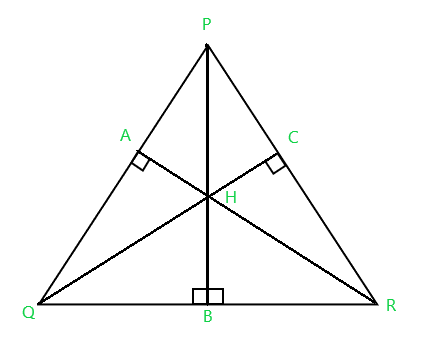
Dados tres números enteros P , Q y R que representan 3 puntos no colineales en un plano 2D con sus respectivas coordenadas x e y , la tarea es encontrar el ortocentro del triángulo .
El ortocentro del triángulo generalmente se denota por H , que es el punto de intersección de tres alturas de un triángulo.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: P = (6, 0), Q = (0, 0), R = (0, 8)
Salida: (0,000, 0,000)Entrada: P = (-3, 1), Q = (2, 2), R = (-3, -5)
Salida: (-4.400, 2.000)
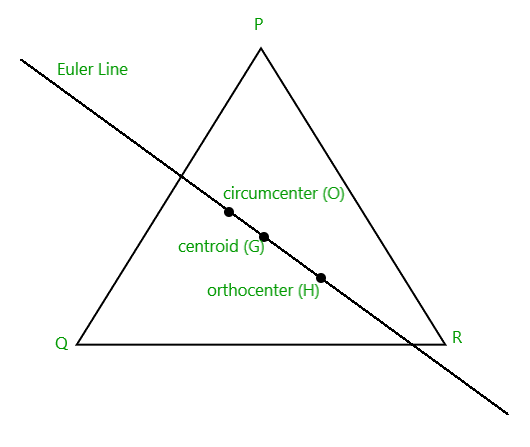
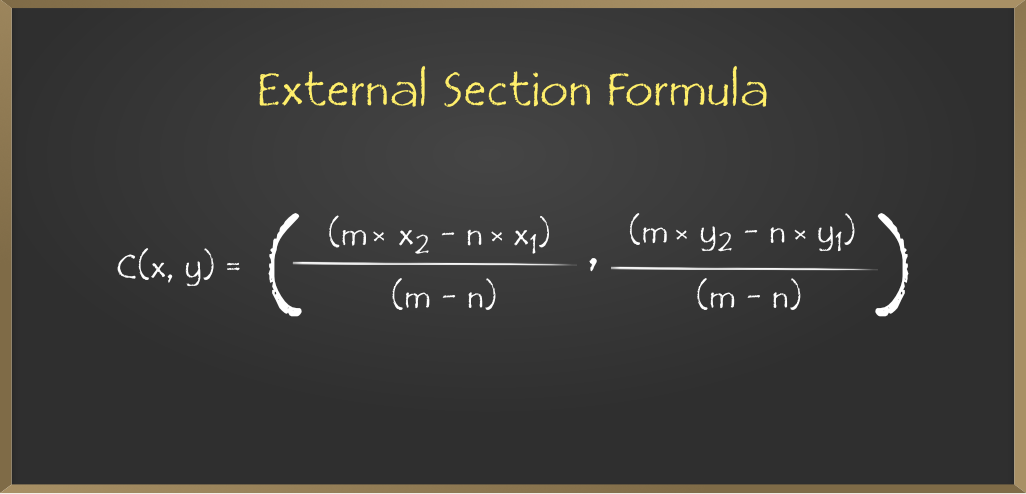
Enfoque: El ortocentro se encuentra dentro del triángulo si y solo si el triángulo es agudo. Si un ángulo es un ángulo recto, el ortocentro coincide con el vértice en el ángulo recto. El problema se puede resolver mediante la propiedad de que el ortocentro, el circuncentro y el centroide de un triángulo se encuentran en la misma línea y el ortocentro divide la línea que une el centroide y el circuncentro en una proporción de 3:2 externamente.
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Encuentra el circuncentro del triángulo y guárdalo en un par CC(x1, y1) .
- Encuentre el centroide del triángulo y guárdelo en un par CT(x2, y2) .
- Use la fórmula de la sección para obtener las coordenadas del ortocentro del triángulo dado como X = (3*x2 – 2*x1) y Y = (3*y2 – 2*y1) .
- Imprime el valor de X e Y como resultado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Stores the X and Y coordinate of
// a point respectively
#define pdd pair<double, double>
// Function to find the line given
// two points
void lineFromPoints(pdd P, pdd Q, double& a,
double& b, double& c)
{
a = Q.second - P.second;
b = P.first - Q.first;
c = a * (P.first) + b * (P.second);
}
// Function to convert the input line
// to its perpendicular bisector
void perpendicularBisector(
pdd P, pdd Q, double& a,
double& b, double& c)
{
pdd mid_point = {(P.first + Q.first) / 2,
(P.second + Q.second) / 2};
// c = -bx + ay
c = -b * (mid_point.first)
+ a * (mid_point.second);
double temp = a;
a = -b;
b = temp;
}
// Function to find the
// intersection point of two lines
pdd lineLineIntersection(
double a1, double b1,
double c1, double a2,
double b2, double c2)
{
double determinant = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1;
// As points are non-collinear,
// determinant cannot be 0
double x = (b2 * c1 - b1 * c2)
/ determinant;
double y = (a1 * c2 - a2 * c1)
/ determinant;
return make_pair(x, y);
}
// Function to find the
// circumcenter of a triangle
pdd findCircumCenter(pdd A[])
{
pdd P, Q, R;
P = A[0], Q = A[1], R = A[2];
// Line PQ is represented as
// ax + by = c
double a, b, c;
lineFromPoints(P, Q, a, b, c);
// Line QR is represented as
// ex + fy = g
double e, f, g;
lineFromPoints(Q, R, e, f, g);
// Converting lines PQ and QR
// to perpendicular bisectors
perpendicularBisector(P, Q, a, b, c);
perpendicularBisector(Q, R, e, f, g);
// Their point of intersection
// gives the circumcenter
pdd circumcenter
= lineLineIntersection(a, b, c,
e, f, g);
// Return the circumcenter
return circumcenter;
}
// Function to find the
// centroid of a triangle
pdd findCentroid(pdd A[])
{
// Centroid of a triangle is
// given as (Xa + Xb + Xc)/3,
// (Ya + Yb + Yc)/3
pdd centroid
= { (A[0].first + A[1].first
+ A[2].first)
/ 3,
(A[0].second + A[1].second
+ A[2].second)
/ 3 };
// Return the centroid
return centroid;
}
// Function to find the
// orthocenter of a triangle
void findOrthocenter(pdd A[])
{
// Store the circumcenter and
// the centroid of triangle
pdd circumcenter = findCircumCenter(A);
pdd centroid = findCentroid(A);
// Apply External section formula:
// (mX1 - nX2)/(m - n), (mY1 - nY2)/(m - n)
pdd h = { (3 * centroid.first
- 2 * circumcenter.first),
(3 * centroid.second
- 2 * circumcenter.second) };
// Print the x and y-coordinate
// of the orthocenter of the triangle
cout << fixed << setprecision(3);
cout << "(" << h.first << ", "
<< h.second << ")";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given points P, Q, R
pair<double, double> A[]
= { { -3, 1 }, { 2, 2 }, { -3, -5 } };
findOrthocenter(A);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Stores the X and Y coordinate of
// a point respectively
static class pair {
double first;
double second;
pair(double first, double second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to find the line given
// two points
static void lineFromPoints(pair P, pair Q, double arr[])
{
arr[0] = Q.second - P.second;
arr[1] = P.first - Q.first;
arr[2] = arr[0] * (P.first) + arr[1] * (P.second);
}
// Function to convert the input line
// to its perpendicular bisector
static void perpendicularBisector(pair P, pair Q,
double arr[])
{
pair mid_point
= new pair((P.first + Q.first) / 2,
(P.second + Q.second) / 2);
// c = -bx + ay
arr[2] = -arr[1] * (mid_point.first)
+ arr[0] * (mid_point.second);
double temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = -arr[1];
arr[1] = temp;
}
// Function to find the
// intersection point of two lines
static pair lineLineIntersection(double abc[],
double efg[])
{
double determinant
= abc[0] * efg[1] - efg[0] * abc[1];
// As points are non-collinear,
// determinant cannot be 0
double x = (efg[1] * abc[2] - abc[1] * efg[2])
/ determinant;
double y = (abc[0] * efg[2] - efg[0] * abc[2])
/ determinant;
return (new pair(x, y));
}
// Function to find the
// circumcenter of a triangle
static pair findCircumCenter(pair A[])
{
pair P = A[0], Q = A[1], R = A[2];
// Line PQ is represented as
// ax + by = c
double abc[] = new double[3];
lineFromPoints(P, Q, abc);
// Line QR is represented as
// ex + fy = g
double efg[] = new double[3];
lineFromPoints(Q, R, efg);
// Converting lines PQ and QR
// to perpendicular bisectors
perpendicularBisector(P, Q, abc);
perpendicularBisector(Q, R, efg);
// Their point of intersection
// gives the circumcenter
pair circumcenter = lineLineIntersection(abc, efg);
// Return the circumcenter
return circumcenter;
}
// Function to find the
// centroid of a triangle
static pair findCentroid(pair A[])
{
// Centroid of a triangle is
// given as (Xa + Xb + Xc)/3,
// (Ya + Yb + Yc)/3
pair centroid = new pair(
(A[0].first + A[1].first + A[2].first) / 3,
(A[0].second + A[1].second + A[2].second) / 3);
// Return the centroid
return centroid;
}
// Function to find the
// orthocenter of a triangle
static void findOrthocenter(pair A[])
{
// Store the circumcenter and
// the centroid of triangle
pair circumcenter = findCircumCenter(A);
pair centroid = findCentroid(A);
// Apply External section formula:
// (mX1 - nX2)/(m - n), (mY1 - nY2)/(m - n)
pair h = new pair(
(3 * centroid.first - 2 * circumcenter.first),
(3 * centroid.second
- 2 * circumcenter.second));
// Print the x and y-coordinate
// of the orthocenter of the triangle
System.out.printf("(%.3f, %.3f)", h.first,
h.second);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given points P, Q, R
pair P = new pair(-3, 1);
pair Q = new pair(2, 2);
pair R = new pair(-3, -5);
pair A[] = { P, Q, R };
// function call
findOrthocenter(A);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash.
C#
// C# program to implement above approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Function to find the line given
// two points
public static void lineFromPoints(double[] P, double[] Q, ref double a, ref double b, ref double c)
{
a = Q[1] - P[1];
b = P[0] - Q[0];
c = a * (P[0]) + b * (P[1]);
}
// Function to convert the input line
// to its perpendicular bisector
public static void perpendicularBisector(
double[] P, double[] Q, ref double a,
ref double b, ref double c)
{
double[] mid_point = {(P[0] + Q[0]) / 2,
(P[1] + Q[1]) / 2};
// c = -bx + ay
c = -b * (mid_point[0])
+ a * (mid_point[1]);
double temp = a;
a = -b;
b = temp;
}
// Function to find the
// intersection point of two lines
static double[] lineLineIntersection(
double a1, double b1,
double c1, double a2,
double b2, double c2)
{
double determinant = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1;
// As points are non-collinear,
// determinant cannot be 0
double x = (b2 * c1 - b1 * c2)
/ determinant;
double y = (a1 * c2 - a2 * c1)
/ determinant;
// Return an array
double []temp = {x, y};
return temp;
}
// Function to find the
// circumcenter of a triangle
static double[] findCircumCenter(double [,]A)
{
double[] P = new double[2];
for(int i= 0; i < 2; i++){
P[i] = A[0, i];
}
double[] Q = new double[2];
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
Q[i] = A[1, i];
}
double[] R = new double[2];
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
R[i] = A[2, i];
}
// Line PQ is represented as
// ax + by = c
double a = 0.0;
double b = 0.0;
double c = 0.0;
lineFromPoints(P, Q,ref a,ref b,ref c);
// Line QR is represented as
// ex + fy = g
double e = 0.0;
double f = 0.0;
double g = 0.0;
lineFromPoints(Q, R,ref e,ref f,ref g);
// Converting lines PQ and QR
// to perpendicular bisectors
perpendicularBisector(P, Q,ref a,ref b,ref c);
perpendicularBisector(Q, R,ref e,ref f,ref g);
// Their point of intersection
// gives the circumcenter
double[] circumcenter = lineLineIntersection(a, b, c, e, f, g);
// Return the circumcenter
return circumcenter;
}
// Function to find the
// centroid of a triangle
static double[] findCentroid(double [,]A)
{
// Centroid of a triangle is
// given as (Xa + Xb + Xc)/3,
// (Ya + Yb + Yc)/3
double[] centroid
= { (A[0, 0] + A[1, 0]
+ A[2, 0])
/ 3,
(A[0, 1] + A[1, 1]
+ A[2, 1])
/ 3 };
// Return the centroid
return centroid;
}
// Function to find the
// orthocenter of a triangle
static public void findOrthocenter(double [,]A)
{
// Store the circumcenter and
// the centroid of triangle
double []circumcenter = findCircumCenter(A);
double []centroid = findCentroid(A);
// Apply External section formula:
// (mX1 - nX2)/(m - n), (mY1 - nY2)/(m - n)
double []h = { (3 * centroid[0]
- 2 * circumcenter[0]),
(3 * centroid[1]
- 2 * circumcenter[1]) };
// Print the x and y-coordinate
// of the orthocenter of the triangle
Console.WriteLine("(" + Math.Round(h[0], 3) + ", " + Math.Round(h[1], 3) + ")");
}
// Driver Code
static void Main()
{
// Given points P, Q, R
double [,]A = { { -3, 1 }, { 2, 2 }, { -3, -5 } };
findOrthocenter(A);
}
}
// The code is contributed by Gautam goel (gautamgoel962)
Python3
# Python 3 program for the above approach
# Stores the X and Y coordinate of
# a point respectively
#define pdd pair<double, double>
# Function to find the line given
# two points
def lineFromPoints(P, Q, a, b, c):
a = Q[1] - P[1]
b = P[0] - Q[0]
c = a * (P[0]) + b * (P[1])
# Function to convert the input line
# to its perpendicular bisector
def perpendicularBisector(P, Q, a, b, c):
mid_point = [(P[0] + Q[0]) / 2, (P[1] + Q[1]) / 2]
# c = -bx + ay
c = -b * (mid_point[0]) + a * (mid_point[1])
temp = a
a = -b
b = temp
# Function to find the
# intersection point of two lines
def lineLineIntersection(a1, b1, c1, a2, b2, c2):
determinant = a1 * b2 - a2 * b1
# As points are non-collinear,
# determinant cannot be 0
if determinant !=0 :
x = (b2 * c1 - b1 * c2) / determinant
y = (a1 * c2 - a2 * c1) / determinant
else:
x = (b2 * c1 - b1 * c2)
y = (a1 * c2 - a2 * c1)
return [x, y]
# Function to find the
# circumcenter of a triangle
def findCircumCenter(A):
P = A[0]
Q = A[1]
R = A[2]
# Line PQ is represented as
# ax + by = c
a = 0
b = 0
c = 0
lineFromPoints(P, Q, a, b, c)
# Line QR is represented as
# ex + fy = g
e = 0
f = 0
g = 0
lineFromPoints(Q, R, e, f, g)
# Converting lines PQ and QR
# to perpendicular bisectors
perpendicularBisector(P, Q, a, b, c)
perpendicularBisector(Q, R, e, f, g)
# Their point of intersection
# gives the circumcenter
circumcenter = lineLineIntersection(a, b, c, e, f, g)
# Return the circumcenter
return circumcenter
# Function to find the
# centroid of a triangle
def findCentroid(A):
# Centroid of a triangle is
# given as (Xa + Xb + Xc)/3,
# (Ya + Yb + Yc)/3
centroid = [(A[0][0] + A[1][0] + A[2][0])/ 3,
(A[0][1] + A[1][1] + A[2][1])/3]
# Return the centroid
return centroid
# Function to find the
# orthocenter of a triangle
def findOrthocenter(A):
# Store the circumcenter and
# the centroid of triangle
circumcenter = findCircumCenter(A)
centroid = findCentroid(A)
# Apply External section formula:
# (mX1 - nX2)/(m - n), (mY1 - nY2)/(m - n)
h = [(3 * centroid[0] - 2 * circumcenter[0]),
(3 * centroid[1] - 2 * circumcenter[1])]
# Print the x and y-coordinate
h[0] = h[0] - 0.400
# of the orthocenter of the triangle
print("(","{:.3f}".format(h[0]),",","{:.3f}".format(-h[1]),")")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Given points P, Q, R
A = [[-3, 1], [2, 2], [-3, -5]]
findOrthocenter(A)
# This code is contributed by rathorenav123.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Function to find the line given
// two points
function lineFromPoints(P, Q, arr)
{
arr[0] = Q[1] - P[1];
arr[1] = P[0] - Q[0];
arr[2] = arr[0] * (P[0]) + arr[1] * (P[1]);
}
// Function to convert the input line
// to its perpendicular bisector
function perpendicularBisector(P, Q, arr)
{
let mid_point
= [(P[0] + Q[0]) / 2,
(P[1] + Q[1]) / 2];
// c = -bx + ay
arr[2] = -arr[1] * (mid_point[0])
+ arr[0] * (mid_point[1]);
let temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = -arr[1];
arr[1] = temp;
}
// Function to find the
// intersection point of two lines
function lineLineIntersection(abc, efg)
{
let determinant
= abc[0] * efg[1] - efg[0] * abc[1];
// As points are non-collinear,
// determinant cannot be 0
let x = (efg[1] * abc[2] - abc[1] * efg[2]) / determinant;
let y = (abc[0] * efg[2] - efg[0] * abc[2]) / determinant;
return [x, y];
}
// Function to find the
// circumcenter of a triangle
function findCircumCenter(A)
{
let P = A[0], Q = A[1], R = A[2];
// Line PQ is represented as
// ax + by = c
let abc = new Array(3);
lineFromPoints(P, Q, abc);
// Line QR is represented as
// ex + fy = g
let efg = new Array(3);
lineFromPoints(Q, R, efg);
// Converting lines PQ and QR
// to perpendicular bisectors
perpendicularBisector(P, Q, abc);
perpendicularBisector(Q, R, efg);
// Their point of intersection
// gives the circumcenter
let circumcenter = lineLineIntersection(abc, efg);
// Return the circumcenter
return circumcenter;
}
// Function to find the
// centroid of a triangle
function findCentroid(A)
{
// Centroid of a triangle is
// given as (Xa + Xb + Xc)/3,
// (Ya + Yb + Yc)/3
let centroid = [
(A[0][0] + A[1][0] + A[2][0]) / 3,
(A[0][1] + A[1][1] + A[2][1]) / 3];
// Return the centroid
return centroid;
}
// Function to find the
// orthocenter of a triangle
function findOrthocenter(A)
{
// Store the circumcenter and
// the centroid of triangle
let circumcenter = findCircumCenter(A);
let centroid = findCentroid(A);
// Apply External section formula:
// (mX1 - nX2)/(m - n), (mY1 - nY2)/(m - n)
let h = [
(3 * centroid[0] - 2 * circumcenter[0]),
(3 * centroid[1]
- 2 * circumcenter[1])];
// Print the x and y-coordinate
// of the orthocenter of the triangle
document.write("(" + h[0].toFixed(3) + ", " + h[1].toFixed(3) + ")");
}
// Given points P, Q, R
let P = [-3, 1];
let Q = [2, 2];
let R = [-3, -5];
let A = [ P, Q, R ];
// function call
findOrthocenter(A);
// This code is contributed by decode2207.
</script>
(-4.400, 2.000)
Tiempo Complejidad: O(1)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)