Dado un número N de personas, la tarea es contar el número de formas de formar grupos de tamaño ? N donde, en cada grupo, el primer elemento del grupo es el líder del grupo.
Nota:
- Los grupos con las mismas personas que tienen diferentes líderes se tratan como un grupo diferente. Por ejemplo: el grupo {1, 2, 3} y {2, 1, 3} se tratan como grupos diferentes ya que tienen diferentes líderes 1 y 2 respectivamente.
- Los grupos con el mismo líder y las mismas personas se tratan como un mismo grupo. Por ejemplo: los grupos {1, 3, 2} y {1, 2, 3} se tratan como el mismo grupo ya que tienen el mismo líder y las mismas personas.
- La respuesta puede ser muy grande, lleve el módulo a (1e9+7).
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 3
Salida: 12
Explicación:
Total Los grupos con líderes son:
Grupos con líder 1:
1. {1}
2. {1, 2}
3. {1, 3}
4. {1, 2, 3}
Grupos con Líder 2:
5. {2}
6. {2, 1}
7. {2, 3}
8. {2, 1, 3}
Grupos con Líder 3:
9. {3}
10. {3, 1}
11 {3, 2}
12. {3, 1, 2}
Entrada: N = 5
Salida: 80
Enfoque: Este problema se puede resolver utilizando el concepto de coeficientes binomiales y exponenciación modular . A continuación se presentan las observaciones a este enunciado del problema:
- El número de formas de seleccionar un líder entre N personas es C(N, 1) .
- Para cada líder podemos seleccionar un grupo de tamaño K donde 0 ≤ K ≤ N-1 para hacer el número posible de agrupamientos.
- Entonces, el número total de formas viene dado por el producto de N y la suma de los elementos de selección K de los elementos restantes (N – 1) como:
Vías Totales =
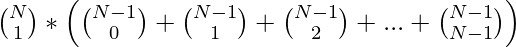
Usando el teorema binomial, la suma del coeficiente binomial se puede escribir como:
Por lo tanto, el número de formas de seleccionar grupos que tienen un solo líder es
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long mod = 1000000007;
// Function to find 2^x using
// modular exponentiation
int exponentMod(int A, int B)
{
// Base cases
if (A == 0)
return 0;
if (B == 0)
return 1;
// If B is even
long long y;
if (B % 2 == 0) {
y = exponentMod(A, B / 2);
y = (y * y) % mod;
}
// If B is odd
else {
y = A % mod;
y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1)
% mod)
% mod;
}
return (int)((y + mod) % mod);
}
// Function to count the number of
// ways to form the group having
// one leader
void countWays(int N)
{
// Find 2^(N-1) using modular
// exponentiation
long long select = exponentMod(2,
N - 1);
// Count total ways
long long ways
= ((N % mod)
* (select % mod));
ways %= mod;
// Print the total ways
cout << ways;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given N number of peoples
int N = 5;
// Function Call
countWays(N);
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static long mod = 1000000007;
// Function to find 2^x using
// modular exponentiation
static int exponentMod(int A, int B)
{
// Base cases
if (A == 0)
return 0;
if (B == 0)
return 1;
// If B is even
long y;
if (B % 2 == 0)
{
y = exponentMod(A, B / 2);
y = (y * y) % mod;
}
// If B is odd
else
{
y = A % mod;
y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1) %
mod) % mod;
}
return (int)((y + mod) % mod);
}
// Function to count the number of
// ways to form the group having
// one leader
static void countWays(int N)
{
// Find 2^(N-1) using modular
// exponentiation
long select = exponentMod(2, N - 1);
// Count total ways
long ways = ((N % mod) * (select % mod));
ways %= mod;
// Print the total ways
System.out.print(ways);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given N number of peoples
int N = 5;
// Function Call
countWays(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach mod = 1000000007 # Function to find 2^x using # modular exponentiation def exponentMod(A, B): # Base cases if (A == 0): return 0; if (B == 0): return 1; # If B is even y = 0; if (B % 2 == 0): y = exponentMod(A, B // 2); y = (y * y) % mod; # If B is odd else: y = A % mod; y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1) % mod) % mod; return ((y + mod) % mod); # Function to count the number of # ways to form the group having # one leader def countWays(N): # Find 2^(N-1) using modular # exponentiation select = exponentMod(2, N - 1); # Count total ways ways = ((N % mod) * (select % mod)); ways %= mod; # Print the total ways print(ways) # Driver code if __name__=='__main__': # Given N number of people N = 5; # Function call countWays(N); # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG{
static long mod = 1000000007;
// Function to find 2^x using
// modular exponentiation
static int exponentMod(int A, int B)
{
// Base cases
if (A == 0)
return 0;
if (B == 0)
return 1;
// If B is even
long y;
if (B % 2 == 0)
{
y = exponentMod(A, B / 2);
y = (y * y) % mod;
}
// If B is odd
else
{
y = A % mod;
y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1) %
mod) % mod;
}
return (int)((y + mod) % mod);
}
// Function to count the number of
// ways to form the group having
// one leader
static void countWays(int N)
{
// Find 2^(N-1) using modular
// exponentiation
long select = exponentMod(2, N - 1);
// Count total ways
long ways = ((N % mod) * (select % mod));
ways %= mod;
// Print the total ways
Console.Write(ways);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given N number of peoples
int N = 5;
// Function Call
countWays(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
let mod = 1000000007;
// Function to find 2^x using
// modular exponentiation
function exponentMod(A, B)
{
// Base cases
if (A == 0)
return 0;
if (B == 0)
return 1;
// If B is even
let y;
if (B % 2 == 0) {
y = exponentMod(A, B / 2);
y = (y * y) % mod;
}
// If B is odd
else {
y = A % mod;
y = (y * exponentMod(A, B - 1)
% mod)
% mod;
}
return ((y + mod) % mod);
}
// Function to count the number of
// ways to form the group having
// one leader
function countWays(N)
{
// Find 2^(N-1) using modular
// exponentiation
let select = exponentMod(2,
N - 1);
// Count total ways
let ways
= ((N % mod)
* (select % mod));
ways %= mod;
// Print the total ways
document.write(ways);
}
// Driver Code
// Given N number of peoples
let N = 5;
// Function Call
countWays(N);
// This code is contributed by Mayank Tyagi
</script>
80
Complejidad temporal: O(log N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por VikasVishwakarma1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA