
// Step 1
if (v ! = 0) {
int u = cyclicity[(int)v];
// Divide a[N] by cyclicity
// of v
int r = a[(int)N] % u;
// If remainder is 0
if (r = = 0) {
// Step 1.1
if (v = = 2
|| v
= = 4
|| v
= = 6
|| v
= = 8) {
return 6;
}
// Step 1.2
else if (v = = 5) {
return 5;
}
// Step 1.3
else if (
v = = 1
|| v
= = 3
|| v
= = 7
|| v
= = 9) {
return 1;
}
}
// If r is non-zero,
// then return (l^r) % 10
else {
return (power(v,
r,
temp)
% 10);
}
}
// Else return 0
else {
return 0;
}
}
// Else return 1
return 1;
}
// Driver's Code
public static void main(String args[])
throws Exception
{
// Given Numbers
int X = 18;
int N = 4;
// Function Call
long result = calculate(X, N);
// Print the result
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function to find a^b using # binary exponentiation def power(a, b, c): # Initialise result result = 1 while (b > 0): # If b is odd then, # multiply result by a if ((b & 1) == 1): result = (result * a) % c # b must be even now # Change b to b/2 b //= 2 # Change a = a^2 a = (a * a) % c return result # Function to find the last digit # of the given equation def calculate(X, N): a = 10 * [0] # To store cyclicity cyclicity = 11 * [0] # Store cyclicity from 1 - 10 cyclicity[1] = 1 cyclicity[2] = 4 cyclicity[3] = 4 cyclicity[4] = 2 cyclicity[5] = 1 cyclicity[6] = 1 cyclicity[7] = 4 cyclicity[8] = 4 cyclicity[9] = 2 cyclicity[10] = 1 # Observation 1 if (N == 0 or N == 1): return (X % 10) # Observation 3 elif (N == 2 or N == 3 or N == 4): temp = 1e18; # To store the last digits # of factorial 2, 3, and 4 a[2] = 2 a[3] = 6 a[4] = 4 # Find the last digit of X v = X % 10 # Step 1 if (v != 0): u = cyclicity[v] # Divide a[N] by cyclicity # of v r = a[N] % u # If remainder is 0 if (r == 0): # Step 1.1 if (v == 2 or v == 4 or v == 6 or v == 8): return 6 # Step 1.2 elif (v == 5): return 5 # Step 1.3 elif (v == 1 or v == 3 or v == 7 or v == 9): return 1 # If r is non-zero, # then return (l^r) % 10 else: return (power(v, r, temp) % 10) # Else return 0 else: return 0 # Else return 1 return 1 # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": # Given numbers X = 18 N = 4 # Function call result = calculate(X, N) # Print the result print(result) # This code is contributed by chitranayal
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to find a^b using
// binary exponentiation
static long power(long a, long b, long c)
{
// Initialise result
long result = 1;
while (b > 0)
{
// If b is odd then,
// multiply result by a
if ((b & 1) == 1)
{
result = (result * a) % c;
}
// b must be even now
// Change b to b/2
b /= 2;
// Change a = a^2
a = (a * a) % c;
}
return result;
}
// Function to find the last digit
// of the given equation
public static long calculate(long X,
long N)
{
int[] a = new int[10];
// To store cyclicity
int[] cyclicity = new int[11];
// Store cyclicity from 1 - 10
cyclicity[1] = 1;
cyclicity[2] = 4;
cyclicity[3] = 4;
cyclicity[4] = 2;
cyclicity[5] = 1;
cyclicity[6] = 1;
cyclicity[7] = 4;
cyclicity[8] = 4;
cyclicity[9] = 2;
cyclicity[10] = 1;
// Observation 1
if (N == 0 || N == 1)
{
return (X % 10);
}
// Observation 3
else if (N == 2 || N == 3 || N == 4)
{
long temp = (long)1e18;
// To store the last digits
// of factorial 2, 3, and 4
a[2] = 2;
a[3] = 6;
a[4] = 4;
// Find the last digit of X
long v = X % 10;
// Step 1
if (v != 0)
{
int u = cyclicity[(int)v];
// Divide a[N] by cyclicity
// of v
int r = a[(int)N] % u;
// If remainder is 0
if (r == 0)
{
// Step 1.1
if (v == 2 || v == 4 ||
v == 6 || v == 8)
{
return 6;
}
// Step 1.2
else if (v == 5)
{
return 5;
}
// Step 1.3
else if ( v == 1 || v == 3 ||
v == 7 || v == 9)
{
return 1;
}
}
// If r is non-zero,
// then return (l^r) % 10
else
{
return (power(v, r, temp) % 10);
}
}
// Else return 0
else
{
return 0;
}
}
// Else return 1
return 1;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// Given numbers
int X = 18;
int N = 4;
// Function call
long result = calculate(X, N);
// Print the result
Console.Write(result);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Function to find a^b using
// binary exponentiation
function power(a, b, c) {
// Initialise result
var result = 1;
while (b > 0) {
// If b is odd then,
// multiply result by a
if ((b & 1) == 1) {
result = (result * a) % c;
}
// b must be even now
// Change b to b/2
b /= 2;
// Change a = a^2
a = (a * a) % c;
}
return result;
}
// Function to find the last digit
// of the given equation
function calculate(X, N) {
var a = [...Array(10)];
// To store cyclicity
var cyclicity = [...Array(11)];
// Store cyclicity from 1 - 10
cyclicity[1] = 1;
cyclicity[2] = 4;
cyclicity[3] = 4;
cyclicity[4] = 2;
cyclicity[5] = 1;
cyclicity[6] = 1;
cyclicity[7] = 4;
cyclicity[8] = 4;
cyclicity[9] = 2;
cyclicity[10] = 1;
// Observation 1
if (N == 0 || N == 1) {
return X % 10;
}
// Observation 3
else if (N == 2 || N == 3 || N == 4) {
var temp = 1e18;
// To store the last digits
// of factorial 2, 3, and 4
a[2] = 2;
a[3] = 6;
a[4] = 4;
// Find the last digit of X
var v = X % 10;
// Step 1
if (v != 0) {
var u = cyclicity[parseInt(v)];
// Divide a[N] by cyclicity
// of v
var r = a[parseInt(N)] % u;
// If remainder is 0
if (r == 0)
{
// Step 1.1
if (v == 2 || v == 4 || v == 6 || v == 8) {
return 6;
}
// Step 1.2
else if (v == 5) {
return 5;
}
// Step 1.3
else if (v == 1 || v == 3 || v == 7 || v == 9) {
return 1;
}
}
// If r is non-zero,
// then return (l^r) % 10
else {
return power(v, r, temp) % 10;
}
}
// Else return 0
else {
return 0;
}
}
// Else return 1
return 1;
}
// Driver Code
// Given Numbers
var X = 18;
var N = 4;
// Function Call
var result = calculate(X, N);
// Print the result
document.write(result);
// This code is contributed by rdtank.
</script>
6
Complejidad de tiempo: O(1)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(11)