Se dice que un número n es un Número Abundante si la suma de todos los divisores propios del número denotado por sum(n) es mayor que el valor del número n. Y la diferencia entre estos dos valores se llama abundancia .
Matemáticamente, si se cumple la siguiente condición, se dice que el número es un número abundante:
sum(n)> n abundance = sum(n) - n sum(n): aliquot sum - The sum of all proper divisors of n
Dado un número n, nuestra tarea es encontrar si este número es un número abundante o no.
Los primeros Números Abundantes son: 12, 18, 20, 24, 30, 36, 40, 42, 48, 54, 56, 60, 66…..
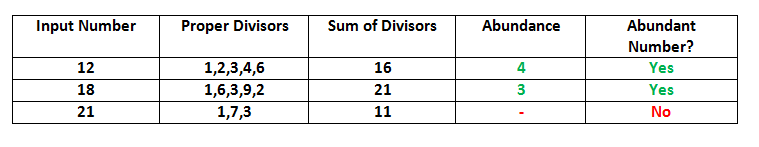
Ejemplos:
Input: 21 Output: NO Input: 12 Output: YES Input: 17 Output: NO
Método 1: una solución simple es iterar todos los números del 1 al n-1 y verificar si el número divide n y calcular la suma. Compruebe si esta suma es mayor que n o no.
C++
// C++ program to find if a given
// number is Abundant number or not.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Returns true if the given number is Abundant
bool isAbundantNumber(int n)
{
// To store the sum of divisors
int sum = 0;
// Loop through the numbers [1,n-1]
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
sum += i;
}
}
// A number n is said to be Abundant Number if
// sum of all the proper divisors of the number
// is greater than the value of the number n.
if (sum > n) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
// Function call
if (isAbundantNumber(12)) {
cout << "YES" << endl;
;
}
else {
cout << "NO" << endl;
;
}
}
// This code is contributed by phasing17
Java
// Java program to find if a given
// number is Abundant number or not.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Returns true if the given number is Abundant
public static boolean isAbundantNumber(int n)
{
// To store the sum of divisors
int sum = 0;
// Loop through the numbers [1,n-1]
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
sum += i;
}
}
// A number n is said to be Abundant Number if
// sum of all the proper divisors of the number
// is greater than the value of the number n.
if (sum > n) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
// Driver program
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Function call
if (isAbundantNumber(12)) {
System.out.println("YES");
}
else {
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by shruti456rawal
Python3
# code
n = 12
s = 0
# iterating loop n times
for i in range(1, n):
# finding proper divisors
if n % i == 0:
# adding proper divisors to the sum s
s += i
# checking if sum is greater than the
# given number then it is called
# anundant so print yes otherwise no
if s > n:
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# this code is contributed by gangarajula laxmi
C#
// C# program to find if a given
// number is Abundant number or not.
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns true if the given number is Abundant
public static bool isAbundantNumber(int n)
{
// To store the sum of divisors
int sum = 0;
// Loop through the numbers [1,n-1]
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
sum += i;
}
}
// A number n is said to be Abundant Number if
// sum of all the proper divisors of the number
// is greater than the value of the number n.
if (sum > n) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
// Driver program
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Function call
if (isAbundantNumber(12)) {
Console.WriteLine("YES");
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by phasing17
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code for the above approach
// Returns true if the given number is Abundant
function isAbundantNumber(n) {
// To store the sum of divisors
let sum = 0;
// Loop through the numbers [1,n-1]
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
sum += i;
}
}
// A number n is said to be Abundant Number if
// sum of all the proper divisors of the number
// is greater than the value of the number n.
if (sum > n) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
// Driver program
// Function call
if (isAbundantNumber(12)) {
document.write("YES");
}
else {
document.write("NO");
}
// This code is contributed by Potta Lokesh
</script>
PHP
<?php
$n=12;
$s=0;
// Loop through the numbers [1,n-1]
for ($i = 1; $i < $n; $i++) {
if ($n % $i == 0) {
$s += $i;
}
}
// A number n is said to be Abundant Number if
// sum of all the proper divisors of the number
// is greater than the value of the number n.
if ($s > $n) {
echo "Yes" ;
}
else {
echo "No";
}
// This code is contributed by laxmigangarajula03
?>
YES
Complejidad temporal: O(n) para un número dado n.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Solución Optimizada:
Si observamos con atención, los divisores del número n están presentes en pares. Por ejemplo, si n = 100, entonces todos los pares de divisores son: (1,100), (2,50), (4,25), (5,20), (10,10) Usando este hecho podemos acelerar
nuestro programa. Al verificar divisores tendremos que tener cuidado si hay dos divisores iguales como en el caso de (10, 10). En tal caso, tomaremos solo uno de ellos en el cálculo de la suma.
Resta el número n de la suma de todos los divisores para obtener la suma de los divisores propios.
C++
// An Optimized Solution to check Abundant Number
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate sum of divisors
int getSum(int n)
{
int sum = 0;
// Note that this loop runs till square root
// of n
for (int i=1; i<=sqrt(n); i++)
{
if (n%i==0)
{
// If divisors are equal,take only one
// of them
if (n/i == i)
sum = sum + i;
else // Otherwise take both
{
sum = sum + i;
sum = sum + (n / i);
}
}
}
// calculate sum of all proper divisors only
sum = sum - n;
return sum;
}
// Function to check Abundant Number
bool checkAbundant(int n)
{
// Return true if sum of divisors is greater
// than n.
return (getSum(n) > n);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
checkAbundant(12)? cout << "YES\n" : cout << "NO\n";
checkAbundant(15)? cout << "YES\n" : cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
Java
// An Optimized Solution to check Abundant Number
// in JAVA
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
// Function to calculate sum of divisors
class GFG{
static int getSum(int n)
{
int sum = 0;
// Note that this loop runs till square
// root of n
for (int i=1; i<=(Math.sqrt(n)); i++)
{
if (n%i==0)
{
// If divisors are equal,take only
// one of them
if (n/i == i)
sum = sum + i;
else // Otherwise take both
{
sum = sum + i;
sum = sum + (n / i);
}
}
}
// calculate sum of all proper divisors
// only
sum = sum - n;
return sum;
}
// Function to check Abundant Number
static boolean checkAbundant(int n)
{
// Return true if sum of divisors is
// greater than n.
return (getSum(n) > n);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String args[])throws
IOException
{
if(checkAbundant(12))
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
if(checkAbundant(15))
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
Python3
# An Optimized Solution to check Abundant Number
# in PYTHON
import math
# Function to calculate sum of divisors
def getSum(n) :
sum = 0
# Note that this loop runs till square root
# of n
i = 1
while i <= (math.sqrt(n)) :
if n%i == 0 :
# If divisors are equal,take only one
# of them
if n//i == i :
sum = sum + i
else : # Otherwise take both
sum = sum + i
sum = sum + (n // i )
i = i + 1
# calculate sum of all proper divisors only
sum = sum - n
return sum
# Function to check Abundant Number
def checkAbundant(n) :
# Return true if sum of divisors is greater
# than n.
if (getSum(n) > n) :
return 1
else :
return 0
# Driver program to test above function */
if(checkAbundant(12) == 1) :
print ("YES")
else :
print ("NO")
if(checkAbundant(15) == 1) :
print ("YES")
else :
print ("NO")
# This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C#
// An Optimized Solution to check Abundant Number
// in C#
// Function to calculate sum of divisors
using System;
class GFG {
// Function to calculate sum of divisors
static int getSum(int n)
{
int sum = 0;
// Note that this loop runs till square
// root of n
for (int i = 1; i <= (Math.Sqrt(n)); i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
// If divisors are equal, take only
// one of them
if (n / i == i)
sum = sum + i;
else // Otherwise take both
{
sum = sum + i;
sum = sum + (n / i);
}
}
}
// calculate sum of all proper divisors
// only
sum = sum - n;
return sum;
}
// Function to check Abundant Number
static bool checkAbundant(int n)
{
// Return true if sum of divisors is
// greater than n.
return (getSum(n) > n);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void Main()
{
if (checkAbundant(12))
Console.WriteLine("YES");
else
Console.WriteLine("NO");
if (checkAbundant(15))
Console.WriteLine("YES");
else
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
PHP
<?php
// PHP program for an Optimized
// solution to check Abundant Number
// Function to calculate
// sum of divisors
function getSum($n)
{
$sum = 0;
// Note that this loop runs
// till square root of n
for ($i = 1; $i <= sqrt($n); $i++)
{
if ($n % $i == 0)
{
// If divisors are equal,take
// only one of them
if ($n / $i == $i)
$sum = $sum + $i;
// Otherwise take both
else
{
$sum = $sum + $i;
$sum = $sum + ($n / $i);
}
}
}
// calculate sum of all
// proper divisors only
$sum = $sum - $n;
return $sum;
}
// Function to check Abundant Number
function checkAbundant($n)
{
// Return true if sum of
// divisors is greater than n.
return (getSum($n) > $n);
}
// Driver Code
$k = checkAbundant(12) ? "YES\n" : "NO\n";
echo($k);
$k = checkAbundant(15) ? "YES\n" : "NO\n";
echo($k);
// This code is contributed by Ajit.
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for an Optimized
// solution to check Abundant Number
// Function to calculate
// sum of divisors
function getSum(n)
{
let sum = 0;
// Note that this loop runs
// till square root of n
for (let i = 1; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++)
{
if (n % i == 0)
{
// If divisors are equal,take
// only one of them
if (n / i == i)
sum = sum + i;
// Otherwise take both
else
{
sum = sum + i;
sum = sum + (n / i);
}
}
}
// calculate sum of all
// proper divisors only
sum = sum - n;
return sum;
}
// Function to check Abundant Number
function checkAbundant(n)
{
// Return true if sum of
// divisors is greater than n.
return (getSum(n) > n);
}
// Driver Code
let k = checkAbundant(12) ? "YES<br>" : "NO<br>";
document.write(k);
k = checkAbundant(15) ? "YES<br>" : "NO<br>";
document.write(k);
// This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal
</script>
YES NO
Complejidad de tiempo: O(sqrt(n))
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Referencias:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abundant_number
Este artículo es una contribución de Harsh Agarwal . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
-Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema discutido anteriormente”.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA