Dado un número x positivo, la tarea es encontrar el logaritmo natural (ln) y logaritmo en base 10 (log 10 ) de este número con la ayuda de la expansión.
Ejemplo:
Input: x = 5
Output: ln 5.000 = 1.609
log10 5.000 = 0.699
Input: x = 10
Output: ln 10.000 = 2.303
log10 10.000 = 1.000
Acercarse:
- La expansión del logaritmo natural de x (ln x) es:
- Por lo tanto, esta serie se puede resumir como:
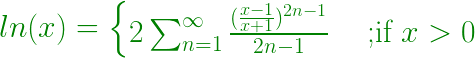
- Por lo tanto, se puede hacer una función para evaluar el enésimo término de la secuencia para 1 ≤ x ≤ n
- Ahora, para calcular log 10 x , se puede usar la siguiente fórmula:

A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// CPP code to Find the ln x and
// log<sub>10</sub> x with the help of expansion
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate ln x using expansion
double calculateLnx(double n)
{
double num, mul, cal, sum = 0;
num = (n - 1) / (n + 1);
// terminating value of the loop
// can be increased to improve the precision
for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++) {
mul = (2 * i) - 1;
cal = pow(num, mul);
cal = cal / mul;
sum = sum + cal;
}
sum = 2 * sum;
return sum;
}
// Function to calculate log10 x
double calculateLogx(double lnx)
{
return (lnx / 2.303);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
double lnx, logx, n = 5;
lnx = calculateLnx(n);
logx = calculateLogx(lnx);
// setprecision(3) is used to display
// the output up to 3 decimal places
cout << fixed << setprecision(3)
<< "ln " << n << " = "
<< lnx << endl;
cout << fixed << setprecision(3)
<< "log10 " << n << " = "
<< logx << endl;
}
Java
// Java code to Find the ln x and
// log<sub>10</sub> x with the help of expansion
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate ln x using expansion
static double calculateLnx(double n)
{
double num, mul, cal, sum = 0;
num = (n - 1) / (n + 1);
// terminating value of the loop
// can be increased to improve the precision
for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++)
{
mul = (2 * i) - 1;
cal = Math.pow(num, mul);
cal = cal / mul;
sum = sum + cal;
}
sum = 2 * sum;
return sum;
}
// Function to calculate log10 x
static double calculateLogx(double lnx)
{
return (lnx / 2.303);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
double lnx, logx, n = 5;
lnx = calculateLnx(n);
logx = calculateLogx(lnx);
// setprecision(3) is used to display
// the output up to 3 decimal places
System.out.println ("ln " + n + " = " + lnx );
System.out.println ("log10 " + n + " = "+ logx );
}
}
// This code is contributed by ajit
Python3
# Python 3 code to Find the ln x and
# log<sub>10</sub> x with the help of expansion
# Function to calculate ln x using expansion
from math import pow
def calculateLnx(n):
sum = 0
num = (n - 1) / (n + 1)
# terminating value of the loop
# can be increased to improve the precision
for i in range(1, 1001, 1):
mul = (2 * i) - 1
cal = pow(num, mul)
cal = cal / mul
sum = sum + cal
sum = 2 * sum
return sum
# Function to calculate log10 x
def calculateLogx(lnx):
return (lnx / 2.303)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 5
lnx = calculateLnx(n)
logx = calculateLogx(lnx)
# setprecision(3) is used to display
# the output up to 3 decimal places
print("ln", "{0:.3f}".format(n),
"=", "{0:.3f}".format(lnx))
print("log10", "{0:.3f}".format(n),
"=", "{0:.3f}".format(logx))
# This code is contributed by
# Surendra_Gangwar
C#
// C# code to Find the ln x and
// log<sub>10</sub> x with the help of expansion
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate ln x using expansion
static double calculateLnx(double n)
{
double num, mul, cal, sum = 0;
num = (n - 1) / (n + 1);
// terminating value of the loop
// can be increased to improve the precision
for (int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++)
{
mul = (2 * i) - 1;
cal = Math.Pow(num, mul);
cal = cal / mul;
sum = sum + cal;
}
sum = 2 * sum;
return sum;
}
// Function to calculate log10 x
static double calculateLogx(double lnx)
{
return (lnx / 2.303);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main (String[] args)
{
double lnx, logx, n = 5;
lnx = calculateLnx(n);
logx = calculateLogx(lnx);
// setprecision(3) is used to display
// the output up to 3 decimal places
Console.WriteLine("ln " + n + " = " + lnx );
Console.WriteLine("log10 " + n + " = "+ logx );
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript code to Find the ln x and
// log<sub>10</sub> x with the help of expansion
// Function to calculate ln x using expansion
function calculateLnx(n)
{
let num, mul, cal, sum = 0;
num = (n - 1) / (n + 1);
// Terminating value of the loop
// can be increased to improve the precision
for(let i = 1; i <= 1000; i++)
{
mul = (2 * i) - 1;
cal = Math.pow(num, mul);
cal = cal / mul;
sum = sum + cal;
}
sum = 2 * sum;
return sum;
}
// Function to calculate log10 x
function calculateLogx(lnx)
{
return (lnx / 2.303);
}
// Driver Code
let lnx, logx, n = 5;
lnx = calculateLnx(n);
logx = calculateLogx(lnx);
// setprecision(3) is used to display
// the output up to 3 decimal places
document.write("ln " + n + " = " + lnx + "<br>");
document.write("log10 " + n + " = "+ logx + "<br>");
// This code is contributed by souravmahato348
</script>
Producción:
ln 5.000 = 1.609 log10 5.000 = 0.699
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por DeveshRattan y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA