Dada una array de Número y dos valores A y B , la tarea es verificar las siguientes Condiciones:
- Si dos números están presentes en la array o no.
- En caso afirmativo, entonces su media aritmética y media armónica también están presentes en la misma array o no.
- Si se cumplen todas las condiciones, imprima la media geométrica de los dos números.
Las respectivas medias de los números se pueden formular de la siguiente manera:
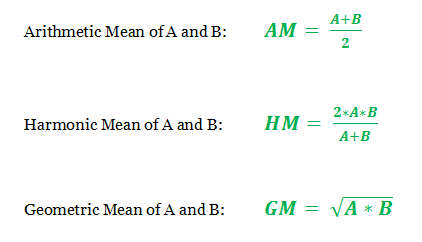
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {1.0, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 6.0}, A = 3, B = 6.
Salida: GM = 4.24
Explicación:
A = 3, B = 6 están presentes en el formación.
AM = 4.5, HM = 4 también están presentes en la array.
Entonces, GM = 4.24
Entrada: arr = {1.0, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 6.0}, A = 4, B = 6.
Salida: AM y HM no encontrados
Acercarse:
- La idea es usar Hashing , mediante el cual podemos simplemente almacenar los elementos de la array en un contenedor Hash y usar operaciones O(1) de tiempo constante para encontrar y rastrear los números y sus medias. Finalmente, la media geométrica se calcula si se cumplen todas las condiciones observando la relación simple AM * HM = GM 2 .
- Una implementación paso a paso del enfoque anterior es la siguiente:
- Se define un contenedor Hash para almacenar los elementos de la array.
- Las medias aritméticas y armónicas se calculan en base a las fórmulas.
- Las declaraciones condicionales simples se utilizan para encontrar los elementos en el contenedor Hash en tiempo constante.
- Siempre que se cumplan todas las condiciones, el GM se calcula a partir de la relación anterior.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to check if two numbers
// are present in an array then their
// AM and HM are also present. Finally,
// find the GM of the numbers
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the Arithmetic Mean
// of 2 numbers
float ArithmeticMean(float A, float B)
{
return (A + B) / 2;
}
// Function to find the Harmonic Mean
// of 2 numbers
float HarmonicMean(float A, float B)
{
return (2 * A * B) / (A + B);
}
// Following function checks and computes the
// desired results based on the means
void CheckArithmeticHarmonic(float arr[],
float A,
float B, int N)
{
// Calculate means
float AM = ArithmeticMean(A, B);
float HM = HarmonicMean(A, B);
// Hash container (Set) to store elements
unordered_set<float> Hash;
// Insertion of array elements in the Set
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
Hash.insert(arr[i]);
}
// Conditionals to check if numbers
// are present in array by Hashing
if (Hash.find(A) != Hash.end()
&& Hash.find(B) != Hash.end()) {
// Conditionals to check if the AM and HM
// of the numbers are present in array
if (Hash.find(AM) != Hash.end()
&& Hash.find(HM) != Hash.end()) {
// If all conditions are satisfied,
// the Geometric Mean is calculated
cout << "GM = ";
printf("%0.2f", sqrt(AM * HM));
}
else
{
// If numbers are found but the
// respective AM and HM are not
// found in the array
cout << "AM and HM not found";
}
}
else
{
// If none of the conditions are satisfied
cout << "Numbers not found";
}
}
int main()
{
float arr[] = {1.0, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 4.0,
4.5, 5.0, 6.0};
int N = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
float A = 3.0;
float B = 6.0;
CheckArithmeticHarmonic(arr, A, B, N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to check if two numbers
// are present in an array then their
// AM and HM are also present. Finally,
// find the GM of the numbers
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to find the Arithmetic Mean
// of 2 numbers
static Double ArithmeticMean(Double A, Double B)
{
return (A + B) / 2;
}
// Function to find the Harmonic Mean
// of 2 numbers
static Double HarmonicMean(Double A, Double B)
{
return (2 * A * B) / (A + B);
}
// Following function checks and computes the
// desired results based on the means
static void CheckArithmeticHarmonic(Double arr[],
Double A,
Double B, int N)
{
// Calculate means
Double AM = ArithmeticMean(A, B);
Double HM = HarmonicMean(A, B);
// Hash container (HashMap) to store elements
HashMap<Double,
Integer> Hash = new HashMap<Double,
Integer>();
// Insertion of array elements in the Set
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
Hash.put(arr[i], 1);
}
// Conditionals to check if numbers
// are present in array by Hashing
if (Hash.get(A) != 0 &&
Hash.get(B) != 0)
{
// Conditionals to check if the AM and HM
// of the numbers are present in array
if (Hash.get(AM) != 0 &&
Hash.get(HM) != 0)
{
// If all conditions are satisfied,
// the Geometric Mean is calculated
System.out.print("GM = ");
System.out.format("%.2f", Math.sqrt(AM * HM));
}
else
{
// If numbers are found but the
// respective AM and HM are not
// found in the array
System.out.print("AM and HM not found");
}
}
else
{
// If none of the conditions are satisfied
System.out.print("numbers not found");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Double arr[] = { 1.0, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0,
4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 6.0};
int N = (arr.length);
Double A = 3.0;
Double B = 6.0;
CheckArithmeticHarmonic(arr, A, B, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher
Python3
# Python3 program to check if two numbers
# are present in an array then their
# AM and HM are also present. Finally,
# find the GM of the numbers
from math import sqrt
# Function to find the arithmetic mean
# of 2 numbers
def ArithmeticMean(A, B):
return (A + B) / 2
# Function to find the harmonic mean
# of 2 numbers
def HarmonicMean(A, B):
return (2 * A * B) / (A + B)
# Following function checks and computes the
# desired results based on the means
def CheckArithmeticHarmonic(arr, A, B, N):
# Calculate means
AM = ArithmeticMean(A, B)
HM = HarmonicMean(A, B)
# Hash container (set) to store elements
Hash = set()
# Insertion of array elements in the set
for i in range(N):
Hash.add(arr[i])
# Conditionals to check if numbers
# are present in array by Hashing
if (A in Hash and B in Hash):
# Conditionals to check if the AM and HM
# of the numbers are present in array
if (AM in Hash and HM in Hash):
# If all conditions are satisfied,
# the Geometric Mean is calculated
print("GM =", round(sqrt(AM * HM), 2))
else:
# If numbers are found but the
# respective AM and HM are not
# found in the array
print("AM and HM not found")
else:
# If none of the conditions are satisfied
print("Numbers not found")
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [ 1.0, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0,
4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 6.0 ]
N = len(arr)
A = 3.0
B = 6.0
CheckArithmeticHarmonic(arr, A, B, N)
# This code is contributed by Samarth
C#
// C# program to check if two numbers
// are present in an array then their
// AM and HM are also present. Finally,
// find the GM of the numbers
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to find the Arithmetic Mean
// of 2 numbers
static Double ArithmeticMean(Double A, Double B)
{
return (A + B) / 2;
}
// Function to find the Harmonic Mean
// of 2 numbers
static Double HarmonicMean(Double A, Double B)
{
return (2 * A * B) / (A + B);
}
// Following function checks and computes the
// desired results based on the means
static void CheckArithmeticHarmonic(Double []arr,
Double A,
Double B, int N)
{
// Calculate means
Double AM = ArithmeticMean(A, B);
Double HM = HarmonicMean(A, B);
// Hash container (Set) to store elements
// HashMap<Double,int> Hash = new HashMap<Double,int>();
Dictionary<Double,
int> Hash = new Dictionary<Double,
int>();
// Insertion of array elements in the Set
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
Hash[arr[i]] = 1;
}
// Conditionals to check if numbers
// are present in array by Hashing
if (Hash.ContainsKey(A) &&
Hash.ContainsKey(B))
{
// Conditionals to check if the AM and HM
// of the numbers are present in array
if (Hash.ContainsKey(AM) &&
Hash.ContainsKey(HM))
{
// If all conditions are satisfied,
// the Geometric Mean is calculated
Console.Write("GM = ");
Console.Write(Math.Round(
Math.Sqrt(AM * HM), 2));
}
else
{
// If numbers are found but the
// respective AM and HM are not
// found in the array
Console.WriteLine("AM and HM not found");
}
}
else
{
// If none of the conditions are satisfied
Console.WriteLine("numbers not found");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
Double []arr = { 1.0, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0,
4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 6.0 };
int N = (arr.Length);
Double A = 3.0;
Double B = 6.0;
CheckArithmeticHarmonic(arr, A, B, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to check if two numbers
// are present in an array then their
// AM and HM are also present. Finally,
// find the GM of the numbers
// Function to find the Arithmetic Mean
// of 2 numbers
function ArithmeticMean(A, B)
{
return ((A + B) / 2);
}
// Function to find the Harmonic Mean
// of 2 numbers
function HarmonicMean(A, B)
{
return (2 * A * B) / (A + B);
}
// Following function checks and computes the
// desired results based on the means
function CheckArithmeticHarmonic(arr, A, B, N)
{
// Calculate means
let AM = ArithmeticMean(A, B);
let HM = HarmonicMean(A, B);
// Hash container (HashMap) to store elements
let Hash = new Map();
// Insertion of array elements in the Set
for(let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
Hash.set(arr[i], 1);
}
// Conditionals to check if numbers
// are present in array by Hashing
if (Hash.get(A) != 0 &&
Hash.get(B) != 0)
{
// Conditionals to check if the AM and HM
// of the numbers are present in array
if (Hash.get(AM) != 0 &&
Hash.get(HM) != 0)
{
// If all conditions are satisfied,
// the Geometric Mean is calculated
document.write("GM = ");
document.write(Math.sqrt(AM * HM).toFixed(2));
}
else
{
// If numbers are found but the
// respective AM and HM are not
// found in the array
document.write("AM and HM not found");
}
}
else
{
// If none of the conditions are satisfied
document.write("numbers not found");
}
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ 1.0, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0,
4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 6.0];
let N = (arr.length);
let A = 3.0;
let B = 6.0;
CheckArithmeticHarmonic(arr, A, B, N);
// This code is contributed by code_hunt.
</script>
GM = 4.24
Análisis de complejidad:
la complejidad de tiempo general del programa anterior se basa en la iteración inicial de los elementos de la array en la entrada definida por el usuario. Las operaciones de búsqueda asociadas con el Conjunto son todas operaciones de tiempo constante O(1). Por lo tanto, la complejidad del programa es O(N) donde N es el tamaño del arreglo.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por PratikBasu y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA