Dada una array arr[] , la tarea es contar el número de arrays únicas que se pueden formar actualizando los elementos de la array dada a cualquier elemento en el rango [1, arr[i]] tal que el Mínimo común múltiplo de la array actualizada es igual al elemento máximo.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {6, 3}
Salida: 13
Explicación:
Las arrays posibles son:
{[1, 1], [1, 2], [2, 1], [2, 2], [1, 3] ,
[3, 1], [3, 3], [4, 1], [4, 2], [5, 1],
[6, 1], [6, 2], [6, 3]}Entrada: arr[] = {1, 4, 3, 2}
Salida: 15
Acercarse:
- Para que el elemento máximo sea el LCM de la array, debemos fijar el elemento máximo de la array.
- Como hemos fijado un número
 como máximo, ahora para que el MCM sea
como máximo, ahora para que el MCM sea  , debemos asegurarnos de que cada elemento en la array sea un múltiplo de
, debemos asegurarnos de que cada elemento en la array sea un múltiplo de  incluir
incluir
- Encontraremos los factores para el número
 y encontraremos el número de formas de colocarlos en la array.
y encontraremos el número de formas de colocarlos en la array. - Digamos que los factores de
 be
be 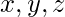 . El conteo de factores es
. El conteo de factores es 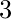 .
. - Supongamos que el número de posiciones que
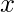 significa
significa  que hay un
que hay un  número de posiciones que tienen un número en la array que es mayor que igual
número de posiciones que tienen un número en la array que es mayor que igual 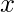 y que
y que 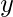 tienen
tienen  posiciones y
posiciones y 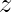 tienen
tienen 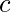 posiciones.
posiciones. - Ahora, el número de formas de distribuir x [/Tex] en
 posiciones,
posiciones, 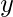 en
en 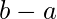 posiciones y
posiciones y 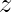 en
en 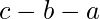 posiciones son
posiciones son 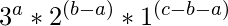 y así sucesivamente.
y así sucesivamente. - Ahora, tendremos que restar aquellas vías que tienen MCM
 pero
pero  no están.
no están. - Tendremos que restar
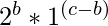 de las formas.
de las formas. - Usaremos BIT (árbol indexado binario) para encontrar un número de posiciones mayor que algún número
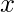 .
.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// Number of ways to change the array
// such that maximum element of the
// array is the LCM of the array
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Modulo
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
// Fenwick tree to find number
// of indexes greater than x
vector<int> BIT(N, 0);
// Function to compute
// x ^ y % MOD
int power(int x, int y)
{
if (x == 0)
return 0;
int ans = 1;
// Loop to compute the
// x^y % MOD
while (y > 0) {
if (y & 1)
ans = (1LL * ans * x) % MOD;
x = (1LL * x * x) % MOD;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
// Function to update the binary
// indexed tree
void updateBIT(int idx, int val)
{
assert(idx > 0);
while (idx < N) {
BIT[idx] += val;
idx += idx & -idx;
}
}
// Function to find the prefix sum
// upto the current index
int queryBIT(int idx)
{
int ans = 0;
while (idx > 0) {
ans += BIT[idx];
idx -= idx & -idx;
}
return ans;
}
// Function to find the number of
// ways to change the array such
// that the LCM of array is
// maximum element of the array
int numWays(int arr[], int n)
{
int mx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Updating BIT with the
// frequency of elements
updateBIT(arr[i], 1);
// Maximum element in the array
mx = max(mx, arr[i]);
}
// 1 is for every element
// is 1 in the array;
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= mx; i++) {
// Vector for storing the factors
vector<int> factors;
for (int j = 1; j * j <= i; j++) {
// finding factors of i
if (i % j == 0) {
factors.push_back(j);
if (i / j != j)
factors.push_back(i / j);
}
}
// Sorting in descending order
sort(factors.rbegin(), factors.rend());
int cnt = 1;
// for storing number of indexex
// greater than the i - 1 element
int prev = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < factors.size(); j++) {
// Number of remaining factors
int remFactors = int(factors.size()) - j;
// Number of indexes in the array
// with element factor[j] and above
int indexes = n - queryBIT(factors[j] - 1);
// Multiplying count with
// remFcators ^ (indexes - prev)
cnt = (1LL
* cnt
* power(remFactors,
indexes - prev))
% MOD;
prev = max(prev, indexes);
}
// Remove those counts which have
// lcm as i but i is not present
factors.erase(factors.begin());
int toSubtract = 1;
prev = 0;
// Loop to find the count which have
// lcm as i but i is not present
for (int j = 0; j < factors.size(); j++) {
int remFactors = int(factors.size()) - j;
int indexes = n - queryBIT(factors[j] - 1);
toSubtract = (1LL
* toSubtract
* power(remFactors,
indexes - prev));
prev = max(prev, indexes);
}
// Adding cnt - toSubtract to answer
ans = (1LL * ans + cnt
- toSubtract + MOD)
% MOD;
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 6, 3 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int ans = numWays(arr, n);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
Python3
# Python implementation to find the # Number of ways to change the array # such that maximum element of the # array is the LCM of the array # Modulo MOD = int(1e9) + 9 MAXN = int(1e5) + 5 # Fenwick tree to find number # of indexes greater than x BIT = [0 for _ in range(MAXN)] # Function to compute # x ^ y % MOD def power(x, y): if x == 0: return 0 ans = 1 # Loop to compute the # x ^ y % MOD while y > 0: if y % 2 == 1: ans = (ans * x) % MOD x = (x * x) % MOD y = y // 2 return ans # Function to update the # Binary Indexed Tree def updateBIT(idx, val): # Loop to update the BIT while idx < MAXN: BIT[idx] += val idx += idx & (-idx) # Function to find # prefix sum upto idx def queryBIT(idx): ans = 0 while idx > 0: ans += BIT[idx] idx -= idx & (-idx) return ans # Function to find number of ways # to change the array such that # MAX of array is same as LCM def numWays(arr): mx = 0 # Updating BIT with the # frequency of elements for i in arr: updateBIT(i, 1) # Maximum element # in the array mx = max(mx, i) ans = 1 for i in range(2, mx + 1): # For storing factors of i factors = [] for j in range(1, i + 1): if j * j > i: break # Finding factors of i if i % j == 0: factors.append(j) if i // j != j: factors.append(i // j) # Sorting in descending order factors.sort() factors.reverse() # For storing ans cnt = 1 # For storing number of indexes # greater than the i - 1 element prev = 0 for j in range(len(factors)): # Number of remaining factors remFactors = len(factors) - j # Number of indexes in the array # with element factor[j] and above indexes = len(arr) - queryBIT(factors[j] - 1) # Multiplying count with # remFcators ^ (indexes - prev) cnt = (cnt * power(remFactors, \ indexes - prev)) % MOD prev = max(prev, indexes) # Remove those counts which have # lcm as i but i is not present factors.remove(factors[0]) toSubtract = 1 prev = 0 for j in range(len(factors)): remFactors = len(factors) - j indexes = len(arr) - queryBIT(factors[j] - 1) toSubtract = (toSubtract *\ power(remFactors, indexes - prev)) prev = max(prev, indexes) # Adding cnt - toSubtract to ans; ans = (ans + cnt - toSubtract + MOD) % MOD; return ans # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [1, 4, 3, 2] ans = numWays(arr); print(ans)
13
Complejidad de tiempo: ![]() , donde
, donde ![]() es el elemento máximo en la array.
es el elemento máximo en la array.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por insiderpants y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA