Hay una serie de números que tienen solo dígitos, 4 y 7, y los números están ordenados en orden creciente. Los primeros números de la serie son 4, 7, 44, 47, 74, 77, 444, etc. Dado un número N , la tarea es encontrar la posición de ese número en la serie dada.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 4
Salida: 1
Explicación:
El primer número de la serie es 4
Entrada: N = 777
Salida: 14
Explicación:
El número 14 de la serie es 777
Enfoque: Este problema se puede resolver utilizando las siguientes observaciones:
- A continuación se muestra el patrón observado en la serie dada. Los números se pueden ver como:
""
/ \
4 7
/ \ / \
44 47 74 77
/ \ / \ / \ / \
- Como podemos observar, el patrón es creciente en potencia de 2 . Por lo tanto, la idea es iterar sobre los dígitos del número a partir del dígito menos significativo y actualizar la posición del número como:
- Si el dígito actual = 7, entonces agregue
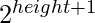 a la posición.
a la posición. - Si el dígito actual = 4, entonces agregue
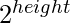 a la posición.
a la posición.
- Si el dígito actual = 7, entonces agregue
- Imprime la posición final después de las operaciones anteriores.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the position
// of the number N
void findPosition(int n)
{
int i = 0;
// To store the position of N
int pos = 0;
// Iterate through all digit of N
while (n > 0) {
// If current digit is 7
if (n % 10 == 7) {
pos = pos + pow(2, i + 1);
}
// If current digit is 4
else {
pos = pos + pow(2, i);
}
i++;
n = n / 10;
}
// Print the final position
cout << pos;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given number of the series
int N = 777;
// Function Call
findPosition(N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find the position
// of the number N
static void findPosition(int n)
{
int i = 0;
// To store the position of N
int pos = 0;
// Iterate through all digit of N
while (n > 0)
{
// If current digit is 7
if (n % 10 == 7)
{
pos = pos + (int)Math.pow(2, i + 1);
}
// If current digit is 4
else
{
pos = pos + (int)Math.pow(2, i);
}
i++;
n = n / 10;
}
// Print the final position
System.out.print(pos);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given number of the series
int N = 777;
// Function Call
findPosition(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function to find the position # of the number N def findPosition(n): i = 0 # To store the position of N pos = 0 # Iterate through all digit of N while (n > 0): # If current digit is 7 if (n % 10 == 7): pos = pos + pow(2, i + 1) # If current digit is 4 else: pos = pos + pow(2, i) i += 1 n = n // 10 # Print the final position print(pos) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Given number of the series N = 777 # Function Call findPosition(N) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to find the position
// of the number N
static void findPosition(int n)
{
int i = 0;
// To store the position of N
int pos = 0;
// Iterate through all digit of N
while (n > 0)
{
// If current digit is 7
if (n % 10 == 7)
{
pos = pos + (int)Math.Pow(2, i + 1);
}
// If current digit is 4
else
{
pos = pos + (int)Math.Pow(2, i);
}
i++;
n = n / 10;
}
// Print the final position
Console.Write(pos);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given number of the series
int N = 777;
// Function Call
findPosition(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Code_Mech
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program for the above approach
// Function to find the position
// of the number N
function findPosition(n)
{
var i = 0;
// To store the position of N
var pos = 0;
// Iterate through all digit of N
while (n > 0) {
// If current digit is 7
if (n % 10 == 7) {
pos = pos + parseInt( Math.pow(2, i + 1));
}
// If current digit is 4
else {
pos = pos + parseInt( Math.pow(2, i));
}
i++;
n = parseInt(n / 10);
}
// Print the final position
document.write(pos);
}
// Driver Code
// Given number of the series
var N = 777;
// Function Call
findPosition(N);
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
</script>
14
Complejidad de tiempo: O(log 10 N * log 2 N) , donde N representa el entero dado.
Espacio auxiliar: O(1) , no se requiere espacio adicional, por lo que es una constante.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por nishanthmolleti9 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA