Dado un número entero N y un número K , la tarea es encontrar los números totales de 0 a N que tienen exactamente K dígitos distintos de cero y la suma de esos dígitos debe ser impar y esa suma debe ser distinta. El número N puede ser tan grande como 10^18 .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 10, K = 1
Salida: 5
Los números que siguen las condiciones son ->
1, 3, 5, 7 y 9
La suma de dígitos de 10 que es (1+0) = 1 también es impar, pero 1 ya está incluido en nuestro conteo.
Entrada: N = 100, K = 2
Salida: 8
Requisitos previos : Enfoque ingenuo de Digit-DP
:
un enfoque ingenuo para el recorrido lineal en O (N) de todos los elementos de 0 a N y calcular la suma de dígitos en log (n) donde n es el número de dígitos en ese número fallará para grandes Entradas de N.
Enfoque Eficiente:
- Podemos usar Programación Dinámica y su técnica muy útil es digit-dp para resolver este problema.
- Entonces, en lugar de mantener un registro de enteros distintos de cero, mantenemos un registro de ceros que podemos mantener en diferentes índices, idx en la variable K. La cantidad de ceros que podemos mantener se puede encontrar inicialmente restando K con la cantidad de dígitos en NORTE.
- Mantenemos todos los dígitos de N en un vector, digamos, dígitos .
- Ahora, calculamos el rango de elementos que podemos mantener en el índice idx analizando K.
- Supongamos que en el índice idx , nos quedamos con K = 1 (un valor distinto de cero), entonces nuestro rango para colocar elementos es [0, j] donde j es el límite superior decidido por el valor ajustado obtenido del índice actual del dígito a partir de dígitos vectoriales.
- Si en idx , nos quedamos con K = 0 , entonces nuestro rango se convierte en [1, j] porque no podemos poner 0 allí.
- Supongamos que en el índice idx , nos quedamos con K = 1 (un valor distinto de cero), entonces nuestro rango para colocar elementos es [0, j] donde j es el límite superior decidido por el valor ajustado obtenido del índice actual del dígito a partir de dígitos vectoriales.
- Ahora, también tome un parámetro que sea sum , que calculará la suma de los dígitos de un número hasta que el caso base sea exitoso.
- Además, se usa un mapa booleano que almacenará todas las sumas impares ya calculadas, por lo que da distintas sumas impares.
- La recurrencia será:
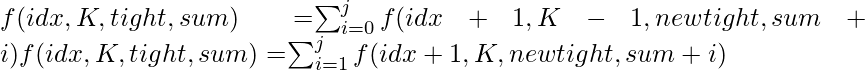
donde j = dígitos[idx] si apretado = 0, si no j = 9
- Caso base:
- Cuando idx = digits.size() , K == 0 y la suma es impar.
Marcamos la suma como verdadera y devolvemos 1, de lo contrario devolvemos 0.
- Si idx > digits.size() entonces devuelve 0.
- Cuando idx = digits.size() , K == 0 y la suma es impar.
Así que creamos una tabla DP, digamos DP[idx][K][tight][sum] que almacenará nuestro resultado de la recurrencia anterior y devolverá el conteo al memorizarlo en esta tabla DP.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to Count the numbers having
// exactly K non-zero digits and sum
// of digits are odd and distinct.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// To store digits of N
vector<int> digits;
// visited map
bool vis[170] = { false };
// DP Table
int dp[19][19][2][170];
// Push all the digits of N into
// digits vector
void ConvertIntoDigit(int n)
{
while (n) {
int dig = n % 10;
digits.push_back(dig);
n /= 10;
}
reverse(digits.begin(), digits.end());
}
// Function returns the count
int solve(int idx, int k,
int tight, int sum)
{
// If desired number is formed
// whose sum is odd
if (idx == digits.size()
&& k == 0 && sum & 1) {
// If it is not present in map,
// mark it as true and return 1
if (!vis[sum]) {
vis[sum] = 1;
return 1;
}
// Sum is present in map already
return 0;
}
// Desired result not found
if (idx > digits.size()) {
return 0;
}
// If that state is already calculated
// just return that state value
if (dp[idx][k][tight][sum]) {
return dp[idx][k][tight][sum];
}
// Upper limit
int j;
if (tight == 0) {
j = digits[idx];
}
else {
j = 9;
}
// To store the count of
// desired numbers
int cnt = 0;
// If k is non-zero, i ranges from
// 0 to j else [1, j]
for (int i = (k ? 0 : 1);
i <= j; i++) {
int newtight = tight;
if (i < j) {
newtight = 1;
}
// If current digit is 0, decrement
// k and recurse sum is not changed
// as we are just adding 0 that
// makes no difference
if (i == 0)
cnt += solve(idx + 1, k - 1,
newtight, sum);
// If i is non zero, then k remains
// unchanged and value is added to sum
else
cnt += solve(idx + 1, k, newtight,
sum + i);
}
// Memoize and return
return dp[idx][k][tight][sum] = cnt;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// K is the number of exact non-zero
// elements to have in number
int N, k;
N = 169, k = 2;
// break N into its digits
ConvertIntoDigit(N);
// We keep record of 0s we need to
// place in the number
k = digits.size() - k;
cout << solve(0, k, 0, 0);
}
Java
// Java program to count the numbers having
// exactly K non-zero digits and sum
// of digits are odd and distinct.
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// To store digits of N
static Vector<Integer> digits = new Vector<Integer>();
// visited map
static boolean []vis = new boolean[170];
// DP Table
static int [][][][]dp = new int[19][19][2][170];
// Push all the digits of N into
// digits vector
static void ConvertIntoDigit(int n)
{
while (n > 0)
{
int dig = n % 10;
digits.add(dig);
n /= 10;
}
Collections.reverse(digits);
}
// Function returns the count
static int solve(int idx, int k,
int tight, int sum)
{
// If desired number is formed
// whose sum is odd
if (idx == digits.size() &&
k == 0 && sum % 2 == 1)
{
// If it is not present in map,
// mark it as true and return 1
if (!vis[sum])
{
vis[sum] = true;
return 1;
}
// Sum is present in map already
return 0;
}
// Desired result not found
if (idx > digits.size())
{
return 0;
}
// If that state is already calculated
// just return that state value
if (dp[idx][k][tight][sum] > 0)
{
return dp[idx][k][tight][sum];
}
// Upper limit
int j;
if (idx < digits.size() && tight == 0)
{
j = digits.get(idx);
}
else
{
j = 9;
}
// To store the count of
// desired numbers
int cnt = 0;
// If k is non-zero, i ranges from
// 0 to j else [1, j]
for(int i = (k > 0 ? 0 : 1); i <= j; i++)
{
int newtight = tight;
if (i < j)
{
newtight = 1;
}
// If current digit is 0, decrement
// k and recurse sum is not changed
// as we are just adding 0 that
// makes no difference
if (i == 0)
cnt += solve(idx + 1, k - 1,
newtight, sum);
// If i is non zero, then k remains
// unchanged and value is added to sum
else
cnt += solve(idx + 1, k, newtight,
sum + i);
}
// Memoize and return
return dp[idx][k][tight][sum] = cnt;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// K is the number of exact non-zero
// elements to have in number
int N, k;
N = 169; k = 2;
// break N into its digits
ConvertIntoDigit(N);
// We keep record of 0s we need to
// place in the number
k = digits.size() - k;
System.out.print(solve(0, k, 0, 0));
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey
Python3
# Python3 program to Count the numbers having # exactly K non-zero digits and sum # of digits are odd and distinct. # To store digits of N digits = [] # visited map vis = [False for i in range(170)] # DP Table dp = [[[[0 for l in range(170)] for k in range(2)] for j in range(19)] for i in range(19)] # Push all the digits of N into # digits vector def ConvertIntoDigit(n): while (n > 0): dig = n % 10; digits.append(dig); n //= 10; digits.reverse() # Function returns the count def solve(idx, k, tight, sum): # If desired number is formed # whose sum is odd if (idx == len(digits) and k == 0 and sum % 2 == 1): # If it is not present in map, # mark it as true and return 1 if (not vis[sum]): vis[sum] = True; return 1; # Sum is present in map already return 0; # Desired result not found if (idx > len(digits)): return 0; # If that state is already calculated # just return that state value if (dp[idx][k][tight][sum]): return dp[idx][k][tight][sum]; # Upper limit j = 0; if (idx<len(digits) and tight == 0): j = digits[idx]; else: j = 9; # To store the count of # desired numbers cnt = 0; # If k is non-zero, i ranges from # 0 to j else [1, j] for i in range(0 if k else 1, j + 1): newtight = tight; if (i < j): newtight = 1; # If current digit is 0, decrement # k and recurse sum is not changed # as we are just adding 0 that # makes no difference if (i == 0): cnt += solve(idx + 1, k - 1, newtight, sum); # If i is non zero, then k remains # unchanged and value is added to sum else: cnt += solve(idx + 1, k, newtight, sum + i); dp[idx][k][tight][sum] = cnt # Memoize and return return cnt; # Driver code if __name__=='__main__': # K is the number of exact non-zero # elements to have in number N = 169 k = 2; # break N into its digits ConvertIntoDigit(N); # We keep record of 0s we need to # place in the number k = len(digits) - k; print(solve(0, k, 0, 0)) # This code is contributed by rutvik_56.
C#
// C# program to count the numbers having
// exactly K non-zero digits and sum
// of digits are odd and distinct.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// To store digits of N
static List<int> digits = new List<int>();
// visited map
static bool []vis = new bool[170];
// DP Table
static int [,,,]dp = new int[ 19, 19, 2, 170 ];
// Push all the digits of N into
// digits vector
static void ConvertIntoDigit(int n)
{
while (n > 0)
{
int dig = n % 10;
digits.Add(dig);
n /= 10;
}
digits.Reverse();
}
// Function returns the count
static int solve(int idx, int k,
int tight, int sum)
{
// If desired number is formed
// whose sum is odd
if (idx == digits.Count &&
k == 0 && sum % 2 == 1)
{
// If it is not present in map,
// mark it as true and return 1
if (!vis[sum])
{
vis[sum] = true;
return 1;
}
// Sum is present in map already
return 0;
}
// Desired result not found
if (idx > digits.Count)
{
return 0;
}
// If that state is already calculated
// just return that state value
if (dp[idx, k, tight, sum] > 0)
{
return dp[idx, k, tight, sum];
}
// Upper limit
int j;
if (idx < digits.Count && tight == 0)
{
j = digits[idx];
}
else
{
j = 9;
}
// To store the count of
// desired numbers
int cnt = 0;
// If k is non-zero, i ranges from
// 0 to j else [1, j]
for(int i = (k > 0 ? 0 : 1); i <= j; i++)
{
int newtight = tight;
if (i < j)
{
newtight = 1;
}
// If current digit is 0, decrement
// k and recurse sum is not changed
// as we are just adding 0 that
// makes no difference
if (i == 0)
cnt += solve(idx + 1, k - 1,
newtight, sum);
// If i is non zero, then k remains
// unchanged and value is added to sum
else
cnt += solve(idx + 1, k, newtight,
sum + i);
}
// Memoize and return
return dp[idx, k, tight, sum] = cnt;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// K is the number of exact non-zero
// elements to have in number
int N, k;
N = 169; k = 2;
// break N into its digits
ConvertIntoDigit(N);
// We keep record of 0s we need to
// place in the number
k = digits.Count - k;
Console.Write(solve(0, k, 0, 0));
}
}
// This code is contributed by amal kumar choubey
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to count the numbers having
// exactly K non-zero digits and sum
// of digits are odd and distinct.
// To store digits of N
let digits = [];
// visited map
let vis = new Array(170);
vis.fill(false);
// DP Table
let dp = new Array(19);
for(let i = 0; i < 19; i++)
{
dp[i] = new Array(19);
for(let j = 0; j < 19; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = new Array(2);
for(let k = 0; k < 2; k++)
{
dp[i][j][k] = new Array(170);
for(let l = 0; l < 170; l++)
{
dp[i][j][k][l] = 0;
}
}
}
}
// Push all the digits of N into
// digits vector
function ConvertIntoDigit(n)
{
while (n > 0)
{
let dig = n % 10;
digits.push(dig);
n = parseInt(n / 10, 10);
}
digits.reverse();
}
// Function returns the count
function solve(idx, k, tight, sum)
{
// If desired number is formed
// whose sum is odd
if (idx == digits.length &&
k == 0 && sum % 2 == 1)
{
// If it is not present in map,
// mark it as true and return 1
if (!vis[sum])
{
vis[sum] = true;
return 1;
}
// Sum is present in map already
return 0;
}
// Desired result not found
if (idx > digits.length)
{
return 0;
}
// If that state is already calculated
// just return that state value
if (dp[idx][k][tight][sum] > 0)
{
return dp[idx][k][tight][sum];
}
// Upper limit
let j;
if (idx < digits.length && tight == 0)
{
j = digits[idx];
}
else
{
j = 9;
}
// To store the count of
// desired numbers
let cnt = 0;
// If k is non-zero, i ranges from
// 0 to j else [1, j]
for(let i = (k > 0 ? 0 : 1); i <= j; i++)
{
let newtight = tight;
if (i < j)
{
newtight = 1;
}
// If current digit is 0, decrement
// k and recurse sum is not changed
// as we are just adding 0 that
// makes no difference
if (i == 0)
cnt += solve(idx + 1, k - 1,
newtight, sum);
// If i is non zero, then k remains
// unchanged and value is added to sum
else
cnt += solve(idx + 1, k, newtight,
sum + i);
}
// Memoize and return
dp[idx][k][tight][sum] = cnt;
return dp[idx][k][tight][sum];
}
// K is the number of exact non-zero
// elements to have in number
let N, k;
N = 169; k = 2;
// break N into its digits
ConvertIntoDigit(N);
// We keep record of 0s we need to
// place in the number
k = digits.length - k;
document.write(solve(0, k, 0, 0));
</script>
12
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por VikasVishwakarma1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA