Dados n puntos en un sistema de coordenadas cartesianas. Cuenta el número de triángulos formados.
Ejemplos:
Input : point[] = {(0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 0), (2, 2)
Output : 3
Three triangles can be formed from above points.
Una solución sencilla es comprobar si el determinante de los tres puntos seleccionados es distinto de cero o no. El siguiente determinante da el área de un Triángulo (también conocida como regla de Cramer).
El área del triángulo con esquinas en (x1, y1), (x2, y2) y (x3, y3) está dada por: 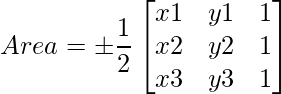
Podemos resolver esto tomando todas las combinaciones posibles de 3 puntos y encontrando el determinante.
C++
// C++ program to count number of triangles that can
// be formed with given points in 2D
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A point in 2D
struct Point
{
int x, y;
};
// Returns determinant value of three points in 2D
int det(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3)
{
return x1*(y2 - y3) - y1*(x2 - x3) + 1*(x2*y3 - y2*x3);
}
// Returns count of possible triangles with given array
// of points in 2D.
int countPoints(Point arr[], int n)
{
int result = 0; // Initialize result
// Consider all triplets of points given in inputs
// Increment the result when determinant of a triplet
// is not 0.
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
for (int j=i+1; j<n; j++)
for (int k=j+1; k<n; k++)
if (det(arr[i].x, arr[i].y, arr[j].x,
arr[j].y, arr[k].x, arr[k].y))
result++;
return result;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Point arr[] = {{0, 0}, {1, 1}, {2, 0}, {2, 2}};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << countPoints(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to count number
// of triangles that can be formed
// with given points in 2D
class GFG{
// Returns determinant value
// of three points in 2D
static int det(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3)
{
return (x1 * (y2 - y3) - y1 *
(x2 - x3) + 1 * (x2 *
y3 - y2 * x3));
}
// Returns count of possible
// triangles with given array
// of points in 2D.
static int countPoints(int [][]Point, int n)
{
int result = 0; // Initialize result
// Consider all triplets of
// points given in inputs
// Increment the result when
// determinant of a triplet is not 0.
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
for(int k = j + 1; k < n; k++)
if(det(Point[i][0], Point[i][1],
Point[j][0], Point[j][1],
Point[k][0], Point[k][1])>=0)
result = result + 1;
return result;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int Point[][] = {{0, 0},{1, 1},{2, 0},{2, 2}};
int n = Point.length;
System.out.println(countPoints(Point, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// mits
Python3
# Python program to count number # of triangles that can be formed # with given points in 2D # Returns determinant value # of three points in 2D def det(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3): return (x1 * (y2 - y3) - y1 * (x2 - x3) + 1 * (x2 * y3 - y2 * x3)) # Returns count of possible # triangles with given array # of points in 2D. def countPoints(Point, n): result = 0 # Initialize result # Consider all triplets of # points given in inputs # Increment the result when # determinant of a triplet is not 0. for i in range(n): for j in range(i + 1, n): for k in range(j + 1, n): if(det(Point[i][0], Point[i][1], Point[j][0], Point[j][1], Point[k][0], Point[k][1])): result = result + 1 return result # Driver code Point = [[0, 0], [1, 1], [2, 0], [2, 2]] n = len(Point) print(countPoints(Point, n)) # This code is contributed by # Sanjit_Prasad
C#
// C# program to count number
// of triangles that can be formed
// with given points in 2D
using System;
class GFG{
// Returns determinant value
// of three points in 2D
static int det(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int x3, int y3)
{
return (x1 * (y2 - y3) - y1 *
(x2 - x3) + 1 * (x2 *
y3 - y2 * x3));
}
// Returns count of possible
// triangles with given array
// of points in 2D.
static int countPoints(int[,] Point, int n)
{
int result = 0; // Initialize result
// Consider all triplets of
// points given in inputs
// Increment the result when
// determinant of a triplet is not 0.
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
for(int k = j + 1; k < n; k++)
if(det(Point[i,0], Point[i,1], Point[j,0], Point[j,1],Point[k,0], Point[k,1])>=0)
result = result + 1;
return result;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[,] Point = new int[,] { { 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 2, 0 }, { 2, 2 } };
int n = Point.Length/Point.Rank;
Console.WriteLine(countPoints(Point, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by mits
PHP
<?php
// PHP program to count number
// of triangles that can be formed
// with given points in 2D
// Returns determinant value
// of three points in 2D
function det($x1, $y1, $x2,
$y2, $x3, $y3)
{
return ($x1 * ($y2 - $y3) - $y1 *
($x2 - $x3) + 1 * ($x2 *
$y3 - $y2 * $x3));
}
// Returns count of possible
// triangles with given array
// of points in 2D.
function countPoints($Point, $n)
{
$result = 0; // Initialize result
// Consider all triplets of
// points given in inputs
// Increment the result when
// determinant of a triplet is not 0.
for($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
for($j = $i + 1; $j < $n; $j++)
for($k = $j + 1; $k < $n; $k++)
if(det($Point[$i][0], $Point[$i][1],
$Point[$j][0], $Point[$j][1],
$Point[$k][0], $Point[$k][1]))
$result = $result + 1;
return $result;
}
// Driver code
$Point = array(array(0, 0),
array(1, 1),
array(2, 0),
array(2, 2));
$n = count($Point);
echo countPoints($Point, $n);
// This code is contributed by
// mits
?>
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to count number
// of triangles that can be formed
// with given points in 2D
// Returns determinant value
// of three points in 2D
function det(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3)
{
return (x1 * (y2 - y3) -
y1 * (x2 - x3) +
1 * (x2 * y3 - y2 * x3));
}
// Returns count of possible
// triangles with given array
// of points in 2D.
function countPoints(Point, n)
{
// Initialize result
let result = 0;
// Consider all triplets of
// points given in inputs
// Increment the result when
// determinant of a triplet is not 0.
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(let j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
for(let k = j + 1; k < n; k++)
if (det(Point[i][0], Point[i][1],
Point[j][0], Point[j][1],
Point[k][0], Point[k][1]) >= 0)
result = result + 1;
return result;
}
// Driver Code
let Point = [ [ 0, 0 ], [ 1, 1 ],
[ 2, 0 ], [ 2, 2 ] ];
let n = Point.length;
document.write(countPoints(Point, n));
// This code is contributed by souravghosh0416
</script>
Producción:
3
Tiempo Complejidad: ![]() .
.
Optimización:
Podemos optimizar la solución anterior para trabajar en O(n 2 ) usando el hecho de que tres puntos no pueden formar un triángulo si son colineales. Podemos usar hashing para almacenar pendientes de todos los pares y encontrar todos los triángulos en tiempo O(n 2 ).
Este artículo es una contribución de Vrushank Upadhyay . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA