Dado un número N. La tarea es comprobar si el número dado es número primo o no.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 987
Salida: No es un número primo
Explicación:
Como, 987 = 3*7*47. Por lo tanto, 987 no es un número primo.
Entrada: N = 67
Salida: Número primo
Método de factorización de rueda:
La factorización de rueda es la mejora del método Tamiz de Eratóstenes . Para la factorización de la rueda, se comienza con una pequeña lista de números, llamada base , generalmente los primeros números primos , luego se genera la lista, llamada rueda , de los enteros que son coprimos con todos los números de la base. Luego, para encontrar el divisor más pequeño del número a factorizar, uno lo divide sucesivamente por los números en la base y en la rueda .
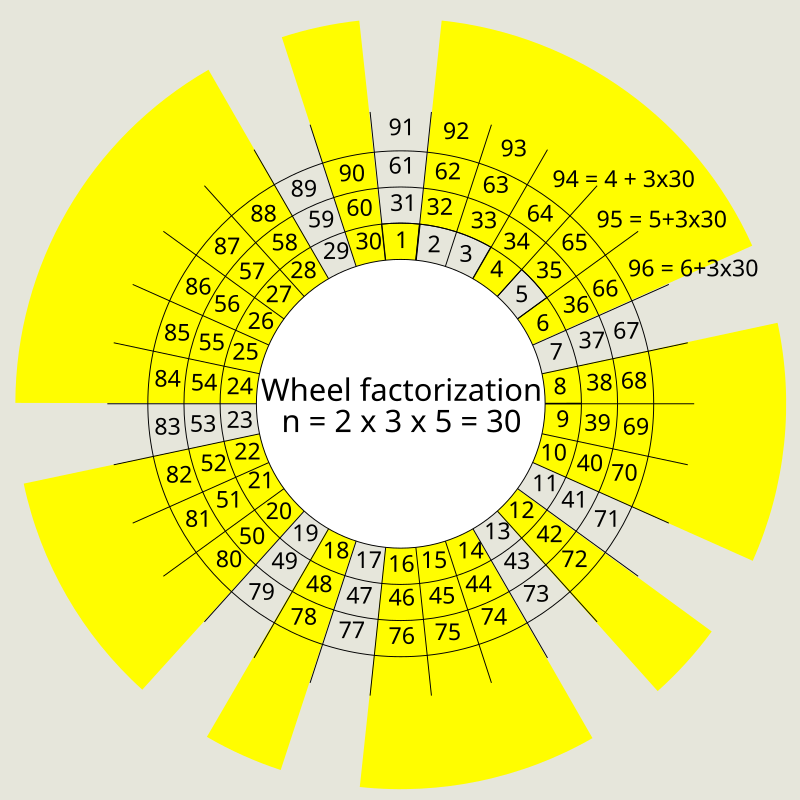
Digamos que seleccionamos la base como {2, 3, 5} y los números que son coprimos con la base son {7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31} se configuran como la rueda .
Para entenderlo más, vea el patrón en la imagen de arriba que exhiben los números. El mcm de los tres primeros números primos es 30. Los números (menos de 30) que terminan en 7, 1 y 3 y no son múltiplos de 2, 3 y 5 y siempre son primos, es decir, {7 , 11 , 13, 17, 19, 23, 29} . Agregando el nro. 31 a esta lista y luego si sumamos múltiplos de 30 a cualquiera de los números de la lista, nos da un Número Primo .
Algoritmo para el método de factorización de ruedas:
For the number N to be Prime or not:
bool isPrime(x) {
if (x < 2) {
return False;
}
for N in {2, 3, 5} {
return False;
}
for p= [0, sqrt(N)] such that p = p + 30: {
for c in [p+7, p+11, p+13, p+17, p+19, p+23, p+29, p+31] {
if c > sqrt(N)
break;
else if N % (c+p) = 0:
return False;
}
}
}
return True;
}
Enfoque:
El siguiente es el enfoque para el algoritmo anterior:
- Para la prueba de primalidad de un número N dado , verifique si el número dado es divisible por cualquiera de los números 2, 3, 5 o no.
- Si el número no es divisible por ninguno de 2, 3, 5, compruebe si el número formado al sumar múltiplos de 30 en la lista [7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31] divide el número dado N o no. En caso afirmativo, el número dado no es un número primo , de lo contrario es un número primo .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to check if the
// given number is prime using
// Wheel Factorization Method
#include "bits/stdc++.h"
using namespace std;
// Function to check if a given
// number x is prime or not
void isPrime(int N)
{
bool isPrime = true;
// The Wheel for checking
// prime number
int arr[8] = { 7, 11, 13, 17,
19, 23, 29, 31 };
// Base Case
if (N < 2) {
isPrime = false;
}
// Check for the number taken
// as basis
if (N % 2 == 0 || N % 3 == 0
|| N % 5 == 0) {
isPrime = false;
}
// Check for Wheel
// Here i, acts as the layer
// of the wheel
for (int i = 0; i < sqrt(N); i += 30) {
// Check for the list of
// Sieve in arr[]
for (int c : arr) {
// If number is greater
// than sqrt(N) break
if (c > sqrt(N)) {
break;
}
// Check if N is a multiple
// of prime number in the
// wheel
else {
if (N % (c + i) == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
// If at any iteration
// isPrime is false,
// break from the loop
if (!isPrime)
break;
}
}
if (isPrime)
cout << "Prime Number";
else
cout << "Not a Prime Number";
}
// Driver's Code
int main()
{
int N = 121;
// Function call for primality
// check
isPrime(N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to check if the
// given number is prime using
// Wheel Factorization Method
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to check if a given
// number x is prime or not
static void isPrime(int N)
{
boolean isPrime = true;
// The Wheel for checking
// prime number
int []arr = { 7, 11, 13, 17,19, 23, 29, 31 };
// Base Case
if (N < 2) {
isPrime = false;
}
// Check for the number taken
// as basis
if (N % 2 == 0 || N % 3 == 0
|| N % 5 == 0) {
isPrime = false;
}
// Check for Wheel
// Here i, acts as the layer
// of the wheel
for (int i = 0; i < Math.sqrt(N); i += 30) {
// Check for the list of
// Sieve in arr[]
for (int c : arr) {
// If number is greater
// than sqrt(N) break
if (c > Math.sqrt(N)) {
break;
}
// Check if N is a multiple
// of prime number in the
// wheel
else {
if (N % (c + i) == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
// If at any iteration
// isPrime is false,
// break from the loop
if (!isPrime)
break;
}
}
if (isPrime)
System.out.println("Prime Number");
else
System.out.println("Not a Prime Number");
}
// Driver's Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int N = 121;
// Function call for primality
// check
isPrime(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Surendra_Gangwar
C#
// C# program to check if the
// given number is prime using
// Wheel Factorization Method
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to check if a given
// number x is prime or not
static void isPrime(int N)
{
bool isPrime = true;
// The Wheel for checking
// prime number
int []arr = { 7, 11, 13, 17,19, 23, 29, 31 };
// Base Case
if (N < 2) {
isPrime = false;
}
// Check for the number taken
// as basis
if (N % 2 == 0 || N % 3 == 0
|| N % 5 == 0) {
isPrime = false;
}
// Check for Wheel
// Here i, acts as the layer
// of the wheel
for (int i = 0; i < (int)Math.Sqrt(N); i += 30) {
// Check for the list of
// Sieve in arr[]
foreach (int c in arr) {
// If number is greater
// than sqrt(N) break
if (c > (int)Math.Sqrt(N)) {
break;
}
// Check if N is a multiple
// of prime number in the
// wheel
else {
if (N % (c + i) == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
// If at any iteration
// isPrime is false,
// break from the loop
if (!isPrime)
break;
}
}
if (isPrime)
Console.WriteLine("Prime Number");
else
Console.WriteLine("Not a Prime Number");
}
// Driver's Code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int N = 121;
// Function call for primality
// check
isPrime(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Yash_R
Python3
# Python3 program to check if the
# given number is prime using
# Wheel Factorization Method
import math
# Function to check if a given
# number x is prime or not
def isPrime( N):
isPrime = True;
# The Wheel for checking
# prime number
arr= [ 7, 11, 13, 17,
19, 23, 29, 31 ]
# Base Case
if (N < 2) :
isPrime = False
# Check for the number taken
# as basis
if (N % 2 == 0 or N % 3 == 0
or N % 5 == 0):
isPrime = False
# Check for Wheel
# Here i, acts as the layer
# of the wheel
for i in range(0,int(math.sqrt(N)), 30) :
# Check for the list of
# Sieve in arr[]
for c in arr:
# If number is greater
# than sqrt(N) break
if (c > int(math.sqrt(N))):
break
# Check if N is a multiple
# of prime number in the
# wheel
else :
if (N % (c + i) == 0) :
isPrime = False
break
# If at any iteration
# isPrime is false,
# break from the loop
if (not isPrime):
break
if (isPrime):
print("Prime Number")
else:
print("Not a Prime Number")
# Driver's Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 121
# Function call for primality
# check
isPrime(N)
# This code is contributed by chitranayal
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to check if the
// given number is prime using
// Wheel Factorization Method
// Function to check if a given
// number x is prime or not
function isPrime(N)
{
let isPrime = true;
// The Wheel for checking
// prime number
let arr = [ 7, 11, 13, 17,
19, 23, 29, 31 ];
// Base Case
if (N < 2) {
isPrime = false;
}
// Check for the number taken
// as basis
if (N % 2 == 0 || N % 3 == 0
|| N % 5 == 0) {
isPrime = false;
}
// Check for Wheel
// Here i, acts as the layer
// of the wheel
for (let i = 0; i < Math.sqrt(N); i += 30) {
// Check for the list of
// Sieve in arr[]
for (let c of arr) {
// If number is greater
// than sqrt(N) break
if (c > Math.sqrt(N)) {
break;
}
// Check if N is a multiple
// of prime number in the
// wheel
else {
if (N % (c + i) == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
// If at any iteration
// isPrime is false,
// break from the loop
if (!isPrime)
break;
}
}
if (isPrime)
document.write("Prime Number");
else
document.write("Not a Prime Number");
}
// Driver's Code
let N = 121;
// Function call for primality
// check
isPrime(N);
// This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal
</script>
Not a Prime Number
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N 3/2 )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por piyush25pv y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA