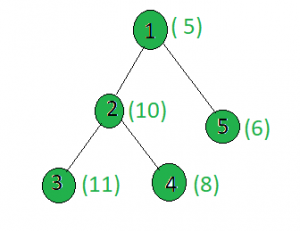
Dado un árbol, y los pesos de todos los Nodes y un número entero x , la tarea es encontrar un Node i tal que peso[i] + x tenga el conjunto máximo de bits. Si dos o más Nodes tienen la misma cantidad de bits establecidos cuando se agregan con x , encuentre el que tiene el valor mínimo.
Ejemplos:
Aporte:
x = 15
Salida: 4
Node 1: setbits(5 + 15) = 2
Node 2: setbits(10 + 15) = 3
Node 3: setbits(11 + 15) = 3
Node 4: setbits(8 + 15) = 4
Node 5: conjunto de bits (6 + 15) = 3
Enfoque: Realice dfs en el árbol y realice un seguimiento del Node cuya suma con x tiene el máximo de bits establecidos. Si dos o más Nodes tienen el mismo número de bits establecidos, elija el que tenga el número mínimo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maximum = INT_MIN, x, ans = INT_MAX;
vector<int> graph[100];
vector<int> weight(100);
// Function to perform dfs to find
// the maximum set bits value
void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If current set bits value is greater than
// the current maximum
int a = __builtin_popcount(weight[node] + x);
if (maximum < a) {
maximum = a;
ans = node;
}
// If count is equal to the maximum
// then choose the node with minimum value
else if (maximum == a)
ans = min(ans, node);
for (int to : graph[node]) {
if (to == parent)
continue;
dfs(to, node);
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
x = 15;
// Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5;
weight[2] = 10;
weight[3] = 11;
weight[4] = 8;
weight[5] = 6;
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].push_back(2);
graph[2].push_back(3);
graph[2].push_back(4);
graph[1].push_back(5);
dfs(1, 1);
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int maximum = Integer.MIN_VALUE, x, ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static Vector<Vector<Integer>> graph = new Vector<Vector<Integer>>();
static Vector<Integer> weight = new Vector<Integer>();
//number of set bits
static int __builtin_popcount(int x)
{
int c = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 60; i++)
if(((x>>i)&1) != 0)c++;
return c;
}
// Function to perform dfs to find
// the maximum value
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If current set bits value is greater than
// the current maximum
int a = __builtin_popcount(weight.get(node) + x);
if (maximum < a)
{
maximum = a;
ans = node;
}
// If count is equal to the maximum
// then choose the node with minimum value
else if (maximum == a)
ans = Math.min(ans, node);
for (int i = 0; i < graph.get(node).size(); i++)
{
if (graph.get(node).get(i) == parent)
continue;
dfs(graph.get(node).get(i), node);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
x = 15;
// Weights of the node
weight.add(0);
weight.add(5);
weight.add(10);;
weight.add(11);;
weight.add(8);
weight.add(6);
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
graph.add(new Vector<Integer>());
// Edges of the tree
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(2).add(3);
graph.get(2).add(4);
graph.get(1).add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
System.out.println( ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Python3
# Python implementation of the approach
from sys import maxsize
maximum, x, ans = -maxsize, None, maxsize
graph = [[] for i in range(100)]
weight = [0] * 100
# Function to perform dfs to find
# the maximum set bits value
def dfs(node, parent):
global x, ans, graph, weight, maximum
# If current set bits value is greater than
# the current maximum
a = bin(weight[node] + x).count('1')
if maximum < a:
maximum = a
ans = node
# If count is equal to the maximum
# then choose the node with minimum value
elif maximum == a:
ans = min(ans, node)
for to in graph[node]:
if to == parent:
continue
dfs(to, node)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = 15
# Weights of the node
weight[1] = 5
weight[2] = 10
weight[3] = 11
weight[4] = 8
weight[5] = 6
# Edges of the tree
graph[1].append(2)
graph[2].append(3)
graph[2].append(4)
graph[1].append(5)
dfs(1, 1)
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by
# sanjeev2552
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int maximum = int.MinValue, x,ans = int.MaxValue;
static List<List<int>> graph = new List<List<int>>();
static List<int> weight = new List<int>();
// number of set bits
static int __builtin_popcount(int x)
{
int c = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 60; i++)
if(((x>>i)&1) != 0)c++;
return c;
}
// Function to perform dfs to find
// the maximum value
static void dfs(int node, int parent)
{
// If current set bits value is greater than
// the current maximum
int a = __builtin_popcount(weight[node] + x);
if (maximum < a)
{
maximum = a;
ans = node;
}
// If count is equal to the maximum
// then choose the node with minimum value
else if (maximum == a)
ans = Math.Min(ans, node);
for (int i = 0; i < graph[node].Count; i++)
{
if (graph[node][i] == parent)
continue;
dfs(graph[node][i], node);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
x = 15;
// Weights of the node
weight.Add(0);
weight.Add(5);
weight.Add(10);
weight.Add(11);;
weight.Add(8);
weight.Add(6);
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
graph.Add(new List<int>());
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].Add(2);
graph[2].Add(3);
graph[2].Add(4);
graph[1].Add(5);
dfs(1, 1);
Console.Write( ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by mits
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of the approach
let maximum = Number.MIN_VALUE, x,
ans = Number.MAX_VALUE;
let graph = new Array(100);
for(let i=0;i<100;i++)
{
graph[i]=[];
}
let weight = [];
//number of set bits
function __builtin_popcount(x)
{
let c = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < 60; i++)
if(((x>>i)&1) != 0)
c++;
return c;
}
// Function to perform dfs to find
// the maximum value
function dfs(node,parent)
{
// If current set bits value is greater than
// the current maximum
let a = __builtin_popcount(weight[node] + x);
if (maximum < a)
{
maximum = a;
ans = node;
}
// If count is equal to the maximum
// then choose the node with minimum value
else if (maximum == a)
ans = Math.min(ans, node);
for (let i = 0; i < graph[node].length; i++)
{
if (graph[node][i] == parent)
continue;
dfs(graph[node][i], node);
}
}
// Driver code
x = 15;
// Weights of the node
weight.push(0);
weight.push(5);
weight.push(10);;
weight.push(11);;
weight.push(8);
weight.push(6);
// Edges of the tree
graph[1].push(2);
graph[2].push(3);
graph[2].push(4);
graph[1].push(5);
dfs(1, 1);
document.write( ans);
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
4
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(N).
En dfs, cada Node del árbol se procesa una vez y, por lo tanto, la complejidad debida a dfs es O(N) si hay un total de N Nodes en el árbol. Además, para procesar cada Node se usa la función builtin_popcount() que tiene una complejidad de O(c) donde c es una constante y dado que esta complejidad es constante, no afecta la complejidad temporal general. Por lo tanto, la complejidad del tiempo es O(N). - Espacio Auxiliar : O(1).
No se requiere ningún espacio adicional, por lo que la complejidad del espacio es constante.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por mohit kumar 29 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA