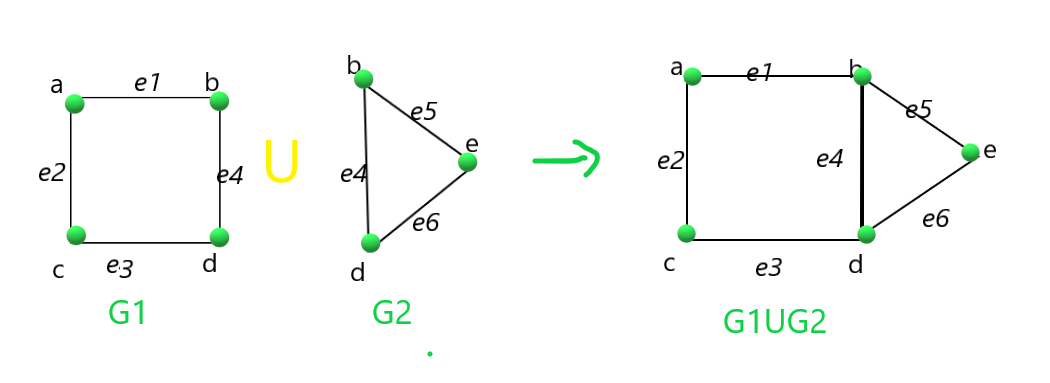
Dados dos gráficos G1 y G2 , la tarea es encontrar la unión y la intersección de los dos gráficos dados, es decir, (G1 ∪ G2) y (G1 ∩ G2) .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: G1 = { («e1», 1, 2), («e2», 1, 3), («e3», 3, 4), («e4», 2, 4) }, G2 = = { (“e4”, 2, 4), (“e5”, 2, 5), (“e6”, 4, 5) }
Salida:
G1 unión G2 es
e1 1 2
e2 1 3
e3 3 4
e4 2 4
e5 2 5
e6 4 5G1 intersección G2 es
e4 2 4
Explicación:
Unión de las gráficas G1 y G2:Intersección de las gráficas G1 y G2:
Enfoque: siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Defina una función, digamos Union(G1, G2) , para encontrar la unión de G1 y G2 :
- Inicialice un mapa , digamos added , que almacena si ya se ha agregado un borde o no.
- Iterar sobre los bordes del gráfico G1 y empujar todos los bordes en un gráfico, digamos G , y marcar todos los bordes visitados en added .
- Ahora, recorra nuevamente los bordes del gráfico G2 y empuje el borde en la G si el borde aún no se ha agregado, y luego marque el borde agregado en el mapa agregado.
- Defina una función, digamos Intersección (G1, G2) para encontrar la Intersección de G1 y G2 :
- Inicialice un mapa , digamos added , que almacena si ya se ha agregado un borde o no.
- Recorra los bordes del gráfico G1 y marque todos los bordes visitados en el mapa agregado.
- Ahora, vuelva a atravesar los bordes del gráfico G2 y empuje el borde en el gráfico G , si el borde ya se ha agregado. Luego, marque el borde agregado en el mapa.
- Ahora imprima las gráficas obtenidas después de la llamada a la función Unión(G1, G2) e Intersección(G1, G2) .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++14
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find union of two graphs
void find_union(
vector<tuple<string, int, int> > G1,
vector<tuple<string, int, int> > G2)
{
// Stores an edge of the graph G1
map<string, pair<int, int> > added;
// Stores the unioun graph G1
vector<tuple<string, int, int> > G;
// Iterate over the edges
// of the graph G1
for (auto p : G1) {
string a = get<0>(p);
// Get the edges
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
// Insert the current
// edges into graph G
G.push_back(
make_tuple(a, b, c));
added[a] = { b, c };
}
// Iterate over the edges
// of the graph G1
for (auto p : G2) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
pair<int, int> x = { b, c };
pair<int, int> y = { c, b };
// If either edge x or
// y is already added
if (added[a] == x || added[a] == y)
continue;
// Otherwise
G.push_back(make_tuple(a, b, c));
}
// Print the unioun
cout << "G1 union G2 is\n";
for (auto p : G) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
cout << a << " " << b << " "
<< c << endl;
}
}
// Function to find intersection of two graphs
void find_intersection(
vector<tuple<string, int, int> > G1,
vector<tuple<string, int, int> > G2)
{
// Stores an edge
map<string, pair<int, int> > added;
// Stores the graph of intersection
vector<tuple<string, int, int> > G;
// Iterate over edges of graph G1
for (auto p : G1) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
added[a] = { b, c };
}
// Iterate over edges of graph G2
for (auto p : G2) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
pair<int, int> x = { b, c };
pair<int, int> y = { c, b };
// If either edge x or
// y is already added
if (added[a] == x || added[a] == y)
G.push_back(make_tuple(a, b, c));
}
// Print the graph G
cout << "G1 intersection G2 is\n";
for (auto p : G) {
string a = get<0>(p);
int b = get<1>(p);
int c = get<2>(p);
cout << a << " " << b
<< " " << c << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
vector<tuple<string, int, int> > G1
= { make_tuple("e1", 1, 2),
make_tuple("e2", 1, 3),
make_tuple("e3", 3, 4),
make_tuple("e4", 2, 4) };
vector<tuple<string, int, int> > G2
= { make_tuple("e4", 2, 4),
make_tuple("e5", 2, 5),
make_tuple("e6", 4, 5) };
// Function call for finding the
// Union of the given graph
find_union(G1, G2);
// Function call for finding the
// Intersection of the given graph
find_intersection(G1, G2);
return 0;
}
G1 union G2 is e1 1 2 e2 1 3 e3 3 4 e4 2 4 e5 2 5 e6 4 5 G1 intersection G2 is e4 2 4
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N * log(N))
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Stream_Cipher y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA