Los números de Fibonacci son los números en la siguiente secuencia de enteros.
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, ……..
En términos matemáticos, la secuencia Fn de los números de Fibonacci está definida por la relación de recurrencia
Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2
con valores semilla
F0 = 0 and F1 = 1.
Dado un número n, imprime el n-ésimo número de Fibonacci.
Ejemplos:
Input : n = 2 Output : 1 Input : n = 9 Output : 34
Escriba una función int fib(int n) que devuelva F n . Por ejemplo, si n = 0, entonces fib() debería devolver 0. Si n = 1, debería devolver 1. Para n > 1, debería devolver F n-1 + F n-2
For n = 9 Output:34
Los siguientes son diferentes métodos para obtener el n-ésimo número de Fibonacci.
Método 1 (Usar recursión)
Un método simple que es una relación de recurrencia matemática de implementación recursiva directa se da arriba.
C++
//Fibonacci Series using Recursion
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(n);
getchar();
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed
// by Akanksha Rai
C
//Fibonacci Series using Recursion
#include<stdio.h>
int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
//Fibonacci Series using Recursion
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python3
#This code gives nth number in fibonacci series - {0,1,1,2,3,5,......}.
def fibonacci(n, second_last, last):
if n-1 == 0:
return second_last
else:
new_last = second_last + last
second_last = last
return fibonacci(n-1, second_last, new_last)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(fibonacci(10, 0, 1))
# This code is contributed by Manan Tyagi.
C#
// C# program for Fibonacci Series
// using Recursion
using System;
public class GFG
{
public static int Fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
{
return n;
}
else
{
return Fib(n - 1) + Fib(n - 2);
}
}
// driver code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 9;
Console.Write(Fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
PHP
<?php
// Fibonacci Series
// using Recursion
// function returns
// the Fibonacci number
function fib($n)
{
if ($n <= 1)
return $n;
return fib($n - 1) +
fib($n - 2);
}
// Driver Code
$n = 9;
echo fib($n);
// This code is contributed by aj_36
?>
Javascript
<script>
//Fibonacci Series using Recursion
let n = 9;
// function returns the Fibonacci number
function fib(n) {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}
//function call
document.write(fib(n));
//This code is contributed by Surbhi Tyagi
</script>
34
Complejidad temporal: Exponencial, ya que toda función llama a otras dos funciones.
Si se implementara el árbol de recursión original, este habría sido el árbol, pero ahora, por n veces, se llama a la función de recursión
Árbol original para recursividad
fib(5)
/ \
fib(4) fib(3)
/ \ / \
fib(3) fib(2) fib(2) fib(1)
/ \ / \ / \
fib(2) fib(1) fib(1) fib(0) fib(1) fib(0)
/ \
fib(1) fib(0)
Árbol optimizado para recursividad para el código anterior
mentira(5)
mentira(4)
mentira(3)
mentira(2)
mentira(1)
Espacio extra: O(n) si consideramos el tamaño de la pila de llamadas de función, de lo contrario O(1).
Método 2 (Usar programación dinámica)
Podemos evitar el trabajo repetido realizado en el método 1 almacenando los números de Fibonacci calculados hasta ahora.
C++
// C++ program for Fibonacci Series
// using Dynamic Programming
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class GFG{
public:
int fib(int n)
{
// Declare an array to store
// Fibonacci numbers.
// 1 extra to handle
// case, n = 0
int f[n + 2];
int i;
// 0th and 1st number of the
// series are 0 and 1
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
//Add the previous 2 numbers
// in the series and store it
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[n];
}
};
// Driver code
int main ()
{
GFG g;
int n = 9;
cout << g.fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by SoumikMondal
C
//Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
#include<stdio.h>
int fib(int n)
{
/* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */
int f[n+2]; // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series
and store it */
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
/* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */
int f[] = new int[n+2]; // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series
and store it */
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python3
# Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming def fibonacci(n): # Taking 1st two fibonacci numbers as 0 and 1 f = [0, 1] for i in range(2, n+1): f.append(f[i-1] + f[i-2]) return f[n] print(fibonacci(9))
C#
// C# program for Fibonacci Series
// using Dynamic Programming
using System;
class fibonacci {
static int fib(int n)
{
// Declare an array to
// store Fibonacci numbers.
// 1 extra to handle
// case, n = 0
int []f = new int[n + 2];
int i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the
series are 0 and 1 */
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers
in the series and store it */
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i - 2];
}
return f[n];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 9;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
PHP
<?php
//Fibonacci Series using Dynamic
// Programming
function fib( $n)
{
/* Declare an array to store
Fibonacci numbers. */
// 1 extra to handle case,
// n = 0
$f = array();
$i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the
series are 0 and 1*/
$f[0] = 0;
$f[1] = 1;
for ($i = 2; $i <= $n; $i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2
numbers in the series
and store it */
$f[$i] = $f[$i-1] + $f[$i-2];
}
return $f[$n];
}
$n = 9;
echo fib($n);
// This code is contributed by
// anuj_67.
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Fibonacci Series using Dynamic Programming
function fib(n)
{
/* Declare an array to store Fibonacci numbers. */
let f = new Array(n+2); // 1 extra to handle case, n = 0
let i;
/* 0th and 1st number of the series are 0 and 1*/
f[0] = 0;
f[1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
/* Add the previous 2 numbers in the series
and store it */
f[i] = f[i-1] + f[i-2];
}
return f[n];
}
let n=9;
document.write(fib(n));
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
34
Método 3 (Método 2 optimizado para el espacio)
Podemos optimizar el espacio utilizado en el método 2 almacenando los dos números anteriores solo porque eso es todo lo que necesitamos para obtener el siguiente número de Fibonacci en serie.
C++
// Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c, i;
if( n == 0)
return a;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Code_Mech
C
// Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method
#include<stdio.h>
int fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c, i;
if( n == 0)
return a;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for Fibonacci Series using Space
// Optimized Method
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c;
if (n == 0)
return a;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Mihir Joshi
Python3
# Function for nth fibonacci number - Space Optimisation
# Taking 1st two fibonacci numbers as 0 and 1
def fibonacci(n):
a = 0
b = 1
if n < 0:
print("Incorrect input")
elif n == 0:
return a
elif n == 1:
return b
else:
for i in range(2,n+1):
c = a + b
a = b
b = c
return b
# Driver Program
print(fibonacci(9))
#This code is contributed by Saket Modi
C#
// C# program for Fibonacci Series
// using Space Optimized Method
using System;
namespace Fib
{
public class GFG
{
static int Fib(int n)
{
int a = 0, b = 1, c = 0;
// To return the first Fibonacci number
if (n == 0) return a;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
// Driver function
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 9;
Console.Write("{0} ", Fib(n));
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.
PHP
<?php
// PHP program for Fibonacci Series
// using Space Optimized Method
function fib( $n)
{
$a = 0;
$b = 1;
$c;
$i;
if( $n == 0)
return $a;
for($i = 2; $i <= $n; $i++)
{
$c = $a + $b;
$a = $b;
$b = $c;
}
return $b;
}
// Driver Code
$n = 9;
echo fib($n);
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for Fibonacci Series using Space Optimized Method
function fib(n)
{
let a = 0, b = 1, c, i;
if( n == 0)
return a;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return b;
}
// Driver code
let n = 9;
document.write(fib(n));
// This code is contributed by Mayank Tyagi
</script>
34
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n)
Espacio extra: O(1)
Método 4 (usando la potencia de la array {{1, 1}, {1, 0}})
Este otro O(n) que se basa en el hecho de que si multiplicamos n veces la array M = {{1,1}, {1,0}} a sí mismo (en otras palabras, calcule la potencia (M, n)), luego obtenemos el (n+1)-ésimo número de Fibonacci como el elemento en la fila y la columna (0, 0) en la array resultante.
La representación matricial da la siguiente expresión cerrada para los números de Fibonacci:
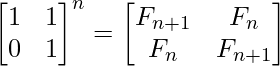
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Helper function that multiplies 2
// matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
// puts the multiplication result
// back to F[][]
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
// Helper function that calculates F[][]
// raise to the power n and puts the
// result in F[][]
// Note that this function is designed
// only for fib() and won't work as
// general power function
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 1, 0 } };
// n - 1 times multiply the
// matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << " " << fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C
#include <stdio.h>
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
/* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the
result in F[][]
Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general
power function */
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
int i;
int M[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
class fibonacci
{
static int fib(int n)
{
int F[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
/* Helper function that multiplies 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
puts the multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Helper function that calculates F[][] raise to the power n and puts the
result in F[][]
Note that this function is designed only for fib() and won't work as general
power function */
static void power(int F[][], int n)
{
int i;
int M[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python3
# Helper function that multiplies
# 2 matrices F and M of size 2*2,
# and puts the multiplication
# result back to F[][]
# Helper function that calculates
# F[][] raise to the power n and
# puts the result in F[][]
# Note that this function is
# designed only for fib() and
# won't work as general
# power function
def fib(n):
F = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]]
if (n == 0):
return 0
power(F, n - 1)
return F[0][0]
def multiply(F, M):
x = (F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0])
y = (F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1])
z = (F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0])
w = (F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1])
F[0][0] = x
F[0][1] = y
F[1][0] = z
F[1][1] = w
def power(F, n):
M = [[1, 1],
[1, 0]]
# n - 1 times multiply the
# matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for i in range(2, n + 1):
multiply(F, M)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 9
print(fib(n))
# This code is contributed
# by ChitraNayal
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int fib(int n)
{
int [,]F = new int[,] {{1, 1},
{1, 0} };
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0,0];
}
/* Helper function that multiplies 2
matrices F and M of size 2*2, and puts
the multiplication result back to F[][] */
static void multiply(int [,]F, int [,]M)
{
int x = F[0,0]*M[0,0] + F[0,1]*M[1,0];
int y = F[0,0]*M[0,1] + F[0,1]*M[1,1];
int z = F[1,0]*M[0,0] + F[1,1]*M[1,0];
int w = F[1,0]*M[0,1] + F[1,1]*M[1,1];
F[0,0] = x;
F[0,1] = y;
F[1,0] = z;
F[1,1] = w;
}
/* Helper function that calculates F[][]
raise to the power n and puts the result
in F[][] Note that this function is designed
only for fib() and won't work as general
power function */
static void power(int [,]F, int n)
{
int i;
int [,]M = new int[,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0} };
// n - 1 times multiply the matrix to
// {{1,0},{0,1}}
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 9;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
PHP
<?php
function fib($n)
{
$F = array(array(1, 1),
array(1, 0));
if ($n == 0)
return 0;
power($F, $n - 1);
return $F[0][0];
}
function multiply(&$F, &$M)
{
$x = $F[0][0] * $M[0][0] +
$F[0][1] * $M[1][0];
$y = $F[0][0] * $M[0][1] +
$F[0][1] * $M[1][1];
$z = $F[1][0] * $M[0][0] +
$F[1][1] * $M[1][0];
$w = $F[1][0] * $M[0][1] +
$F[1][1] * $M[1][1];
$F[0][0] = $x;
$F[0][1] = $y;
$F[1][0] = $z;
$F[1][1] = $w;
}
function power(&$F, $n)
{
$M = array(array(1, 1),
array(1, 0));
// n - 1 times multiply the
// matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for ($i = 2; $i <= $n; $i++)
multiply($F, $M);
}
// Driver Code
$n = 9;
echo fib($n);
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayal
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Note that this function is designed
// only for fib() and won't work as
// general power function
function fib( n)
{
var F = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ];
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
// Helper function that multiplies 2
// matrices F and M of size 2*2, and
// puts the multiplication result
// back to F[][]
function multiply( F, M )
{
x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] +
F[0][1] * M[1][0];
y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] +
F[0][1] * M[1][1];
z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] +
F[1][1] * M[1][0];
w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] +
F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
// Helper function that calculates F[][]
// raise to the power n and puts the
// result in F[][]
function power( F, n)
{
var i;
var M = [[ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ]];
// n - 1 times multiply the
// matrix to {{1,0},{0,1}}
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver code
var n = 9;
document.write (" " + fib(n));
//This code is contributed by sweetyty
</script>
34
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n)
Espacio extra: O(1)
Método 5 (Método optimizado 4)
El método 4 se puede optimizar para trabajar en una complejidad de tiempo O (Iniciar sesión). Podemos hacer una multiplicación recursiva para obtener potencia (M, n) en el método anterior (similar a la optimización realizada en esta publicación)
C++
// Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
// Function that returns nth Fibonacci number
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
// Optimized version of power() in method 4
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
if(n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
power(F, n / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(9);
getchar();
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Nidhi_biet
C
#include <stdio.h>
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2]);
void power(int F[2][2], int n);
/* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */
int fib(int n)
{
int F[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
/* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */
void power(int F[2][2], int n)
{
if( n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[2][2] = {{1,1},{1,0}};
power(F, n/2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n%2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
void multiply(int F[2][2], int M[2][2])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(9));
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
//Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method
class fibonacci
{
/* function that returns nth Fibonacci number */
static int fib(int n)
{
int F[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n-1);
return F[0][0];
}
static void multiply(int F[][], int M[][])
{
int x = F[0][0]*M[0][0] + F[0][1]*M[1][0];
int y = F[0][0]*M[0][1] + F[0][1]*M[1][1];
int z = F[1][0]*M[0][0] + F[1][1]*M[1][0];
int w = F[1][0]*M[0][1] + F[1][1]*M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
/* Optimized version of power() in method 4 */
static void power(int F[][], int n)
{
if( n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int M[][] = new int[][]{{1,1},{1,0}};
power(F, n/2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n%2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python3
# Fibonacci Series using # Optimized Method # function that returns nth # Fibonacci number def fib(n): F = [[1, 1], [1, 0]] if (n == 0): return 0 power(F, n - 1) return F[0][0] def multiply(F, M): x = (F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0]) y = (F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1]) z = (F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0]) w = (F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1]) F[0][0] = x F[0][1] = y F[1][0] = z F[1][1] = w # Optimized version of # power() in method 4 def power(F, n): if( n == 0 or n == 1): return; M = [[1, 1], [1, 0]]; power(F, n // 2) multiply(F, F) if (n % 2 != 0): multiply(F, M) # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": n = 9 print(fib(n)) # This code is contributed # by ChitraNayal
C#
// Fibonacci Series using
// Optimized Method
using System;
class GFG
{
/* function that returns
nth Fibonacci number */
static int fib(int n)
{
int[,] F = new int[,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0}};
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0, 0];
}
static void multiply(int[,] F,
int[,] M)
{
int x = F[0, 0] * M[0, 0] +
F[0, 1] * M[1, 0];
int y = F[0, 0] * M[0, 1] +
F[0, 1] * M[1, 1];
int z = F[1, 0] * M[0, 0] +
F[1, 1] * M[1, 0];
int w = F[1, 0] * M[0, 1] +
F[1, 1] * M[1, 1];
F[0, 0] = x;
F[0, 1] = y;
F[1, 0] = z;
F[1, 1] = w;
}
/* Optimized version of
power() in method 4 */
static void power(int[,] F, int n)
{
if( n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
int[,] M = new int[,]{{1, 1},
{1, 0}};
power(F, n / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 9;
Console.Write(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayal
Javascript
<script>
// Fibonacci Series using Optimized Method
// Function that returns nth Fibonacci number
function fib(n)
{
var F = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ];
if (n == 0)
return 0;
power(F, n - 1);
return F[0][0];
}
function multiply(F, M)
{
var x = F[0][0] * M[0][0] + F[0][1] * M[1][0];
var y = F[0][0] * M[0][1] + F[0][1] * M[1][1];
var z = F[1][0] * M[0][0] + F[1][1] * M[1][0];
var w = F[1][0] * M[0][1] + F[1][1] * M[1][1];
F[0][0] = x;
F[0][1] = y;
F[1][0] = z;
F[1][1] = w;
}
// Optimized version of power() in method 4 */
function power(F, n)
{
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return;
var M = [ [ 1, 1 ], [ 1, 0 ] ];
power(F, n / 2);
multiply(F, F);
if (n % 2 != 0)
multiply(F, M);
}
// Driver code
var n = 9;
document.write(fib(n));
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
34
Complejidad de tiempo: O (Inicio de sesión)
Espacio adicional: O (Inicio de sesión) si consideramos el tamaño de la pila de llamadas a la función, de lo contrario O (1).
Método 6 (Tiempo O(Log n))
A continuación se muestra una fórmula de recurrencia más interesante que se puede usar para encontrar el número n de Fibonacci en el tiempo O(Log n).
If n is even then k = n/2: F(n) = [2*F(k-1) + F(k)]*F(k) If n is odd then k = (n + 1)/2 F(n) = F(k)*F(k) + F(k-1)*F(k-1)
¿Cómo funciona esta fórmula?
La fórmula se puede derivar de la ecuación matricial anterior.
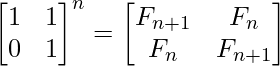
Taking determinant on both sides, we get (-1)n = Fn+1Fn-1 - Fn2 Moreover, since AnAm = An+m for any square matrix A, the following identities can be derived (they are obtained from two different coefficients of the matrix product) FmFn + Fm-1Fn-1 = Fm+n-1 ---------------------------(1) By putting n = n+1 in equation(1), FmFn+1 + Fm-1Fn = Fm+n --------------------------(2) Putting m = n in equation(1). F2n-1 = Fn2 + Fn-12 Putting m = n in equation(2) F2n = (Fn-1 + Fn+1)Fn = (2Fn-1 + Fn)Fn (Source: Wiki) -------- ( By putting Fn+1 = Fn + Fn-1 ) To get the formula to be proved, we simply need to do the following If n is even, we can put k = n/2 If n is odd, we can put k = (n+1)/2
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea anterior.
C++
// C++ Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in
// with O(Log n) arithmetic operations
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
// Create an array for memoization
int f[MAX] = {0};
// Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[]
int fib(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n])
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1)? (n+1)/2 : n/2;
// Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1
// if n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1)? (fib(k)*fib(k) + fib(k-1)*fib(k-1))
: (2*fib(k-1) + fib(k))*fib(k);
return f[n];
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d ", fib(n));
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to find n'th fibonacci
// Number with O(Log n) arithmetic operations
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int MAX = 1000;
static int f[];
// Returns n'th fibonacci number using
// table f[]
public static int fib(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n] != 0)
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1) == 1? (n + 1) / 2
: n / 2;
// Applying above formula [Note value
// n&1 is 1 if n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1) == 1? (fib(k) * fib(k) +
fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1))
: (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k))
* fib(k);
return f[n];
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9;
f= new int[MAX];
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal.
Python3
# Python3 Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in # with O(Log n) arithmetic operations MAX = 1000 # Create an array for memoization f = [0] * MAX # Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[] def fib(n) : # Base cases if (n == 0) : return 0 if (n == 1 or n == 2) : f[n] = 1 return (f[n]) # If fib(n) is already computed if (f[n]) : return f[n] if( n & 1) : k = (n + 1) // 2 else : k = n // 2 # Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1 # if n is odd, else 0. if((n & 1) ) : f[n] = (fib(k) * fib(k) + fib(k-1) * fib(k-1)) else : f[n] = (2*fib(k-1) + fib(k))*fib(k) return f[n] # Driver code n = 9 print(fib(n)) # This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.
C#
// C# Program to find n'th
// fibonacci Number with
// O(Log n) arithmetic operations
using System;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1000;
static int[] f;
// Returns n'th fibonacci
// number using table f[]
public static int fib(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0)
return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already
// computed
if (f[n] != 0)
return f[n];
int k = (n & 1) == 1 ? (n + 1) / 2
: n / 2;
// Applying above formula
// [Note value n&1 is 1 if
// n is odd, else 0.
f[n] = (n & 1) == 1 ? (fib(k) * fib(k) +
fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1))
: (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k)) *
fib(k);
return f[n];
}
// Driver Code
static void Main()
{
int n = 9;
f = new int[MAX];
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by mits
PHP
<?php
// PHP Program to find n'th
// fibonacci Number in with
// O(Log n) arithmetic operations
$MAX = 1000;
// Returns n'th fibonacci
// number using table f[]
function fib($n)
{
global $MAX;
// Create an array for memoization
$f = array_fill(0, $MAX, NULL);
// Base cases
if ($n == 0)
return 0;
if ($n == 1 || $n == 2)
return ($f[$n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already computed
if ($f[$n])
return $f[$n];
$k = ($n & 1) ? ($n + 1) / 2 : $n / 2;
// Applying above formula
// [Note value n&1 is 1 if
// n is odd, else 0.
$f[$n] = ($n & 1) ? (fib($k) * fib($k) +
fib($k - 1) * fib($k - 1)) :
(2 * fib($k - 1) + fib($k)) * fib($k);
return $f[$n];
}
// Driver Code
$n = 9;
echo fib($n);
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayal
?>
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Program to find n'th fibonacci Number in
// with O(Log n) arithmetic operations
const MAX = 1000;
// Create an array for memoization
var f = [...Array(MAX)];
f.fill(0);
// Returns n'th fibonacci number using table f[]
function fib(n) {
// Base cases
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (n == 1 || n == 2) return (f[n] = 1);
// If fib(n) is already computed
if (f[n]) return f[n];
var k = n & 1 ? (n + 1) / 2 : n / 2;
// Applying above formula [Note value n&1 is 1
// if n is odd, else 0.
f[n] =
n & 1
? fib(k) * fib(k) + fib(k - 1) * fib(k - 1)
: (2 * fib(k - 1) + fib(k)) * fib(k);
return f[n];
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
var n = 9;
document.write(fib(n));
// This code is contributed by rdtank.
</script>
34
La complejidad temporal de esta solución es O(Log n) ya que dividimos el problema a la mitad en cada llamada recursiva.
Método 7
Otro enfoque (usando la fórmula):
en este método, implementamos directamente la fórmula para el término n en la serie de Fibonacci.
F norte = {[(√5 + 1)/2] ^ n } / √5
Referencia: http://www.maths.surrey.ac.uk/hosted-sites/R.Knott/Fibonacci/fibFormula.html
C++
// C++ Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
int fib(int n) {
double phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
return round(pow(phi, n) / sqrt(5));
}
// Driver Code
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
std::cout << fib(n) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
//This code is contributed by Lokesh Mohanty.
C
// C Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int fib(int n) {
double phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
return round(pow(phi, n) / sqrt(5));
}
int main ()
{
int n = 9;
printf("%d", fib(n));
return 0;
}
Java
// Java Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int fib(int n) {
double phi = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2;
return (int) Math.round(Math.pow(phi, n)
/ Math.sqrt(5));
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 9;
System.out.println(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python3
# Python3 program to find n'th # fibonacci Number import math def fibo(n): phi = (1 + math.sqrt(5)) / 2 return round(pow(phi, n) / math.sqrt(5)) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': n = 9 print(fibo(n)) # This code is contributed by prasun_parate
C#
// C# Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
using System;
public class GFG
{
static int fib(int n)
{
double phi = (1 + Math.Sqrt(5)) / 2;
return (int) Math.Round(Math.Pow(phi, n)
/ Math.Sqrt(5));
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int n = 9;
Console.WriteLine(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
PHP
<?php
// PHP Program to find n'th
// fibonacci Number
function fib($n)
{
$phi = (1 + sqrt(5)) / 2;
return round(pow($phi, $n) / sqrt(5));
}
// Driver Code
$n = 9;
echo fib($n) ;
// This code is contributed by Ryuga
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript Program to find n'th fibonacci Number
function fib(n) {
let phi = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2;
return Math.round(Math.pow(phi, n) / Math.sqrt(5));
}
let n = 9;
document.write(fib(n));
// This code is contributed by mukesh07.
</script>
34
Complejidad de tiempo: O(logn), esto se debe a que calcular phi^n toma tiempo de logn
Complejidad de espacio: O(1)
Método 8
DP usando memorización (enfoque de arriba hacia abajo)
Podemos evitar el trabajo repetido realizado en el método 1 almacenando los números de Fibonacci calculados hasta ahora. Solo necesitamos almacenar todos los valores en una array.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dp[10];
int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
cout << fib(n);
getchar();
return 0;
// This code is contributed by Bhavneet Singh
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Initialize array of dp
static int[] dp = new int[10];
static int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// Temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// Memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 9;
Arrays.fill(dp, -1);
System.out.print(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by sujitmeshram
Python3
# Initialize array of dp dp = [-1 for i in range(10)] def fib(n): if (n <= 1): return n; global dp; # Temporary variables to store # values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2) first = 0; second = 0; if (dp[n - 1] != -1): first = dp[n - 1]; else: first = fib(n - 1); if (dp[n - 2] != -1): second = dp[n - 2]; else: second = fib(n - 2); dp[n] = first + second; # Memoization return dp[n] ; # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': n = 9; print(fib(n)); # This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
C#
using System;
class GFG {
// Initialize array of dp
static int[] dp = new int[10];
static int fib(int n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// Temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
int first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// Memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int n = 9;
Array.Fill(dp, -1);
Console.Write(fib(n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.
Javascript
<script>
// Initialize array of dp
dp = Array.from({length: 10}, (_, i) => -1);
function fib(n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
// Temporary variables to store
// values of fib(n-1) & fib(n-2)
var first, second;
if (dp[n - 1] != -1)
first = dp[n - 1];
else
first = fib(n - 1);
if (dp[n - 2] != -1)
second = dp[n - 2];
else
second = fib(n - 2);
// Memoization
return dp[n] = first + second;
}
// Driver Code
var n = 9;
document.write(fib(n));
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
</script>
34
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LwZRsM7qhrI
Chirag Agarwal contribuye con este método.
Método 9 (usando la fórmula de Binet para el enésimo Fibonacci)
Implica el uso de nuestro número de sección áurea Phi.
Phi = ( sqrt(5) + 1 ) / 2
Usar la ecuación de aproximación es lo suficientemente bueno aquí, ya que sabemos que N >= 0 && N <= 30, podemos usar con seguridad la siguiente función redondeada
Fib(N) = round( ( Phi ^N ) / sqrt(5) )
Explicación matemática completa de la fórmula de Binet: https://r-knott.surrey.ac.uk/Fibonacci/fibFormula.html
C++
// Fibonacci Series using Binet's Nth-term Formula
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fib(int n)
{
double phi = (sqrt(5) + 1) / 2;
return round(pow(phi, n) / sqrt(5));
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 9;
cout << fib(n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Sapna Kul
Complejidad de tiempo: O(1)
Complejidad de espacio: O(1)
Artículos relacionados:
Números grandes de Fibonacci en Java
Escriba comentarios si encuentra que los códigos/algoritmos anteriores son incorrectos o encuentra otras formas de resolver el mismo problema.
Referencias:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibonacci_number
http://www.ics.uci.edu/~eppstein/161/960109.html
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA