Similitud Jaro
Jaro Similarity es la medida de similitud entre dos strings. El valor de la distancia de Jaro varía de 0 a 1, donde 1 significa que las strings son iguales y 0 significa que no hay similitud entre las dos strings.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: s1 = “CAJA”, s2 = “TRAZA”;
Salida: Similitud Jaro = 0.733333Entrada: s1 = “DwAyNE”, s2 = “DuANE”;
Salida: Similitud Jaro = 0.822222
Algoritmo:
La similitud de Jaro se calcula utilizando la siguiente fórmula
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[ Jaro\hspace{1mm}similarity\hspace{1mm}= \left \{ \begin{tabular}{cc} 0, if m=0\\ \[\cfrac{1}{3}\]\Big(\[\cfrac{m}{\big| s1 \big|}\] + \[\cfrac{m}{\big| s2 \big|}\]+\[\cfrac{m-t}{m}\]\Big), for m!=0 \end{tabular} } \]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1055eb185cac54888ab3f469fa70693c_l3.png)
dónde:
- m es el número de caracteres coincidentes
- t es la mitad del número de transposiciones
- donde |s1| y |s2| son las longitudes de las strings s1 y s2 respectivamente.
Se dice que los caracteres coinciden si son iguales y los caracteres no están más allá de 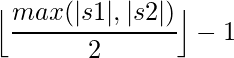
Las transposiciones son la mitad del número de caracteres coincidentes en ambas strings, pero en un orden diferente.
Cálculo:
- Sea s1=”arnab”, s2=”raanb”, por lo que la distancia máxima con la que se empareja cada carácter es 1.
- Es evidente que ambas strings tienen 5 caracteres coincidentes, pero el orden no es el mismo, por lo que el número de caracteres que no están en orden es 4, por lo que el número de transposiciones es 2.
- Por lo tanto, la similitud de Jaro se puede calcular de la siguiente manera:
Similitud de Jaro = (1/3) * {(5/5) + (5/5) + (5-2)/5 } = 0.86667
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ implementation of above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate the
// Jaro Similarity of two strings
double jaro_distance(string s1, string s2)
{
// If the strings are equal
if (s1 == s2)
return 1.0;
// Length of two strings
int len1 = s1.length(),
len2 = s2.length();
// Maximum distance upto which matching
// is allowed
int max_dist = floor(max(len1, len2) / 2) - 1;
// Count of matches
int match = 0;
// Hash for matches
int hash_s1[s1.length()] = { 0 },
hash_s2[s2.length()] = { 0 };
// Traverse through the first string
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++) {
// Check if there is any matches
for (int j = max(0, i - max_dist);
j < min(len2, i + max_dist + 1); j++)
// If there is a match
if (s1[i] == s2[j] && hash_s2[j] == 0) {
hash_s1[i] = 1;
hash_s2[j] = 1;
match++;
break;
}
}
// If there is no match
if (match == 0)
return 0.0;
// Number of transpositions
double t = 0;
int point = 0;
// Count number of occurrences
// where two characters match but
// there is a third matched character
// in between the indices
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
if (hash_s1[i]) {
// Find the next matched character
// in second string
while (hash_s2[point] == 0)
point++;
if (s1[i] != s2[point++])
t++;
}
t /= 2;
// Return the Jaro Similarity
return (((double)match) / ((double)len1)
+ ((double)match) / ((double)len2)
+ ((double)match - t) / ((double)match))
/ 3.0;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
string s1 = "CRATE", s2 = "TRACE";
// Print jaro Similarity of two strings
cout << jaro_distance(s1, s2) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of above approach
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate the
// Jaro Similarity of two Strings
static double jaro_distance(String s1, String s2)
{
// If the Strings are equal
if (s1 == s2)
return 1.0;
// Length of two Strings
int len1 = s1.length(),
len2 = s2.length();
// Maximum distance upto which matching
// is allowed
int max_dist = (int) (Math.floor(Math.max(len1, len2) / 2) - 1);
// Count of matches
int match = 0;
// Hash for matches
int hash_s1[] = new int[s1.length()];
int hash_s2[] = new int[s2.length()];
// Traverse through the first String
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
{
// Check if there is any matches
for (int j = Math.max(0, i - max_dist);
j < Math.min(len2, i + max_dist + 1); j++)
// If there is a match
if (s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(j) && hash_s2[j] == 0)
{
hash_s1[i] = 1;
hash_s2[j] = 1;
match++;
break;
}
}
// If there is no match
if (match == 0)
return 0.0;
// Number of transpositions
double t = 0;
int point = 0;
// Count number of occurrences
// where two characters match but
// there is a third matched character
// in between the indices
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
if (hash_s1[i] == 1)
{
// Find the next matched character
// in second String
while (hash_s2[point] == 0)
point++;
if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(point++) )
t++;
}
t /= 2;
// Return the Jaro Similarity
return (((double)match) / ((double)len1)
+ ((double)match) / ((double)len2)
+ ((double)match - t) / ((double)match))
/ 3.0;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String s1 = "CRATE", s2 = "TRACE";
// Print jaro Similarity of two Strings
System.out.print(jaro_distance(s1, s2) +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python3
# Python3 implementation of above approach from math import floor, ceil # Function to calculate the # Jaro Similarity of two s def jaro_distance(s1, s2): # If the s are equal if (s1 == s2): return 1.0 # Length of two s len1 = len(s1) len2 = len(s2) # Maximum distance upto which matching # is allowed max_dist = floor(max(len1, len2) / 2) - 1 # Count of matches match = 0 # Hash for matches hash_s1 = [0] * len(s1) hash_s2 = [0] * len(s2) # Traverse through the first for i in range(len1): # Check if there is any matches for j in range(max(0, i - max_dist), min(len2, i + max_dist + 1)): # If there is a match if (s1[i] == s2[j] and hash_s2[j] == 0): hash_s1[i] = 1 hash_s2[j] = 1 match += 1 break # If there is no match if (match == 0): return 0.0 # Number of transpositions t = 0 point = 0 # Count number of occurrences # where two characters match but # there is a third matched character # in between the indices for i in range(len1): if (hash_s1[i]): # Find the next matched character # in second while (hash_s2[point] == 0): point += 1 if (s1[i] != s2[point]): t += 1 point += 1 t = t//2 # Return the Jaro Similarity return (match/ len1 + match / len2 + (match - t) / match)/ 3.0 # Driver code s1 = "CRATE" s2 = "TRACE" # Prjaro Similarity of two s print(round(jaro_distance(s1, s2),6)) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# implementation of above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate the
// Jaro Similarity of two Strings
static double jaro_distance(string s1, string s2)
{
// If the Strings are equal
if (s1 == s2)
return 1.0;
// Length of two Strings
int len1 = s1.Length ;
int len2 = s2.Length;
// Maximum distance upto which matching
// is allowed
int max_dist = (int)(Math.Floor((double)(
(Math.Max(len1, len2) / 2) - 1)));
// Count of matches
int match = 0;
// Hash for matches
int []hash_s1 = new int[s1.Length];
int []hash_s2 = new int[s2.Length];
// Traverse through the first String
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
{
// Check if there is any matches
for (int j = Math.Max(0, i - max_dist);
j < Math.Min(len2, i + max_dist + 1); j++)
// If there is a match
if (s1[i] == s2[j] && hash_s2[j] == 0)
{
hash_s1[i] = 1;
hash_s2[j] = 1;
match++;
break;
}
}
// If there is no match
if (match == 0)
return 0.0;
// Number of transpositions
double t = 0;
int point = 0;
// Count number of occurrences
// where two characters match but
// there is a third matched character
// in between the indices
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
if (hash_s1[i] == 1)
{
// Find the next matched character
// in second String
while (hash_s2[point] == 0)
point++;
if (s1[i] != s2[point++] )
t++;
}
t /= 2;
// Return the Jaro Similarity
return (((double)match) / ((double)len1)
+ ((double)match) / ((double)len2)
+ ((double)match - t) / ((double)match))
/ 3.0;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
string s1 = "CRATE", s2 = "TRACE";
// Print jaro Similarity of two Strings
Console.WriteLine(jaro_distance(s1, s2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of above approach
// Function to calculate the
// Jaro Similarity of two strings
function jaro_distance(s1, s2)
{
// If the strings are equal
if (s1 == s2)
return 1.0;
// Length of two strings
var len1 = s1.length,
len2 = s2.length;
// Maximum distance upto which matching
// is allowed
var max_dist = Math.floor(Math.max(len1, len2) / 2) - 1;
// Count of matches
var match = 0;
// Hash for matches
var hash_s1 = Array(s1.length).fill(0);
var hash_s2 = Array(s1.length).fill(0);
// Traverse through the first string
for (var i = 0; i < len1; i++) {
// Check if there is any matches
for (var j = Math.max(0, i - max_dist);
j < Math.min(len2, i + max_dist + 1); j++)
// If there is a match
if (s1[i] == s2[j] && hash_s2[j] == 0) {
hash_s1[i] = 1;
hash_s2[j] = 1;
match++;
break;
}
}
// If there is no match
if (match == 0)
return 0.0;
// Number of transpositions
var t = 0;
var point = 0;
// Count number of occurrences
// where two characters match but
// there is a third matched character
// in between the indices
for (var i = 0; i < len1; i++)
if (hash_s1[i]) {
// Find the next matched character
// in second string
while (hash_s2[point] == 0)
point++;
if (s1[i] != s2[point++])
t++;
}
t /= 2;
// Return the Jaro Similarity
return ((match) / (len1)
+ (match) / (len2)
+ (match - t) / (match))
/ 3.0;
}
// Driver code
var s1 = "CRATE", s2 = "TRACE";
// Print jaro Similarity of two strings
document.write( jaro_distance(s1, s2).toFixed(5));
</script>
0.733333
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N * M), donde N es la longitud de la string s1 y M es la longitud de la string s2.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N + M)
Similitud de Jaro-Winkler
La similitud de Jaro-Winkler es una métrica de string que mide la distancia de edición entre dos strings. Jaro – Winkler Similarity es muy similar a Jaro Similarity. Ambos difieren cuando el prefijo de dos strings coincide. Jaro – Winkler Similarity utiliza una escala de prefijo ‘p’ que da una respuesta más precisa cuando las strings tienen un prefijo común hasta una longitud máxima definida l.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: s1 = “DwAyNE”, s2 = “DuANE”;
Salida: Similitud Jaro-Winkler =0.84Entrada: s1=”TRATAR”, s2=”RASTREO”;
Salida: similitud Jaro-Winkler = 0,906667
Cálculo:
- La similitud de Jaro Winkler se define de la siguiente manera
Sw = Sj + P * L * (1 – Sj)
donde,- Sj, es jaro similitud
- Sw, es la similitud jaro-winkler
- P es el factor de escala (0.1 por defecto)
- L es la longitud del prefijo coincidente hasta un máximo de 4 caracteres.
- Sea s1=”arnab”, s2=”aranb”. La similitud de Jaro de las dos strings es 0,933333 (del cálculo anterior).
- La longitud del prefijo coincidente es 2 y tomamos el factor de escala como 0,1.
- Sustituyendo en la fórmula;
Similitud Jaro-Winkler = 0,9333333 + 0,1 * 2 * (1-0,9333333) = 0,946667
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ implementation of above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate the
// Jaro Similarity of two strings
double jaro_distance(string s1, string s2)
{
// If the strings are equal
if (s1 == s2)
return 1.0;
// Length of two strings
int len1 = s1.length(),
len2 = s2.length();
if (len1 == 0 || len2 == 0)
return 0.0;
// Maximum distance upto which matching
// is allowed
int max_dist = floor(max(len1, len2) / 2) - 1;
// Count of matches
int match = 0;
// Hash for matches
int hash_s1[s1.length()] = { 0 },
hash_s2[s2.length()] = { 0 };
// Traverse through the first string
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++) {
// Check if there is any matches
for (int j = max(0, i - max_dist);
j < min(len2, i + max_dist + 1); j++)
// If there is a match
if (s1[i] == s2[j] && hash_s2[j] == 0) {
hash_s1[i] = 1;
hash_s2[j] = 1;
match++;
break;
}
}
// If there is no match
if (match == 0)
return 0.0;
// Number of transpositions
double t = 0;
int point = 0;
// Count number of occurrences
// where two characters match but
// there is a third matched character
// in between the indices
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
if (hash_s1[i]) {
// Find the next matched character
// in second string
while (hash_s2[point] == 0)
point++;
if (s1[i] != s2[point++])
t++;
}
t /= 2;
// Return the Jaro Similarity
return (((double)match) / ((double)len1)
+ ((double)match) / ((double)len2)
+ ((double)match - t) / ((double)match))
/ 3.0;
}
// Jaro Winkler Similarity
double jaro_Winkler(string s1, string s2)
{
double jaro_dist = jaro_distance(s1, s2);
// If the jaro Similarity is above a threshold
if (jaro_dist > 0.7) {
// Find the length of common prefix
int prefix = 0;
for (int i = 0;
i < min(s1.length(), s2.length()); i++) {
// If the characters match
if (s1[i] == s2[i])
prefix++;
// Else break
else
break;
}
// Maximum of 4 characters are allowed in prefix
prefix = min(4, prefix);
// Calculate jaro winkler Similarity
jaro_dist += 0.1 * prefix * (1 - jaro_dist);
}
return jaro_dist;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
string s1 = "TRATE", s2 = "TRACE";
// Print Jaro-Winkler Similarity of two strings
cout << "Jaro-Winkler Similarity ="
<< jaro_Winkler(s1, s2) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of above approach
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate the
// Jaro Similarity of two strings
static double jaro_distance(String s1, String s2)
{
// If the strings are equal
if (s1 == s2)
return 1.0;
// Length of two strings
int len1 = s1.length(),
len2 = s2.length();
if (len1 == 0 || len2 == 0)
return 0.0;
// Maximum distance upto which matching
// is allowed
int max_dist = (int)Math.floor(Math.max(len1, len2) / 2) - 1;
// Count of matches
int match = 0;
// Hash for matches
int hash_s1[] = new int [s1.length()];
int hash_s2[] = new int[s2.length()];
// Traverse through the first string
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
{
// Check if there is any matches
for (int j = Math.max(0, i - max_dist);
j < Math.min(len2, i + max_dist + 1); j++)
// If there is a match
if (s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(j) &&
hash_s2[j] == 0)
{
hash_s1[i] = 1;
hash_s2[j] = 1;
match++;
break;
}
}
// If there is no match
if (match == 0)
return 0.0;
// Number of transpositions
double t = 0;
int point = 0;
// Count number of occurrences
// where two characters match but
// there is a third matched character
// in between the indices
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
if (hash_s1[i] == 1)
{
// Find the next matched character
// in second string
while (hash_s2[point] == 0)
point++;
if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(point++))
t++;
}
t /= 2;
// Return the Jaro Similarity
return (((double)match) / ((double)len1)
+ ((double)match) / ((double)len2)
+ ((double)match - t) / ((double)match))
/ 3.0;
}
// Jaro Winkler Similarity
static double jaro_Winkler(String s1, String s2)
{
double jaro_dist = jaro_distance(s1, s2);
// If the jaro Similarity is above a threshold
if (jaro_dist > 0.7)
{
// Find the length of common prefix
int prefix = 0;
for (int i = 0;
i < Math.min(s1.length(), s2.length()); i++)
{
// If the characters match
if (s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(i))
prefix++;
// Else break
else
break;
}
// Maximum of 4 characters are allowed in prefix
prefix = Math.min(4, prefix);
// Calculate jaro winkler Similarity
jaro_dist += 0.1 * prefix * (1 - jaro_dist);
}
return jaro_dist;
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
String s1 = "TRATE", s2 = "TRACE";
// Print Jaro-Winkler Similarity of two strings
System.out.println("Jaro-Winkler Similarity =" +
jaro_Winkler(s1, s2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
Python3
# Python3 implementation of above approach
from math import floor
# Function to calculate the
# Jaro Similarity of two strings
def jaro_distance(s1, s2) :
# If the strings are equal
if (s1 == s2) :
return 1.0;
# Length of two strings
len1 = len(s1);
len2 = len(s2);
if (len1 == 0 or len2 == 0) :
return 0.0;
# Maximum distance upto which matching
# is allowed
max_dist = (max(len(s1), len(s2)) // 2 ) - 1;
# Count of matches
match = 0;
# Hash for matches
hash_s1 = [0] * len(s1) ;
hash_s2 = [0] * len(s2) ;
# Traverse through the first string
for i in range(len1) :
# Check if there is any matches
for j in range( max(0, i - max_dist),
min(len2, i + max_dist + 1)) :
# If there is a match
if (s1[i] == s2[j] and hash_s2[j] == 0) :
hash_s1[i] = 1;
hash_s2[j] = 1;
match += 1;
break;
# If there is no match
if (match == 0) :
return 0.0;
# Number of transpositions
t = 0;
point = 0;
# Count number of occurrences
# where two characters match but
# there is a third matched character
# in between the indices
for i in range(len1) :
if (hash_s1[i]) :
# Find the next matched character
# in second string
while (hash_s2[point] == 0) :
point += 1;
if (s1[i] != s2[point]) :
point += 1;
t += 1;
else :
point += 1;
t /= 2;
# Return the Jaro Similarity
return ((match / len1 + match / len2 +
(match - t) / match ) / 3.0);
# Jaro Winkler Similarity
def jaro_Winkler(s1, s2) :
jaro_dist = jaro_distance(s1, s2);
# If the jaro Similarity is above a threshold
if (jaro_dist > 0.7) :
# Find the length of common prefix
prefix = 0;
for i in range(min(len(s1), len(s2))) :
# If the characters match
if (s1[i] == s2[i]) :
prefix += 1;
# Else break
else :
break;
# Maximum of 4 characters are allowed in prefix
prefix = min(4, prefix);
# Calculate jaro winkler Similarity
jaro_dist += 0.1 * prefix * (1 - jaro_dist);
return jaro_dist;
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
s1 = "TRATE"; s2 = "TRACE";
# Print Jaro-Winkler Similarity of two strings
print("Jaro-Winkler Similarity =", jaro_Winkler(s1, s2)) ;
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
C#
// C# implementation of above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to calculate the
// Jaro Similarity of two strings
static double jaro_distance(string s1, string s2)
{
// If the strings are equal
if (s1 == s2)
return 1.0;
// Length of two strings
int len1 = s1.Length,
len2 = s2.Length;
if (len1 == 0 || len2 == 0)
return 0.0;
// Maximum distance upto which matching
// is allowed
int max_dist = (int)Math.Floor((double)
Math.Max(len1, len2) / 2) - 1;
// Count of matches
int match = 0;
// Hash for matches
int []hash_s1 = new int [s1.Length];
int []hash_s2 = new int[s2.Length];
// Traverse through the first string
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
{
// Check if there is any matches
for (int j = Math.Max(0, i - max_dist);
j < Math.Min(len2, i + max_dist + 1); j++)
// If there is a match
if (s1[i] == s2[j] &&
hash_s2[j] == 0)
{
hash_s1[i] = 1;
hash_s2[j] = 1;
match++;
break;
}
}
// If there is no match
if (match == 0)
return 0.0;
// Number of transpositions
double t = 0;
int point = 0;
// Count number of occurrences
// where two characters match but
// there is a third matched character
// in between the indices
for (int i = 0; i < len1; i++)
if (hash_s1[i] == 1)
{
// Find the next matched character
// in second string
while (hash_s2[point] == 0)
point++;
if (s1[i] != s2[point++])
t++;
}
t /= 2;
// Return the Jaro Similarity
return (((double)match) / ((double)len1)
+ ((double)match) / ((double)len2)
+ ((double)match - t) / ((double)match))
/ 3.0;
}
// Jaro Winkler Similarity
static double jaro_Winkler(string s1, string s2)
{
double jaro_dist = jaro_distance(s1, s2);
// If the jaro Similarity is above a threshold
if (jaro_dist > 0.7)
{
// Find the length of common prefix
int prefix = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Math.Min(s1.Length,
s2.Length); i++)
{
// If the characters match
if (s1[i] == s2[i])
prefix++;
// Else break
else
break;
}
// Maximum of 4 characters are allowed in prefix
prefix = Math.Min(4, prefix);
// Calculate jaro winkler Similarity
jaro_dist += 0.1 * prefix * (1 - jaro_dist);
}
return jaro_dist;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main ()
{
string s1 = "TRATE", s2 = "TRACE";
// Print Jaro-Winkler Similarity of two strings
Console.WriteLine("Jaro-Winkler Similarity =" +
jaro_Winkler(s1, s2));
}
}
// This code is contributed by AnkitRai01
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript implementation of above approach
// Function to calculate the
// Jaro Similarity of two strings
function jaro_distance(s1, s2)
{
// If the strings are equal
if (s1 == s2)
return 1.0;
// Length of two strings
let len1 = s1.length, len2 = s2.length;
if (len1 == 0 || len2 == 0)
return 0.0;
// Maximum distance upto which matching
// is allowed
let max_dist = Math.floor(Math.max(len1, len2) / 2) - 1;
// Count of matches
let match = 0;
// Hash for matches
let hash_s1 = new Array(s1.length);
hash_s1.fill(0);
let hash_s2 = new Array(s2.length);
hash_s2.fill(0);
// Traverse through the first string
for (let i = 0; i < len1; i++)
{
// Check if there is any matches
for (let j = Math.max(0, i - max_dist);
j < Math.min(len2, i + max_dist + 1); j++)
// If there is a match
if (s1[i] == s2[j] &&
hash_s2[j] == 0)
{
hash_s1[i] = 1;
hash_s2[j] = 1;
match++;
break;
}
}
// If there is no match
if (match == 0)
return 0.0;
// Number of transpositions
let t = 0;
let point = 0;
// Count number of occurrences
// where two characters match but
// there is a third matched character
// in between the indices
for (let i = 0; i < len1; i++)
if (hash_s1[i] == 1)
{
// Find the next matched character
// in second string
while (hash_s2[point] == 0)
point++;
if (s1[i] != s2[point++])
t++;
}
t /= 2;
// Return the Jaro Similarity
return ((match) / (len1)
+ (match) / (len2)
+ (match - t) / (match))
/ 3.0;
}
// Jaro Winkler Similarity
function jaro_Winkler(s1, s2)
{
let jaro_dist = jaro_distance(s1, s2);
// If the jaro Similarity is above a threshold
if (jaro_dist > 0.7)
{
// Find the length of common prefix
let prefix = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < Math.min(s1.length,s2.length); i++)
{
// If the characters match
if (s1[i] == s2[i])
prefix++;
// Else break
else
break;
}
// Maximum of 4 characters are allowed in prefix
prefix = Math.min(4, prefix);
// Calculate jaro winkler Similarity
jaro_dist += 0.1 * prefix * (1 - jaro_dist);
}
return jaro_dist.toFixed(6);
}
let s1 = "TRATE", s2 = "TRACE";
// Print Jaro-Winkler Similarity of two strings
document.write("Jaro-Winkler Similarity =" +
jaro_Winkler(s1, s2));
</script>
Jaro-Winkler Similarity =0.906667
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N * M), donde N es la longitud de la string s1 y M es la longitud de la string s2.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N + M)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por andrew1234 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA