Dados dos números enteros N y K , la tarea es contar los números hasta N dígitos de modo que no haya dos ceros adyacentes y el rango de dígitos sea de 0 a K-1.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 2, K = 3
Salida: 8
Explicación:
Hay 8 números tales que los dígitos son solo del 0 al 2, sin ningún 0 adyacente: {1, 2, 10, 11, 12, 20, 21, 22 }
Entrada: N = 3, K = 3
Salida: 22
Enfoque: La idea es utilizar Programación Dinámica para resolver este problema.
Sea DP[i][j] el número de números deseables hasta el i-ésimo dígito del número, y su último dígito como j .
Observaciones:
- El número de formas de llenar un lugar es
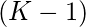
- Como sabemos, los ceros no pueden ser adyacentes. Entonces, cuando nuestro último elemento es 0, significa que el índice anterior se llena de 1 manera, es decir, 0. Por lo tanto, el lugar actual solo se puede llenar con (K-1) dígitos.
- Si el último lugar se llena con (K-1) dígitos, entonces el lugar del dígito actual se puede llenar con 0 o (K-1) dígitos.
Caso base:
- Si n == 1 y último == K, entonces podemos llenar este lugar con (K-1) dígitos, devolver (K-1)
- De lo contrario, devuelve 1
Relación de recurrencia:
Cuando el lugar del último dígito no se llena con cero, entonces
Cuando el lugar del último dígito se llena con cero, entonces
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dp[15][10];
// Function to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
int solve(int n, int last, int k)
{
// Condition to check if only
// one element remains
if (n == 1) {
// If last element is non
// zero, return K-1
if (last == k) {
return (k - 1);
}
// If last element is 0
else {
return 1;
}
}
// Condition to check if value
// calculated already
if (dp[n][last])
return dp[n][last];
// If last element is non zero,
// then two cases arise,
// current element can be either
// zero or non zero
if (last == k) {
// Memoize this case
return dp[n][last]
= (k - 1)
* solve(n - 1, k, k)
+ (k - 1)
* solve(n - 1, 1, k);
}
// If last is 0, then current
// can only be non zero
else {
// Memoize and return
return dp[n][last]
= solve(n - 1, k, k);
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given N and K
int n = 2, k = 3;
// Function Call
int x = solve(n, k, k)
+ solve(n, 1, k);
cout << x;
}
Java
// Java implementation to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
class GFG{
static int[][] dp = new int[15][10];
// Function to count the numbers
// upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
static int solve(int n, int last, int k)
{
// Condition to check if only
// one element remains
if (n == 1)
{
// If last element is non
// zero, return K-1
if (last == k)
{
return (k - 1);
}
// If last element is 0
else
{
return 1;
}
}
// Condition to check if
// value calculated already
if (dp[n][last] == 1)
return dp[n][last];
// If last element is non zero,
// then two cases arise, current
// element can be either zero
// or non zero
if (last == k)
{
// Memoize this case
return dp[n][last] = (k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, k, k) +
(k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, 1, k);
}
// If last is 0, then current
// can only be non zero
else
{
// Memoize and return
return dp[n][last] = solve(n - 1, k, k);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given N and K
int n = 2, k = 3;
// Function Call
int x = solve(n, k, k) +
solve(n, 1, k);
System.out.print(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ritik Bansal
Python3
# Python3 implementation to count the # numbers upto N digits such that # no two zeros are adjacent dp = [[0] * 10 for j in range(15)] # Function to count the numbers # upto N digits such that no two # zeros are adjacent def solve(n, last, k): # Condition to check if only # one element remains if (n == 1): # If last element is non # zero, return K-1 if (last == k): return (k - 1) # If last element is 0 else: return 1 # Condition to check if value # calculated already if (dp[n][last]): return dp[n][last] # If last element is non zero, # then two cases arise, current # element can be either zero or # non zero if (last == k): # Memoize this case dp[n][last] = ((k - 1) * solve(n - 1, k, k) + (k - 1) * solve(n - 1, 1, k)) return dp[n][last] # If last is 0, then current # can only be non zero else: # Memoize and return dp[n][last] = solve(n - 1, k, k) return dp[n][last] # Driver code # Given N and K n = 2 k = 3 # Function call x = solve(n, k, k) + solve(n, 1, k) print(x) # This code is contributed by himanshu77
C#
// C# implementation to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
using System;
class GFG{
public static int [,]dp = new int[15, 10];
// Function to count the numbers
// upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
public static int solve(int n, int last, int k)
{
// Condition to check if only
// one element remains
if (n == 1)
{
// If last element is non
// zero, return K-1
if (last == k)
{
return (k - 1);
}
// If last element is 0
else
{
return 1;
}
}
// Condition to check if
// value calculated already
if (dp[n, last] == 1)
return dp[n, last];
// If last element is non zero,
// then two cases arise, current
// element can be either zero
// or non zero
if (last == k)
{
// Memoize this case
return dp[n, last] = (k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, k, k) +
(k - 1) *
solve(n - 1, 1, k);
}
// If last is 0, then current
// can only be non zero
else
{
// Memoize and return
return dp[n, last] = solve(n - 1, k, k);
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Given N and K
int n = 2, k = 3;
// Function Call
int x = solve(n, k, k) +
solve(n, 1, k);
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
}
// This code is contributed by SoumikMondal
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
var dp = Array.from(Array(15),
() => Array(10).fill(0));
// Function to count the
// numbers upto N digits such that
// no two zeros are adjacent
function solve(n, last, k)
{
// Condition to check if only
// one element remains
if (n == 1) {
// If last element is non
// zero, return K-1
if (last == k) {
return (k - 1);
}
// If last element is 0
else {
return 1;
}
}
// Condition to check if value
// calculated already
if ((dp[n][last])!=0)
return dp[n][last];
// If last element is non zero,
// then two cases arise,
// current element can be either
// zero or non zero
if (last == k) {
// Memoize this case
return dp[n][last]
= (k - 1)
* solve(n - 1, k, k)
+ (k - 1)
* solve(n - 1, 1, k);
}
// If last is 0, then current
// can only be non zero
else {
// Memoize and return
dp[n][last]
= solve(n - 1, k, k);
return dp[n][last];
}
}
// Driver Code
// Given N and K
var n = 2, k = 3;
// Function Call
var x = solve(n, k, k)
+ solve(n, 1, k);
document.write(x);
</script>
8
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N*10)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por VikasVishwakarma1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA