Una serie geométrica es una serie con una razón constante entre términos sucesivos. El primer término de la serie se denota por a y la razón común se denota por r . La serie se ve así:- ![]()
La tarea es encontrar la suma de tal serie, mod M.
Ejemplos:
Input: a = 1, r = 2, N = 10000, M = 10000 Output: 8751 Input: a = 1, r = 4, N = 10000, M = 100000 Output: 12501
Acercarse:
- Para encontrar la suma de series
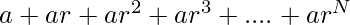 , podemos tomar fácilmente a como común y encontrar la suma de
, podemos tomar fácilmente a como común y encontrar la suma de 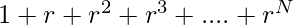 y multiplicarla por a.
y multiplicarla por a. - Pasos para encontrar la suma de la serie anterior.
- Aquí, se puede resolver que:
![Procesado por QuickLaTeX.com [1 + r + r^2 + r^3 + . . . + r^(2*n+1)] = (1+r)*(1 + (r^2) + (r^2)^2 + (r^2)^3 + . . . + (r^ 2)^n)](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c5c0047135be8e0d7abe9ebe94b9a606_l3.png)
- Aquí, se puede resolver que:
Si denotamos,
entonces,
y,
Esto funcionará como nuestro caso recursivo.
- Entonces, los casos base son:
Sum(r, 0) = 1. Sum(r, 1) = 1 + r.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ implementation to
// illustrate the program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate the sum
// recursively
int SumGPUtil(long long int r,
long long int n,
long long int m)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 1)
return (1 + r) % m;
long long int ans;
// If n is odd
if (n % 2 == 1)
{
ans = (1 + r) *
SumGPUtil((r * r) % m,
(n - 1) / 2, m);
}
else
{
// If n is even
ans = 1 + (r * (1 + r) *
SumGPUtil((r * r) % m,
(n / 2) - 1, m));
}
return (ans % m);
}
// Function to print the long value of Sum
void SumGP(long long int a,
long long int r,
long long int N,
long long int M)
{
long long int answer;
answer = a * SumGPUtil(r, N, M);
answer = answer % M;
cout << answer << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// First element
long long int a = 1;
// Common difference
long long int r = 4;
// Number of elements
long long int N = 10000;
// Mod value
long long int M = 100000;
SumGP(a, r, N, M);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62
Java
// Java implementation to
// illustrate the program
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Function to calculate the sum
// recursively
static long SumGPUtil(long r, long n,
long m)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 1)
return (1 + r) % m;
long ans;
// If n is odd
if (n % 2 == 1)
{
ans = (1 + r) *
SumGPUtil((r * r) % m,
(n - 1) / 2, m);
}
else
{
// If n is even
ans = 1 + (r * (1 + r) *
SumGPUtil((r * r) % m,
(n / 2) - 1, m));
}
return (ans % m);
}
// Function to print the value of Sum
static void SumGP(long a, long r,
long N, long M)
{
long answer;
answer = a * SumGPUtil(r, N, M);
answer = answer % M;
System.out.println(answer);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// First element
long a = 1;
// Common difference
long r = 4;
// Number of elements
long N = 10000;
// Mod value
long M = 100000;
SumGP(a, r, N, M);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62
Python3
# Python3 implementation to illustrate the program # Function to calculate the sum # recursively def SumGPUtil (r, n, m): # Base cases if n == 0: return 1 if n == 1: return (1 + r) % m # If n is odd if n % 2 == 1: ans = (1 + r) * SumGPUtil(r * r % m, (n - 1)//2, m) else: #If n is even ans = 1 + r * (1 + r) * SumGPUtil(r * r % m, n//2 - 1, m) return ans % m # Function to print the value of Sum def SumGP (a, r, N, M): answer = a * SumGPUtil(r, N, M) answer = answer % M print(answer) #Driver Program if __name__== '__main__': a = 1 # first element r = 4 # common difference N = 10000 # Number of elements M = 100000 # Mod value SumGP(a, r, N, M)
C#
// C# implementation to
// illustrate the program
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to calculate the sum
// recursively
static long SumGPUtil(long r, long n,
long m)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 1)
return (1 + r) % m;
long ans;
// If n is odd
if (n % 2 == 1)
{
ans = (1 + r) *
SumGPUtil((r * r) % m,
(n - 1) / 2, m);
}
else
{
// If n is even
ans = 1 + (r * (1 + r) *
SumGPUtil((r * r) % m,
(n / 2) - 1, m));
}
return (ans % m);
}
// Function to print the value of Sum
static void SumGP(long a, long r,
long N, long M)
{
long answer;
answer = a * SumGPUtil(r, N, M);
answer = answer % M;
Console.WriteLine(answer);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// First element
long a = 1;
// Common difference
long r = 4;
// Number of elements
long N = 10000;
// Mod value
long M = 100000;
SumGP(a, r, N, M);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to
// illustrate the program
// Function to calculate the sum
// recursively
function SumGPUtil(r, n, m)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 1;
if (n == 1)
return (1 + r) % m;
let ans;
// If n is odd
if (n % 2 == 1)
{
ans = (1 + r) *
SumGPUtil((r * r) % m,
(n - 1) / 2, m);
}
else
{
// If n is even
ans = 1 + (r * (1 + r) *
SumGPUtil((r * r) % m,
(n / 2) - 1, m));
}
return (ans % m);
}
// Function to print the value of Sum
function SumGP(a, r, N, M)
{
let answer;
answer = a * SumGPUtil(r, N, M);
answer = answer % M;
document.write(answer);
}
// Driver Code
// First element
let a = 1;
// Common difference
let r = 4;
// Number of elements
let N = 10000;
// Mod value
let M = 100000;
SumGP(a, r, N, M);
</script>
Producción:
12501
Complejidad del tiempo: O(log N)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)